Learn how to build an application that can claim an mDoc via OID4VCI
Introduction
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the mDocs Holder SDKs to build an application that can claim an mDoc issued via both the OID4VCI Authorization Code and Pre-authorized Code flows.
- The user launches the application and scans a QR code received from an issuer.
- The application displays what credential is being offered to the user and by what issuer.
- The user agrees to claiming the offered credential.
- The user is redirected to complete authentication (Only in the Authorization Code flow).
- Upon successful authentication, the credential is issued to the user's application, where they can now store, view and present it.
The result will look something like this:
Prerequisites
Before you get started, let's make sure you have everything you need.
Prior knowledge
-
The issuance workflow described in this tutorial is based on the OID4VCI specification. If you are unfamiliar with this specification, refer to the following resources for more information:
- What is credential issuance?
- Breakdown of the OID4VCI workflow.
- Understand the difference between the Authorization Code and Pre-authorized Code flows.
- What are mDocs?
-
We assume you have experience developing applications in the relevant programming languages and frameworks (Swift for iOS, Kotlin for Android and TypeScript for React Native).
If you need to get a holding solution up and running quickly with minimal development resources and in-house domain expertise, talk to us about our white-label MATTR GO Hold app which might be a good fit for you.
Assets
- As part of your onboarding process you should have been provided with access to the following
assets (Contact us if you are interested in trialing the SDK):
- ZIP file which includes the required framework:
(
MobileCredentialHolderSDK-*version*.xcframework.zip). - Sample Wallet app: You can use this app for reference as you work through this tutorial.
- ZIP file which includes the required framework:
(
This tutorial is only meant to be used with the most recent version of the iOS mDocs Holder SDK.
- As part of your onboarding process you should have been provided with access to the following
assets (Contact us if you are interested in trialing the SDK):
- ZIP file that includes the required library (
mobile-credential-holder-*version*.zip). - Sample Wallet app: You can use this app for reference as you work through this tutorial.
- ZIP file that includes the required library (
This tutorial is only meant to be used with the most recent version of the Android mDocs Holder SDK.
- You will need access to the SDK and additional MATTR dependencies to complete this tutorial. Contact us if you are interested in trialing the SDK.
This tutorial is only meant to be used with the most recent version of the React Native mDocs Holder SDK.
Development environment
- Xcode setup with either:
- Local build settings if you are developing locally.
- iOS developer account if you intend to publish your app.
- Code editor (such as VS Code).
- Android Studio.
- Xcode.
- yarn (v1.22.22 was used during development).
- Java v17.
This tutorial uses Expo Go, leveraging Development Builds.
Dependencies
All dependencies are included in the project's package.json file and are automatically installed
as part of the environment setup.
Testing device
- Supported iOS device to run the built application on, setup with:
- Biometric authentication (Face ID, Touch ID).
- Available internet connection.
- Supported Android device to run the built application on, setup with:
- Biometric authentication (Face recognition, fingerprint recognition).
- Available internet connection.
- Debugging enabled.
- Supported iOS and/or Android device to run the built application on, setup with:
- Available internet connection.
- iOS:
- Biometric authentication (Face ID, Touch ID).
- Android:
- Biometric authentication (Face recognition, fingerprint recognition).
- Debugging enabled.
Got everything? Let's get going!
Environment setup
Perform the following steps to setup and configure your development environment:
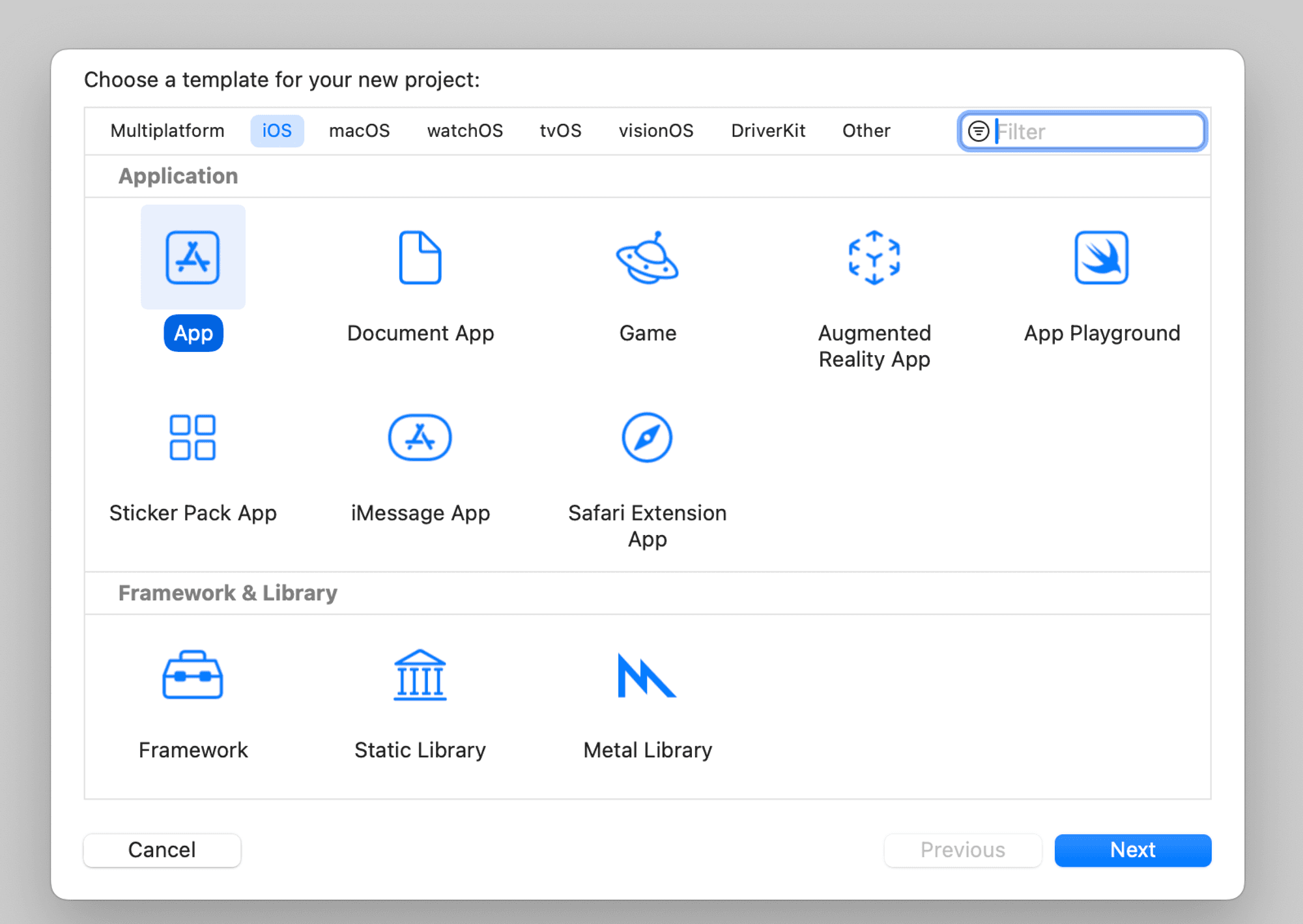
Step 1: Create a new project
Please follow the detailed instructions to Create a new Xcode project and add your organization’s identifier.
Step 2: Unzip the dependencies file
- Unzip the
MobileCredentialHolderSDK-*version*.xcframework.zipfile. - Drag the
MobileCredentialHolderSDK-*version*.xcframeworkfolder into your project. - Configure
MobileCredentialHolderSDK.xcframeworkto Embed & sign.
See Add existing files and folders for detailed instructions.
This should result in the the following framework being added to your project:

Step 3: Configure required resources
-
Create a new file named
Constants.swiftwithin your project. -
Add the following string resources to represent the Authentication provider you will use for this tutorial:
Constants.swift enum Constants { static let redirectUri: String = "io.mattrlabs.sample.mobilecredentialholderapp://credentials/callback" static let clientId: String = "ios-sample-mobile-credential-holder-app" }redirectUri: This is the path the SDK will redirect to once the user completes Authentication with the issuer. Our best practice recommendation is to configure this to be{redirect.scheme}://credentials/callbackas shown in the example above. However, it can be any path as long as it is handled by your application and registered with the issuer against the correspondingclientId.clientId: This is the identifier that is used by the issuer to recognize the wallet application. This is only used internally in the interaction between the wallet and the issuer and can be any string as long as it is registered with the issuer as a trusted wallet application.
Both of these parameters are only used in the Authorization Code flow and must be registered as a key pair as part of the issuer's OID4VCI workflow configuration. In this tutorial you will be claiming a credential from a MATTR Labs issuer which is configured with the parameters detailed above. We will help you configure your unique values as you move your implementation into production.
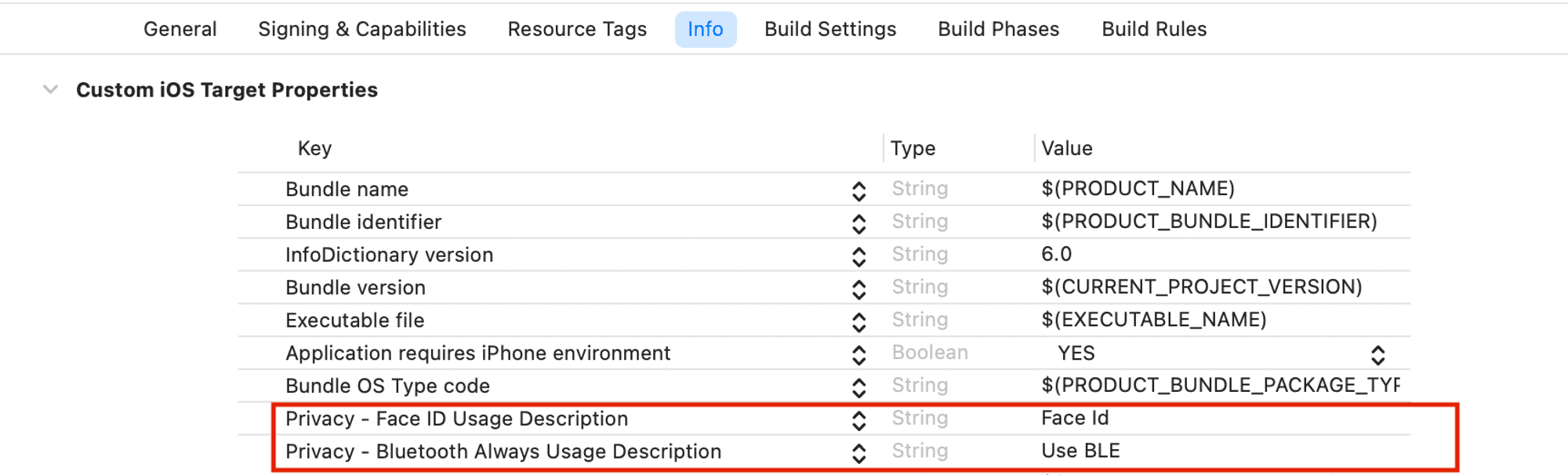
Step 4: Add Bluetooth and biometric permissions
The SDK requires access to the mobile device Bluetooth and biometric capabilities for the different
workflows built in this tutorial.
Configure these permissions in the Info
tab of the Application target:
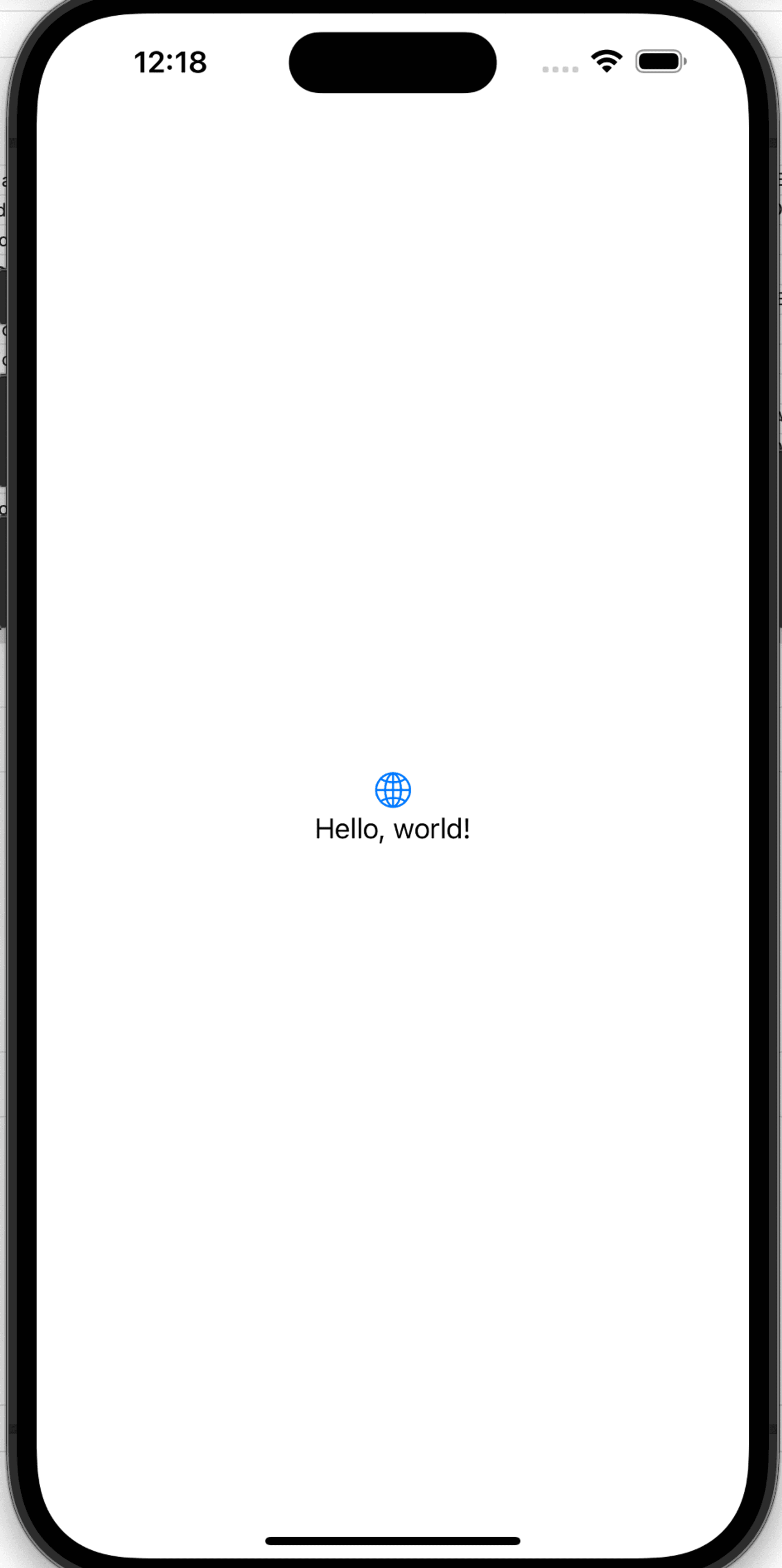
Step 5: Run the application
Select Run and make sure the application launches with a “Hello, world!” text in the middle of the display, as shown in the following image:
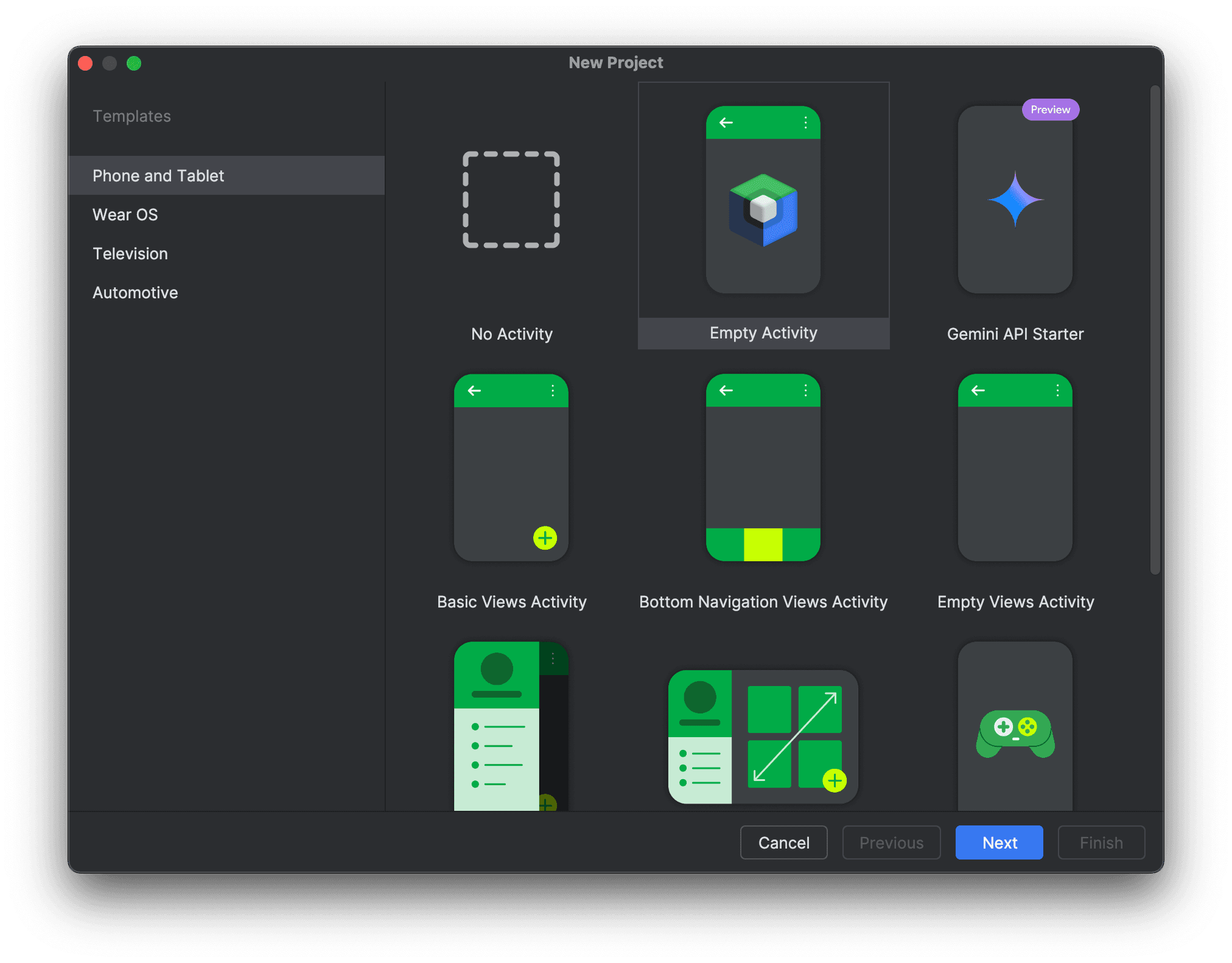
Step 1: Create a new project
- Create a new Android Studio project, using the Empty Activity template.
- Name the project
Holder Tutorial. - Select API 24 as the
Minimum SDKversion. - Select Kotlin DSL as the
Build configuration language.
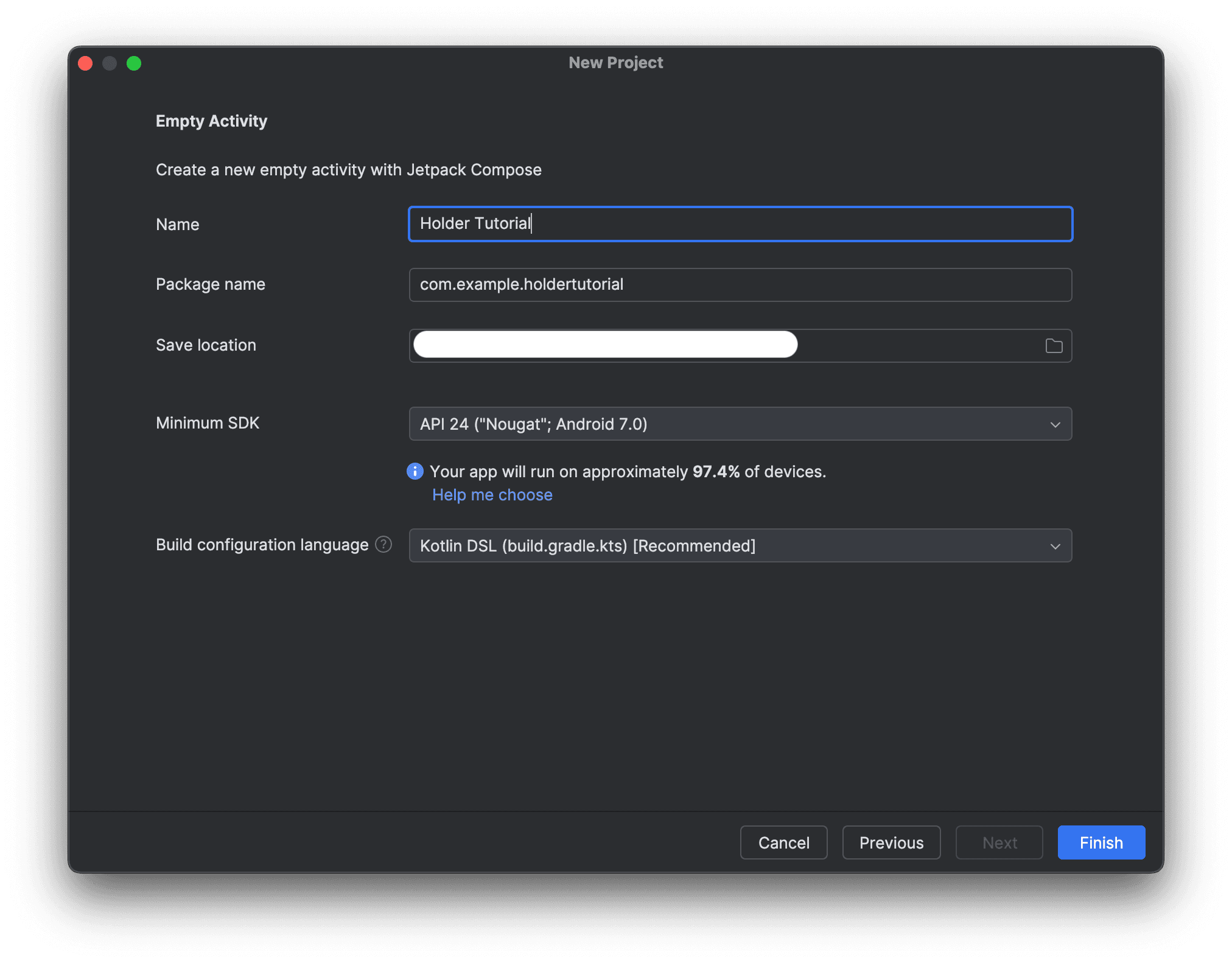
- Select Finish.
- Sync the project with Gradle files.
Step 2: Add required dependencies
-
Select the Project view.
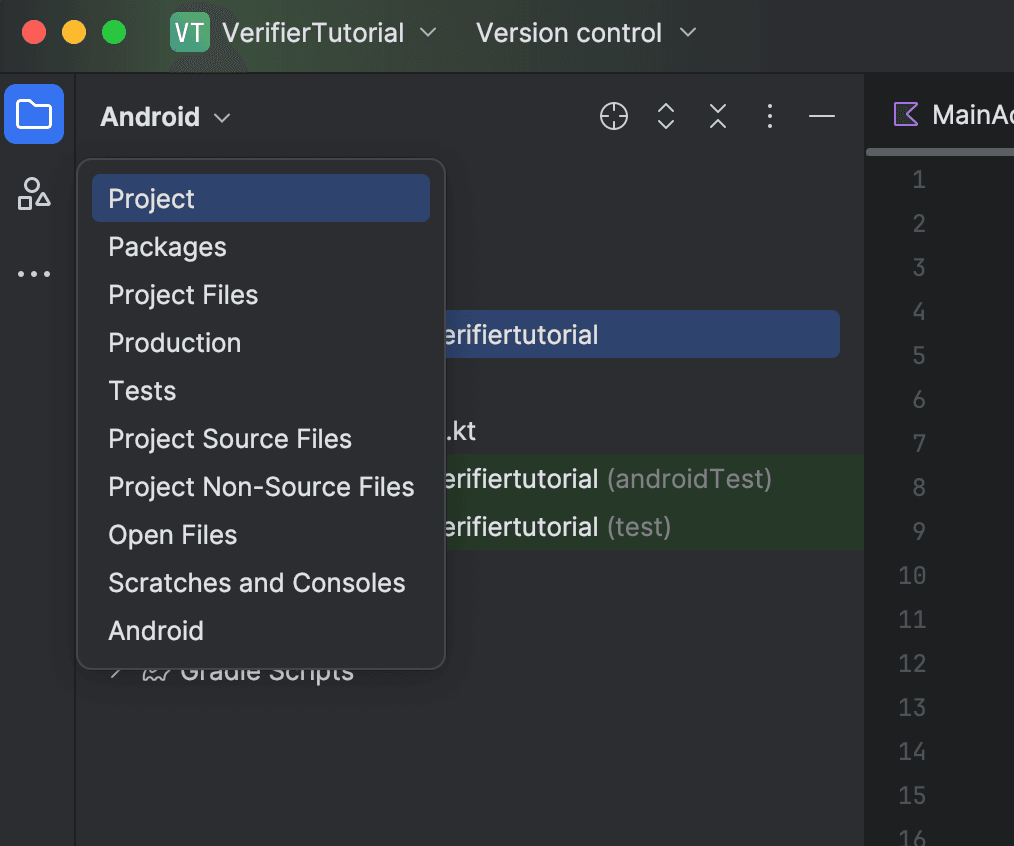
-
Create a new directory named
repoin your project's folder. -
Unzip the
mobile-credential-holder-*version*.zipfile and copy the unzippedglobalfolder into the newrepofolder.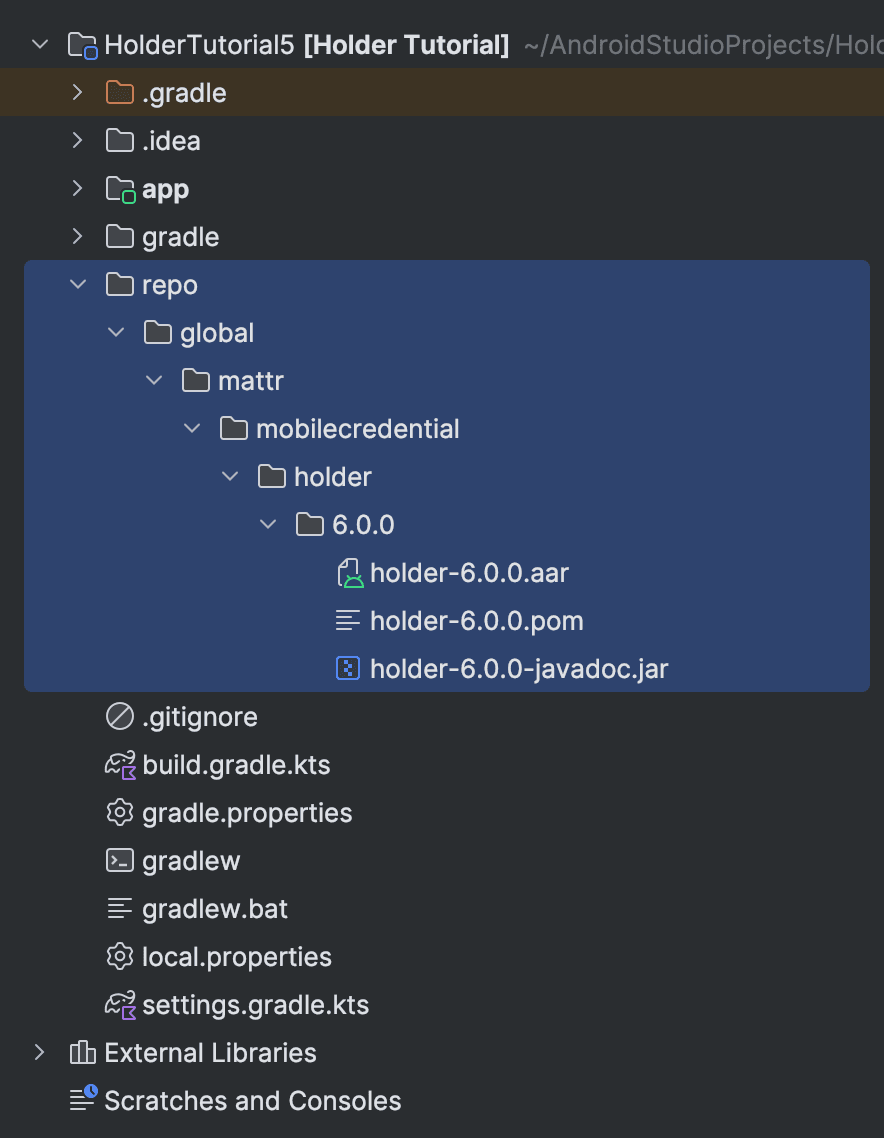
-
Open the
settings.gradle.ktsfile in theHolderTutorialfolder and add the following Maven repository to thedependencyResolutionManagement.repositoriesblock:settings.gradle.kts maven { url = uri("repo") } -
Open the
app/build.gradle.ktsfile in yourappfolder and add the following dependencies to thedependenciesblock:app/build.gradle.kts implementation("global.mattr.mobilecredential:holder:6.0.0") implementation("androidx.navigation:navigation-compose:2.9.0")
- The
holderdependency version should match the version of the unzippedmobile-credential-holder-*version*.zipfile you copied to therepofolder. - The required
navigation-composeversion may differ based on your version of the IDE, Gradle, and other project dependencies.
-
In your app's
AndroidManifest.xmlfile, add the followingactivitydeclaration. This represents the Authentication provider you will use for this tutorial:AndroidManifest.xml <activity android:name="global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.webcallback.WebCallbackActivity" tools:ignore="IntentFilterExportedReceiver" tools:node="merge"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /> <data android:host="credentials" android:scheme="io.mattrlabs.sample.mobilecredentialtutorialholderapp" /> </intent-filter> </activity>These values are part of the
redirect URIthe SDK will redirect the user to once they complete Authentication with the issuer:host: Thehostcan be any path, but our best practice recommendation is to configure this to becredentials, as the standard format for theredirect URIis{redirect.scheme}://credentials/callback.scheme: Theschemecan be any path that is handled by your application and registered with the issuer.
These values (alongside the client ID, which will be discussed later) are only
used in the Authorization Code flow and must be registered as part of the
issuer's OID4VCI workflow redirect URI. In this tutorial you will be
claiming a credential from a MATTR Labs issuer which is already configured
with the parameters detailed above. We will help you configure your unique
values as you move your implementation into production.
-
Sync the project with Gradle files.
-
Open the Build tab and select
Syncto make sure that the project has synced successfully.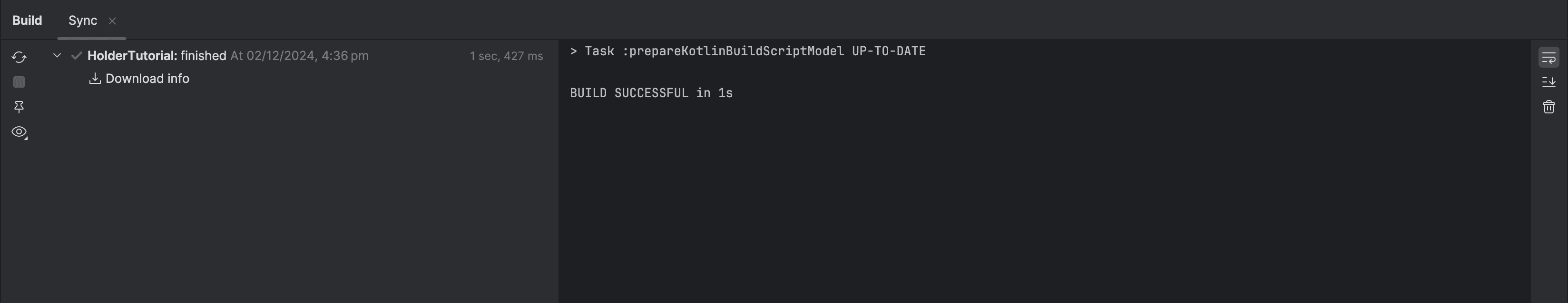
Step 3: Run the application
-
Connect a debuggable Android mobile device to your machine.
-
Build and run the app on the connected mobile device.
The app should launch with a “Hello, Android!” text displayed.
Step 1: Access the tutorial codebase
-
Access the tutorial starter codebase by either:
-
Cloning the MATTR sample apps repository:
Clone the repository git clone https://github.com/mattrglobal/sample-apps.gitor
-
Downloading the starter directory using the download-directory.github.io utility.
-
-
Open the tutorial project in your code editor. You can find it in the sample-apps/react-native-mdocs-holder-tutorial/react-native-mdocs-holder-tutorial-starter/ directory.
When cloning the entire sample apps repository, you can find the completed tutorial code in the sample-apps/react-native-mdocs-holder-tutorial/react-native-mdocs-holder-tutorial-complete directory and use it as a reference.
Step 2: iOS Application configuration
-
Open the
app.config.tsfile and update thebundleIdentifiervalue under the// Update the bundle identifiercomment to a unique value for your application, e.g.com.mycompany.myapp.app.config.ts bundleIdentifier: "com.mycompany.myapp",
iOS requires each app to have a unique bundle identifier for App Store and development environments.
-
Add the following Face ID (
NSFaceIDUsageDescription) and camera usage (NSCameraUsageDescription) permissions to theios.infoPlistobject under the// Add Face ID and Camera usage permissionscomment:app.config.ts NSFaceIDUsageDescription: "Face ID is used to secure your credentials.", NSCameraUsageDescription: "Camera is used to scan QR codes.",These permissions are required for the SDK to use biometric authentication and the camera for QR code scanning.
-
Add the following code under the
// Add Bluetooth permissions.comment in theapp.config.tsfile to add Bluetooth permissions to the application:app.config.ts NSBluetoothAlwaysUsageDescription: "This app uses Bluetooth to communicate with verifiers or holders.", NSBluetoothPeripheralUsageDescription: "This app uses Bluetooth to communicate with verifiers or holders.",These permissions will be required for the SDK to use Bluetooth for device engagement and communication in the proximity presentation tutorial.
Step 3: Configure the SDK plugins
Add the following code under the // Configure the SDK plugins comment to import required plugin
configurations:
"./withAndroidHolderSDK.js",
"./withRemoveAPNSCapability.js",The SDK requires platform-specific configurations to work correctly. The plugin files have already been created in your project root directory. You can also follow the instructions in the mDocs Holder SDK Docs to perform these platform-specific configuration manually.
Step 4: Install the dependencies
- Open a terminal in the project's root and navigate to the starter project directory:
cd sample-apps/react-native-mdocs-holder-tutorial/react-native-mdocs-holder-tutorial-starter/- Install the application dependencies:
yarn installStep 5: Generate the iOS and Android project files
Run the following command to generate the iOS and Android project files:
yarn expo prebuildYou should now see the ios and android folders in your project root.
Step 6: Start the application
Connect your testing device(s) and run the following command to start the application(s):
iOS
yarn ios --deviceAndroid
yarn android --deviceNice work, your application is now all set to begin using the SDK!
Tutorial steps
In this part of the tutorial you will build the capabilities for the user to interact with an OID4VCI credential offer and claim an mDoc.
To achieve this, you will break this capability down into the following steps:
- Initialize the SDK.
- Interact with a Credential offer.
- Retrieve offer details and present them to the Holder.
- Obtain user consent and initiate Credential issuance.
Step 1: Initialize the SDK
The first capability you will build into your app is to initialize the SDK so that your app can use
SDK methods and classes. To achieve this, you need to import the MobilecredentialHolderSDK
framework and then initialize the MobileCredentialHolder class:
- Open the
ContentViewclass in your new app project and replace any existing code with the following:
import SwiftUI
import Combine
// Claim Credential - Step 1.2: Import MobileCredentialHolderSDK
struct ContentView: View {
@ObservedObject var viewModel: ViewModel = ViewModel()
var body: some View {
NavigationStack(path: $viewModel.navigationPath) {
VStack {
Button("Scan Credential Offer") {
viewModel.navigationPath.append(NavigationState.qrScan)
}
.padding()
createQRCodeButton
if viewModel.shouldDisplayOnlinePresentation {
Button("View Online Presentation Session") {
viewModel.navigationPath.append(NavigationState.onlinePresentation)
}
.padding()
}
Spacer()
}
.padding()
.navigationDestination(for: NavigationState.self) { destination in
switch destination {
case .qrScan:
codeScannerView
case .credentialOffer:
credentialOfferView
case .transactionCodeInput:
transactionCodeInputView
case .retrievedCredentials:
retrievedCredentialsView
case .onlinePresentation:
// Online Presentation - Step 3.3: Display online presentation view
EmptyView()
case .presentCredentials:
qrCodeView
case .proximityPresentation:
// Proximity Presentation - Step 2.5: Display proximity presentation view
EmptyView()
}
}
// Online Presentation - Step 2.4: Create session from request URI
}
}
// MARK: - Credential Retrieval Views
var codeScannerView: some View {
// Claim Credential - Step 2.4 Create QRScannerView
EmptyView()
}
var credentialOfferView: some View {
// Claim Credential - Step 3.5: Display Credential offer
EmptyView()
}
var transactionCodeInputView: some View {
// Claim Credential - Step: 3.4 Display transaction code input view.
EmptyView()
}
var retrievedCredentialsView: some View {
// Claim Credential - Step 4.4: Display retrieved credentials
EmptyView()
}
// MARK: - Proximity Presentation Views
var createQRCodeButton: some View {
// Proximity Presentation - Step 1.5: Add button to generate QR code
EmptyView()
}
func generateQRCode(data: Data) -> Data? {
// Proximity Presentation - Step 1.6: Generate QR code
return nil
}
var qrCodeView: some View {
// Proximity Presentation - Step 1.7: Create QR code view
EmptyView()
}
}
class ViewModel: ObservableObject {
@Published var navigationPath = NavigationPath()
// Claim Credential - Step 1.3: Add MobileCredentialHolder var
// Claim Credential - Step 3.1: Add DiscoveredCredentialOffer and discoveredCredentialOfferURL vars
// Claim Credential - Step 4.1: Add retrievedCredentials var
// Proximity Presentation - Step 1.2: Create deviceEngagementString and proximityPresentationSession variables
// Proximity and Online Presentation: Create variables for credential presentations
// Online Presentation - Step 2.1: Create a variable to hold the online presentation session object
var shouldDisplayOnlinePresentation: Bool {
// Online Presentation - Step 3.4: View Online Presentation
return false
}
// Claim Credential - Step 1.4: Initialize MobileCredentialHolder SDK
@MainActor
func getCredential(id: String) {
// Proximity and Online Presentation: Retrieve a credential from storage
print("This method will get a credential from storage and update the viewModel")
}
}
// MARK: - Credential Retrieval
extension ViewModel {
@MainActor
func discoverCredentialOffer(_ offer: String) {
// Claim Credential - Step 3.2: Add discover credential offer logic
print("This method will discover a credentials offer and update viewModel")
}
@MainActor
func retrieveCredential(transactionCode: String?) {
// Claim Credential - Step 4.2: Call retrieveCredential method
print("This method will save a credential from offer and store it in the application's storage ")
}
}
// MARK: - Online Presentation
extension ViewModel {
@MainActor
func createOnlinePresentationSession(authorizationRequestURI: String) async {
// Online Presentation - Step 2.3: Create online presentation session
print("This method will create an online presentation session and update viewModel")
}
@MainActor
func sendOnlinePresentationSessionResponse(id: String) {
// Online Presentation - Step 4.1: Send online presentation response
print("This method will be passed to a view and send a response with selected credentials")
}
}
// MARK: - Proximity Presentation
extension ViewModel {
func createDeviceEngagementString() {
// Proximity Presentation - Step 1.3: Create function to create a proximity presentation session and generate QR code
print("This method will create a device engagement string that will be converted to a QR code")
}
// Proximity Presentation - Step 1.4: Update function signature
func onRequestReceived() {
// Proximity Presentation - Step 2.2: Store credential requests and matched credentials
print("The signature of this method will need to be updated to include the correct parameters")
print("This is a method that will be called when a proximity presentation request is received")
}
@MainActor
func sendProximityPresentationResponse(id: String) {
// Proximity Presentation - Step 3.1: Send a credential response
print("This method will be passed to a view and send a response with selected credentials")
}
}
// MARK: - Navigation
enum NavigationState: Hashable {
case qrScan
case credentialOffer
case transactionCodeInput
case retrievedCredentials
case onlinePresentation
case presentCredentials
case proximityPresentation
}This will serve as the basic structure for your application for this and the future tutorials.
We will copy and paste different
code snippets into specific locations to achieve the different functionalities.
These locations are indicated by comments that reference both the section and the step (e.g.
// Claim Credential - Step 1.2: Import MobileCredentialHolderSDK).
We recommend copying and pasting the comment text to easily locate it in the code.
-
Add the following code after the
// Claim Credential - Step 1.2: Import MobileCredentialHolderSDKcomment to importMobileCredentialHolderSDKand enable using its capabilities in your application:ContentView import MobileCredentialHolderSDK -
Add the following code after the
// Claim Credential - Step 1.3: Add MobileCredentialHolder varcomment to create a variable that holds themobileCredentialHolderinstance:ContentView var mobileCredentialHolder: MobileCredentialHolder -
Add the following code after the
// Claim Credential - Step 1.4: Initialize MobileCredentialHolder SDKcomment to initialize the SDK and make it available for your application:ContentView init() { do { mobileCredentialHolder = MobileCredentialHolder.shared try mobileCredentialHolder.initialize( userAuthenticationConfiguration: UserAuthenticationConfiguration(userAuthenticationBehavior: .onDeviceKeyAccess), credentialIssuanceConfiguration: CredentialIssuanceConfiguration( redirectUri: Constants.redirectUri, autoTrustMobileCredentialIaca: true ) ) } catch { print(error) } }Let's review the parameters that are passed into
initialize:
-
userAuthenticationConfiguration: Defines when is user authentication required. In this example, authentication will only be required when a credential is issued and/or presented. Refer to the SDK Docs to see all options. -
CredentialIssuanceConfiguration:redirectUri: This is the URI that the SDK uses to redirect the user back to your wallet application after authentication is complete. It must match the value you configured earlier in the development environment setup. This value is only used and required in the Authorization Code flow.autoTrustMobileCredentialIaca: Controls how the SDK handles issuer IACA certificates during credential issuance.- If set to
true, the SDK will automatically download and trust the issuer’s IACA certificate(s) when claiming a credential. This allows credentials to be claimed from any issuer. - If set to
false, the SDK will only accept credentials from issuers whose IACA certificates have already been manually added to the SDK’s trusted issuers list (see addTrustedIssuerCertificates). This requires the application to manually manage IACA certificates.
- If set to
- Run the app to make sure it compiles properly.
The first capability you will build into your app is to initialize the SDK so that your app can use
SDK functions and classes. To achieve this, you need to initialize the MobileCredentialHolder
class:
-
Open the
MainActivityfile in your project and replace any existing code with the following:MainActivity.kt package com.example.holdertutorial import android.app.Activity import android.content.Intent import android.os.Bundle import android.util.Log import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.ComponentActivity import androidx.activity.compose.setContent import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Arrangement import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Spacer import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.LazyColumn import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.items import androidx.compose.material3.Button import androidx.compose.material3.Card import androidx.compose.material3.OutlinedTextField import androidx.compose.material3.Scaffold import androidx.compose.material3.Text import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf import androidx.compose.runtime.remember import androidx.compose.runtime.rememberCoroutineScope import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope import androidx.navigation.NavController import androidx.navigation.compose.NavHost import androidx.navigation.compose.composable import androidx.navigation.compose.rememberNavController import androidx.navigation.navDeepLink import com.example.holdertutorial.ui.theme.HolderTutorialTheme import global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.dto.MobileCredential import global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.MobileCredentialHolder import global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.ProximityPresentationSession import global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.issuance.CredentialIssuanceConfiguration import global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.issuance.dto.DiscoveredCredentialOffer import kotlinx.coroutines.CoroutineScope import kotlinx.coroutines.launch class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) enableEdgeToEdge() // Claim Credential - Step 1.2: Initialize the SDK setContent { HolderTutorialTheme { val navController = rememberNavController() Scaffold { innerPadding -> NavHost( modifier = Modifier .fillMaxSize() .padding(innerPadding) .padding(8.dp), startDestination = "home", navController = navController, ) { composable("home") { HomeScreen(this@MainActivity, navController) } composable("scanOffer") { // Claim Credential - Step 2.5: Add "Scan Offer" screen call } composable("retrievedCredential") { // Claim Credential - Step 4.9: Add "Retrieved Credential" screen call } composable("presentationQr") { // Proximity Presentation - Step 1.2: Add "QR Presentation" screen call } composable("presentationSelectCredentials") { // Proximity Presentation - Step 2.6: Add "Select Credential" screen call } // Online Presentation - Step 2.2: Add "Online Presentation" screen call } } } } } } @Composable fun HomeScreen(activity: Activity, navController: NavController) { val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope() var transactionCode by remember { mutableStateOf("") } Column(verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(8.dp)) { Button(onClick = { navController.navigate("scanOffer") }, Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { Text("Scan Credential Offer") } // Proximity Presentation - Step 1.3: Add button for starting the credentials presentation workflow // Claim Credential - Step 3.3: Display discovered credential offer } } // Claim Credential - Step 4.4: Create function to retrieve credentials object SharedData { // Claim Credential - Step 3.1: Add discovered credential offer variables // Claim Credential - Step 4.2: Add retrieved credentials variable // Proximity Presentation - Step 2.1: Add proximity presentation request variable }
This will serve as the basic structure for your application. We will copy and paste different code snippets into specific locations in this codebase to achieve the different functionalities. These locations are indicated by comments that reference both the section and the step.
We recommend leaving the comment text (e.g. // Claim Credential - Step 1.2: Initialize the SDK)
even after you have pasted the code snippet, as it will later help you to easily locate the
step in the code.
-
Add the following code after the
// Claim Credential - Step 1.2: Initialize the SDKcomment to initialize the SDK by creating a new instance of theMobileCredentialHolderclass:MainActivity.kt lifecycleScope.launch { try { MobileCredentialHolder.getInstance().initialize( context = this@MainActivity, // Step 4.1: Add credential issuance configuration ) } catch (e: Exception) { Log.e("MainActivity", "SDK initialization failed", e) } }
This will initialize the SDK, making it available for your application.
- Run the app to make sure it compiles properly.
The first capability you will build is to initialize the SDK so that your app can use its methods and classes. To achieve this you will create a React Context that will allow accessing an SDK instance and its helper functions throughout the application.
-
In your project's
providersdirectory, create a new file namedHolderProvider.tsxand add the following scaffolding code:/providers/HolderProvider.tsx import { type MobileCredentialMetadata, UserAuthenticationBehavior, UserAuthenticationType, deleteCredential, getCredentials, initialize, isInitialized, } from "@mattrglobal/mobile-credential-holder-react-native"; // Online Presentation - Step 2.3: Import expo-linking and expo-router import type React from "react"; import { createContext, useCallback, useContext, useEffect, useMemo, useState } from "react"; import { Alert } from "react-native"; type HolderContextProps = { isHolderInitialized: boolean; getMobileCredentials: () => Promise<void>; mobileCredentials: MobileCredentialMetadata[]; deleteMobileCredential: (credentialId: string) => Promise<void>; error: string | null; isLoading: boolean; }; const HolderContext = createContext<HolderContextProps | undefined>( undefined, ); export function HolderProvider({ children }: { children: React.ReactNode }) { const [isHolderInitialized, setIsHolderInitialized] = useState<boolean>(false); const [mobileCredentials, setMobileCredentials] = useState< MobileCredentialMetadata[] >([]); const [error, setError] = useState<string | null>(null); const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState<boolean>(true); // Online Presentation - Step 2.4: Initialize router variable // Claim a Credential - Step 1.2: Initialize the Holder SDK const getMobileCredentials = useCallback(async () => { if (!isHolderInitialized) return; const credentials = await getCredentials(); setMobileCredentials(credentials); }, [isHolderInitialized]); // When the holder is initialized, get the mobile credentials to display in the app useEffect(() => { if (isHolderInitialized) { getMobileCredentials(); } }, [isHolderInitialized, getMobileCredentials]); // An example implementation of deleting a credential, used for demonstration purposes const deleteMobileCredential = useCallback( async (credentialId: string) => { if (!isHolderInitialized) return; Alert.alert( "Confirm Deletion", "Are you sure you want to delete this credential?", [ { text: "Cancel", style: "cancel" }, { text: "Delete", style: "destructive", onPress: async () => { try { await deleteCredential(credentialId); Alert.alert("Success", "Credential deleted successfully."); await getMobileCredentials(); } catch (err) { console.error("Error deleting credential:", err); Alert.alert( "Error", err instanceof Error ? err.message : "Failed to delete credential.", ); } }, }, ], ); }, [isHolderInitialized, getMobileCredentials], ); // Online Presentation - Step 2.5: Handle deep link const contextValue = useMemo( () => ({ isHolderInitialized, error, isLoading, getMobileCredentials, mobileCredentials, deleteMobileCredential, }), [ isHolderInitialized, error, isLoading, getMobileCredentials, mobileCredentials, deleteMobileCredential, ], ); return ( <HolderContext.Provider value={contextValue}> {children} </HolderContext.Provider> ); } export function useHolder() { const context = useContext(HolderContext); if (context === undefined) { throw new Error("useHolder must be used within a HolderProvider"); } return context; }
This will serve as the basic structure for your application. You will copy and paste different code snippets into specific locations in this codebase to achieve the different functionalities. These locations are indicated by comments that reference both the section and the step number.
We recommend copying and pasting the comment's text (e.g.
// Claim a Credential - Step 1.2: Initialize the Holder) to easily locate it in the code.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim a Credential - Step 1.2: Initialize the Holder SDKcomment to call the SDK'sinitializemethod and initialize the SDK:/providers/HolderProvider.tsx const initializeHolder = useCallback(async () => { try { // Check if SDK is already initialized const alreadyInitialized = await isInitialized(); if (alreadyInitialized) { setIsHolderInitialized(true); return; } // Initialize the SDK with authentication and credential issuance configuration const result = await initialize({ userAuthenticationConfiguration: { userAuthenticationBehavior: UserAuthenticationBehavior.OnInitialize, userAuthenticationType: UserAuthenticationType.BiometricOrPasscode, }, credentialIssuanceConfiguration: { autoTrustMobileCredentialIaca: true, redirectUri: "io.mattrlabs.sample.reactnativemobilecredentialholdertutorialapp://credentials/callback" } }); if (result.isErr()) { setError(result.error.message || "Failed to initialize holder."); } else { setIsHolderInitialized(true); } } catch (err) { setError( err instanceof Error ? err.message : "Unknown error during initialization" ); } finally { setIsLoading(false); } }, []); useEffect(() => { initializeHolder(); }, [initializeHolder]); -
Open the
/app/_layout.tsxfile and replace its content with the following code to wrap the application with theHolderProvidercontext:/app/_layout.tsx import { HolderProvider } from "@/providers/HolderProvider"; import { Stack } from "expo-router"; export default function RootLayout() { return ( // Claim a Credential - Step 1.3: Wrap the app in the HolderProvider component to make the HolderContext available to any child components <HolderProvider> <Stack> <Stack.Screen name="index" options={{ headerTitle: "Home", }} /> </Stack> </HolderProvider> ); }
Your application can now use the SDK's methods and classes. Next, you will build the capability to interact with a Credential offer.
The application will now require biometric authentication whenever the SDK is initialized.
Step 2: Interact with a Credential offer
Users can receive OID4VCI Credential offers as deep-links or QR codes. In this tutorial you will use a MATTR Labs OID4VCI Credential offer rendered as a QR code.
Creating your own Credential offer is not within the scope of the current tutorial. You can follow the OID4VCI guide that will walk you through creating one.
Your application needs to let users interact with Credential offers. Since this tutorial uses a QR code to deliver the offer, your application must be able to scan and process QR codes.
For ease of implementation, you will use a third party framework to achieve this:
- Add camera usage permissions to the app target:
- Add the CodeScanner library via Swift Package Manager.
-
Create a new swift file named
QRScannerViewand add the following code into it to implement the QR scanning capability:QRScannerView import SwiftUI import CodeScanner import AVFoundation struct QRScannerView: View { private let completionHandler: (String) -> Void init(completion: @escaping (String) -> Void) { completionHandler = completion } var body: some View { CodeScannerView(codeTypes: [.qr]) { result in switch result { case .failure(let error): print(error.localizedDescription) case .success(let result): print(result.string) completionHandler(result.string) } } } } -
Return to the
ContentViewfile and replace theEmptyView()under the// Claim Credential - Step 2.4 Create QRScannerViewcomment with the following code to create a newQRScannerViewview in the application for scanning QR codes:ContentView QRScannerView( completion: { credentialOffer in viewModel.discoverCredentialOffer(credentialOffer) } ) -
Run the app and tap the Scan Credential Offer button. When prompted, grant camera access to allow QR code scanning.
You should see a result similar to the following:
As the user selects the Scan Credential Offer button, the app launches the device camera to enable the user to scan a QR code.
You might notice that nothing happens after scanning a QR code - this is expected. In the next step you will implement the logic that retrieves the credential offer details from the QR code and presents them to the user.
For ease of implementation, you will use a third party library to achieve this:
-
Add the following dependencies to your
app/build.gradle.ktsfile:app/build.gradle.kts implementation("com.google.accompanist:accompanist-permissions:0.36.0") implementation("com.journeyapps:zxing-android-embedded:4.3.0") -
Sync your project with Gradle files.
-
In your package, create a new file named
ScanOfferScreen.kt.
-
Add the following code to the new file:
ScanOfferScreen.kt package com.example.holdertutorial import android.Manifest import android.app.Activity import android.content.Context import android.util.Log import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.compose.rememberLauncherForActivityResult import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize import androidx.compose.material3.CircularProgressIndicator import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.runtime.DisposableEffect import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf import androidx.compose.runtime.remember import androidx.compose.runtime.rememberCoroutineScope import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.platform.LocalContext import androidx.compose.ui.viewinterop.AndroidView import androidx.navigation.NavController import com.google.accompanist.permissions.ExperimentalPermissionsApi import com.google.accompanist.permissions.isGranted import com.google.accompanist.permissions.rememberPermissionState import com.journeyapps.barcodescanner.BarcodeCallback import com.journeyapps.barcodescanner.DecoratedBarcodeView import global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.MobileCredentialHolder import kotlinx.coroutines.CoroutineScope import kotlinx.coroutines.launch // Gets the permissions and shows the screen content, when the permissions are obtained @OptIn(ExperimentalPermissionsApi::class) @Composable fun ScanOfferScreen(navController: NavController) { val cameraPermissionState = rememberPermissionState(Manifest.permission.CAMERA) val requestPermissionLauncher = rememberLauncherForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestPermission()) {} LaunchedEffect(cameraPermissionState) { if (!cameraPermissionState.status.isGranted) { requestPermissionLauncher.launch(Manifest.permission.CAMERA) } } if (cameraPermissionState.status.isGranted) Content(navController) } // Screen content @Composable private fun Content(navController: NavController) { val context = LocalContext.current val barcodeView = remember { DecoratedBarcodeView(context) } val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope() var isQrScanned by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } val barcodeCallback = remember { BarcodeCallback { result -> // Executed when the QR code was scanned coroutineScope.launch { onQrScanned(context, result.text, navController) } barcodeView.pause() isQrScanned = true } } // Setting up the QR scanner DisposableEffect(Unit) { barcodeView.decodeContinuous(barcodeCallback) barcodeView.resume() onDispose { barcodeView.pause() } } // Showing the scanner until the QR is scanned. Showing a progress bar after that if (!isQrScanned) { AndroidView(factory = { barcodeView }, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) } else { Box(Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { CircularProgressIndicator(Modifier.align(Alignment.Center)) } } } private suspend fun onQrScanned(context: Context, offer: String, navController: NavController) { // Step 3.2: Discover credential offer } -
Back in the
MainActivityfile, add the following code under the// Claim Credential - Step 2.5: Add Scan Offer screen callcomment to connect the created composable to the navigation graph:MainActivity.kt ScanOfferScreen(navController) -
Run the app and select the Scan Credential Offer button.
As the user selects the Scan Credential Offer button, the app asks for camera permission, and launches the device camera to enable the user to scan a QR code.
-
Replace the code in
/app/index.tsxwith the following:/app/index.tsx // The Index component displays the list of credentials and enables claiming new credentials using a QR code scanner. import { useRouter } from "expo-router"; import React, { useState } from "react"; import { ActivityIndicator, Modal, StyleSheet, Text, TouchableOpacity, View, } from "react-native"; import CredentialsList from "@/components/CredentialsList"; // Claim a Credential - Step 2.3: Import the QRCodeScanner component import { useHolder } from "@/providers/HolderProvider"; export default function Index() { const router = useRouter(); const { isHolderInitialized, error, isLoading, mobileCredentials, deleteMobileCredential, } = useHolder(); const [isScannerVisible, setIsScannerVisible] = useState(false); // Claim a Credential - Step 2.4: Define the handleScanComplete function if (isLoading) { return ( <View style={styles.centered}> <ActivityIndicator size="large" color="#0000ff" /> <Text>Loading...</Text> </View> ); } if (error) { return ( <View style={styles.centered}> <Text>Error: {error}</Text> <Text>Restart the app.</Text> </View> ); } if (!isHolderInitialized) { return ( <View style={styles.centered}> <Text>No holder instance</Text> </View> ); } return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Text style={styles.headerText}>Welcome to the mDoc Holder App</Text> {/* UI to enable the QR code scanner */} <View style={styles.buttonContainer}> <TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={() => setIsScannerVisible(true)} > <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Claim Credential</Text> </TouchableOpacity> {/* Proximity Presentation - Step 1.5: Add Proximity Presentation button */} {/* Online Presentation - Step 2.7: Add Online Presentation button */} </View> {/* Display the list of credentials and their metadata */} <CredentialsList mobileCredentials={mobileCredentials} deleteMobileCredential={deleteMobileCredential} /> {/* Modal to display the QR code scanner */} {/* Claim a Credential - Step 2.5: Add the QRCodeScanner component */} </View> ); } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, paddingTop: 16, paddingHorizontal: 16, }, centered: { flex: 1, alignItems: "center", justifyContent: "center", }, headerText: { fontSize: 20, fontWeight: "600", marginBottom: 20, }, buttonContainer: { marginBottom: 20, gap: 10, }, button: { backgroundColor: "#007AFF", paddingVertical: 12, paddingHorizontal: 20, borderRadius: 8, alignItems: "center", justifyContent: "center", }, buttonText: { color: "white", fontSize: 16, fontWeight: "600", }, closeButton: { marginBottom: 20, backgroundColor: "#FF3B30", }, modalContainer: { flex: 1, justifyContent: "center", }, }); -
In your project's
componentsdirectory, create a new file namedQRCodeScanner.tsxand add the following code:
import React, { useRef } from "react";
import {
Dimensions,
StyleSheet,
Text,
TouchableOpacity,
View,
} from "react-native";
import {
Camera,
useCameraDevice,
useCameraPermission,
useCodeScanner,
} from "react-native-vision-camera";
type QRCodeScannerProps = {
onScanComplete: (scannedValue: string) => void;
};
const { width, height } = Dimensions.get("window");
const overlaySize = width * 0.7;
export default function QRCodeScanner({ onScanComplete }: QRCodeScannerProps) {
const device = useCameraDevice("back");
const { hasPermission, requestPermission } = useCameraPermission();
// Ref to track if a scan has been handled
const scanHandledRef = useRef(false);
const codeScanner = useCodeScanner({
codeTypes: ["qr"],
onCodeScanned: ([code]) => {
if (code?.value && !scanHandledRef.current) {
console.log("Scanned QR Code:", code.value);
scanHandledRef.current = true;
onScanComplete(code.value);
}
},
});
// Handle cases where permissions are not granted
if (!hasPermission) {
return (
<View style={styles.centered}>
<TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={requestPermission}>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>Request Camera Permission</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
);
}
// Handle cases where no camera device is found
if (!device) {
return (
<View style={styles.centered}>
<Text style={styles.errorText}>No back camera device found.</Text>
</View>
);
}
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
{/* Render the Camera component */}
<Camera
device={device}
isActive={true}
style={styles.camera}
codeScanner={codeScanner}
/>
{/* QR Code Overlay */}
<View style={styles.overlayContainer}>
<View style={styles.topOverlay} />
<View style={styles.middleOverlay}>
<View style={styles.sideOverlay} />
<View style={styles.focusedArea} />
<View style={styles.sideOverlay} />
</View>
<View style={styles.bottomOverlay} />
</View>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
},
centered: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
},
camera: {
flex: 1,
},
errorText: {
fontSize: 16,
color: "red",
},
overlayContainer: {
position: "absolute",
top: 0,
left: 0,
width: width,
height: height,
justifyContent: "space-between",
alignItems: "center",
},
topOverlay: {
width: width,
height: (height - overlaySize) / 2,
backgroundColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)",
},
middleOverlay: {
flexDirection: "row",
},
sideOverlay: {
width: (width - overlaySize) / 2,
height: overlaySize,
backgroundColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)",
},
focusedArea: {
width: overlaySize,
height: overlaySize,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "blue",
backgroundColor: "transparent",
},
bottomOverlay: {
width: width,
height: (height - overlaySize) / 2,
backgroundColor: "rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)",
},
button: {
backgroundColor: "#007AFF",
paddingVertical: 12,
paddingHorizontal: 20,
borderRadius: 8,
alignItems: "center",
},
buttonText: {
color: "white",
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: "600",
},
});This component uses the react-native-vision-camera library to provide QR code scanning
functionality with the following features:
- Camera Integration: Uses the device's camera and handles permission requests.
- Visual Guidance: Displays an overlay with a focused scanning area to help users position QR codes correctly,
- Error Handling: Provides clear UI feedback when:
- Camera permissions haven't been granted,
- No compatible camera device is found,
- Scan Processing: Captures QR code data and passes it to the parent component via the
onScanCompletecallback,
-
Next, return to the
index.tsxfile and import theQRCodeScannercomponent by adding the following code under the// Claim a Credential - Step 2.3: Import the QRCodeScanner componentcomment:/app/index.tsx import QRCodeScanner from "@/components/QRCodeScanner";
When the QRCodeScanner decodes the QR code, it will call the onScanComplete callback with the
scanned value. This should be a URI that starts with openid-credential-offer://.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim a Credential - Step 2.4: Define the handleScanComplete functioncomment to handle the scanned QR code:/app/index.tsx const handleScanComplete = (scannedValue: string) => { setIsScannerVisible(false); if (!scannedValue) return; if (scannedValue.startsWith("openid-credential-offer://")) { router.push({ pathname: "/claim-credential", params: { scannedValue }, }); } // Online Presentation - Step 2.2: Handle the 'mdoc-openid4vp://' scheme prefix };When called, the
handleScanCompletefunction would redirect the user to the/claim-credentialscreen with thescannedValueparameter obtained from the QR code. This is the screen where we will display the offer details to the user and enable them to accept the offered credential.
Your code editor will likely show a warning as we will only create the
/claim-credential screen later in the tutorial.
- Add the following code under the
{/* Claim a Credential - Step 2.5: Add the QRCodeScanner component */}comment to combine theQRCodeScannercomponent with thehandleScanCompletefunction:
<Modal
visible={isScannerVisible}
animationType="slide"
onRequestClose={() => setIsScannerVisible(false)}
>
<View style={styles.modalContainer}>
<QRCodeScanner onScanComplete={handleScanComplete} />
<TouchableOpacity
style={[styles.button, styles.closeButton]}
onPress={() => setIsScannerVisible(false)}
>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>Close Scanner</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
</Modal>Now, when the Claim Credential button is selected the app will display the QRCodeScanner
component in a modal. When a QR code is successfully scanned, the onScanComplete callback
(handleScanComplete) is triggered, which will navigate the user to the /claim-credential screen
with the information obtained from the QR code passed as a scannedValue parameter.
- Run the app.
The application will now display a Claim Credential button on the home screen. As the user selects this button they will be prompted for permission to access the camera, and then the QR code scanner will be displayed.
You should see a result similar to the following:
Step 3: Retrieve offer details and present them to the user
Next, you'll add the ability to display the details of the Credential offer to the user before they decide to claim any credentials. This process, known as credential discovery, allows your wallet application to retrieve and present the offer details, including:
- What Issuer is offering the credentials?
- What credentials are being offered, in what format and what claims do they include?
To display this information to the user, your application should call the SDK's
discoverCredentialOffer
method. We are going to implement this within the ViewModel class.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim Credential - Step 3.1: Add DiscoveredCredentialOffer and discoveredCredentialOfferURL varscomment to add new variables that will hold the credential offer details:ContentView @Published var discoveredCredentialOffer: DiscoveredCredentialOffer? var discoveredCredentialOfferURL = "" -
Replace the
printstatement under the// Claim Credential - Step 3.2: Add discover credential offer logiccomment with the following code to create a function that calls the SDK'sdiscoverCredentialOffermethod:ContentView Task { do { discoveredCredentialOffer = try await mobileCredentialHolder.discoverCredentialOffer(offer) // save the url to use for credential retrieval discoveredCredentialOfferURL = offer // present credential offer screen, as soon as credential offer is discovered navigationPath.append(NavigationState.credentialOffer) } catch { print(error) } }This function is called from our
QRScannerViewcallback, so that when the user scans a QR Code that includes a credential offer, thediscoverCredentialOffermethod is called and accepts the returnedcredentialOfferstring as itsofferparameter.This is a URL-encoded Credential offer which in our example is embedded in a QR code. In other implementations you might have to retrieve this parameter from a deep-link.
The
discoverCredentialOffermethod makes a request to theofferURL to retrieve the offer details and returns it as aDiscoveredCredentialOfferobject:Swift struct DiscoveredCredentialOffer { let issuer: URL let credentials: [OfferedCredential] let transactionCode: TransactionCode? }The application can now use the
issuerandcredentialsproperties and present this information for the user to review. Once an application has discovered a credential offer, the user is navigated to thecredentialOfferViewview, which you are going to implement next.Next you will use the
transactionCodeproperty to inspect whether or not the issuer requires a transaction code to claim the credential. This will enable the app to handle offers with and without a transaction code. -
Create a new file named
transactionCodeInputViewand paste the following code to create a view that allows the user to input a transaction code when it is required by the issuer:transactionCodeInputView import SwiftUI struct TransactionCodeInputView: View { @ObservedObject var viewModel: ViewModel @State private var transactionCode = "" @Environment(\.dismiss) private var dismiss var body: some View { VStack(spacing: 20) { Text("Transaction Code Required") .font(.title2) .fontWeight(.bold) Text("Please enter the transaction code to proceed with credential retrieval.") .multilineTextAlignment(.center) .foregroundColor(.secondary) TextField("Enter transaction code", text: $transactionCode) .textFieldStyle(RoundedBorderTextFieldStyle()) .padding(.horizontal) HStack(spacing: 20) { Button("Cancel") { dismiss() } .buttonStyle(.bordered) Button("Retrieve Credentials") { viewModel.retrieveCredential(transactionCode: transactionCode) } .buttonStyle(.borderedProminent) .disabled(transactionCode.isEmpty) } Spacer() } .padding() .navigationTitle("Transaction Code") .navigationBarBackButtonHidden(false) } }The application will only show this view when the credential offer indicates a transaction code is required. The user will then be able to input a transaction code they had received separately from the issuer.
-
Return to
ContentViewfile and replace theEmptyViewunder the// Claim Credential - Step: 3.4 Display transaction code input viewcomment with the following code to make use of the new view:Swift TransactionCodeInputView(viewModel: viewModel) -
Replace the
EmptyViewunder the// Claim Credential - Step 3.5: Display Credential offercomment with the following code to navigate the user to thecredentialOfferViewview when a credential offer is discovered:ContentView VStack { Text("Received \(viewModel.discoveredCredentialOffer?.credentials.count ?? 0) Credential Offer(s)") .font(.headline) Text("from \(viewModel.discoveredCredentialOffer?.issuer.absoluteString ?? "unknown issuer")") .font(.subheadline) List(viewModel.discoveredCredentialOffer?.credentials ?? [], id: \.docType) { credential in Section { HStack { Text("Name:") .bold() Spacer() Text("\(credential.name ?? "")") } HStack { Text("Doctype:") .bold() Spacer() Text("\(credential.docType)") } HStack { Text("No. of claims:") .bold() Spacer() Text("\(credential.claims.count)") } } } Button { if viewModel.discoveredCredentialOffer?.transactionCode != nil { viewModel.navigationPath.append(NavigationState.transactionCodeInput) return } viewModel.retrieveCredential(transactionCode: nil) } label: { Text("Consent and retrieve Credential(s)") .font(.title3) } .buttonStyle(.borderedProminent) .clipShape(Capsule()) }The app now handles selection of the Consent and retrieve Credential(s) button based on the retrieved offer details:
- For Pre-authorized Code offers:
- If a transaction code is required, it will navigate the user to the
TransactionCodeInputViewview. - If no transaction code is required, it will call
viewModel.retrieveCredential(transactionCode: nil)to retrieve the credential.
- If a transaction code is required, it will navigate the user to the
- For Authorization Code offers:
- The SDK will automatically redirect the user to a web browser to authenticate with issuer before continuing to retrieve the credential.
- For Pre-authorized Code offers:
-
Run the app, select the Scan Credential Offer button and scan the following QR code:

You should see a result similar to the following:
As the user scans the QR code, the application displays the credential offer details.
You might notice that nothing happens if you select the Consent and retrieve Credential(s) button. This is expected - in the next step you will implement the logic that initiates the credential issuance once the user provides their consent.
To display this information to the user, your application should call the
discoverCredentialOffer
function.
-
In your
MainActivityfile, add the following code under the// Claim Credential - Step 3.1: Add discovered credential offer variablescomment to add new variables that will hold the credential offer details:MainActivity.kt var scannedOffer: String? = null var discoveredCredentialOffer: DiscoveredCredentialOffer? = null -
In your
ScanOfferScreenfile, add the following code under the// Step 3.2: Discover credential offercomment to handle the credential offer upon scanning a QR code:ScanOfferScreen.kt try { SharedData.scannedOffer = offer SharedData.discoveredCredentialOffer = MobileCredentialHolder.getInstance().discoverCredentialOffer(offer) } catch (e: Exception) { Toast.makeText(context, "Failed to discover offer", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } navController.navigateUp()Now, once the user scans a QR Code, the
discoverCredentialOfferfunction is called and accepts the returnedofferstring as its parameter.This is a URL-encoded Credential offer which in our example was embedded in a QR code. In other implementations you might have to retrieve this parameter from a deep-link.
The
discoverCredentialOfferfunction makes a request to theofferURL to retrieve the offer information and returns it as aDiscoveredCredentialOfferobject:DiscoveredCredentialOffer structure DiscoveredCredentialOffer { issuer: String, credentials: [OfferedCredential], transactionCode: TransactionCode? }- The application can now use the
issuerandcredentialsproperties and present this information for the user to review. - The
transactionCodeproperty is optional and is only used in the Pre-authorized Code flow when the issuer configures it as part of the issuance flow.
- The application can now use the
-
In your
MainActivityfile, add the following code under the// Claim Credential - Step 3.3: Display discovered credential offerto display the offer details to the user:MainActivity.kt SharedData.discoveredCredentialOffer?.let { discoveredOffer -> Text("Received Credential Offer from ${discoveredOffer.issuer}") LazyColumn(Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { items(discoveredOffer.credentials, key = { it.doctype }) { credential -> Card(Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { Column(Modifier.padding(4.dp)) { Text("Name: ${credential.name ?: ""}") Text("DocType: ${credential.doctype}") } } } } // Claim Credential - Step 4.3: Add transaction code input // Claim Credential - Step 4.5: Add consent button } -
Run the app, select the Scan Credential Offer button and scan the following QR code:

You should see a result similar to the following:
As the user scans the QR code, the application displays the Credential offer details.
To display this information to the user, your holder application should call the SDK's
discoverCredentialOffer
function, passing the OpenID4VCI credential offer endpoint's URI as its uri parameter. This URI is
retrieved by the application from the scanned QR code.
-
Create a new file named
/app/claim-credential.tsxand add the following scaffolding code:/app/claim-credential.tsx import { useGlobalSearchParams, useRouter } from "expo-router"; import React, { useCallback, useEffect, useState } from "react"; import { ActivityIndicator, Alert, ScrollView, StyleSheet, Text, TextInput, TouchableOpacity, View } from "react-native"; import { useHolder } from "@/providers/HolderProvider"; import { discoverCredentialOffer, retrieveCredentials, } from "@mattrglobal/mobile-credential-holder-react-native"; import type { DiscoveredCredentialOffer, OfferedCredential, } from "@mattrglobal/mobile-credential-holder-react-native/lib/types/index"; // Claim a Credential - Step 4.1: define the CLIENT_ID constant export default function ClaimCredential() { const router = useRouter(); const { scannedValue } = useGlobalSearchParams<{ scannedValue: string }>(); const { isHolderInitialized, getMobileCredentials } = useHolder(); const [credentialOffer, setCredentialOffer] = useState<DiscoveredCredentialOffer>(); const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true); const [error, setError] = useState<string | null>(null); const [transactionCode, setTransactionCode] = useState<string>(""); useEffect(() => { const discoverOffer = async () => { if (!isHolderInitialized || !scannedValue) { setError("Missing holder instance or scanned value."); setIsLoading(false); return; } // Claim Credential - Step 3.2: Discover Credential Offer }; discoverOffer(); }, [isHolderInitialized, scannedValue]); const handleConsent = useCallback(async () => { if (!credentialOffer || !isHolderInitialized) { Alert.alert("Error", "Missing offer information or holder instance."); router.back(); return; } // Claim a Credential - Step 4.2: Retrieve Credentials }, [credentialOffer, isHolderInitialized, getMobileCredentials, router, scannedValue, transactionCode]); if (isLoading) { return ( <View style={styles.centered}> <ActivityIndicator size="large" color="#007AFF" /> <Text style={styles.text}>Discovering offer...</Text> </View> ); } if (error || !credentialOffer) { return ( <View style={styles.centered}> <Text style={[styles.text, styles.errorText]}> Error: {error || "No discovery offer found."} </Text> <TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={() => router.back()} > <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Go Back</Text> </TouchableOpacity> </View> ); } // Claim a Credential - Step 3.3: Display the offer details to the user } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, padding: 16, backgroundColor: "#fff", }, centered: { flex: 1, alignItems: "center", justifyContent: "center", }, title: { fontSize: 22, fontWeight: "600", marginBottom: 10, color: "#000", }, text: { fontSize: 16, color: "#333", marginBottom: 10, }, card: { marginBottom: 16, padding: 10, backgroundColor: "#F5F5F5", borderRadius: 8, borderWidth: 1, borderColor: "#E0E0E0", }, cardTitle: { fontWeight: "700", fontSize: 18, marginBottom: 5, color: "#000", }, button: { backgroundColor: "#007AFF", paddingVertical: 12, paddingHorizontal: 20, borderRadius: 8, alignItems: "center", }, buttonText: { color: "white", fontSize: 16, fontWeight: "600", }, buttonContainer: { marginBottom: 20, gap: 10, }, errorText: { color: "#FF3B30", textAlign: "center", }, transactionCodeContainer: { marginBottom: 16, padding: 16, backgroundColor: "#F8F9FA", borderRadius: 8, borderWidth: 1, borderColor: "#E0E0E0", }, description: { fontSize: 14, color: "#666", marginBottom: 8, fontStyle: "italic", }, textInput: { borderWidth: 1, borderColor: "#DDD", borderRadius: 8, padding: 12, fontSize: 16, backgroundColor: "white", marginTop: 8, }, }); -
Add the following code under the
// Claim a Credential - Step 3.2: Discover Credential Offercomment to call the SDK'sdiscoverCredentialOfferfunction and discover the credential offer:/app/claim-credential.tsx const discoveryResult = await discoverCredentialOffer(scannedValue); if (discoveryResult.isErr()) { setError(`Error discovering credential offer: ${discoveryResult.error.message || discoveryResult.error.type}`); } else { console.log("Discovered Credential Offer:", discoveryResult.value); setCredentialOffer(discoveryResult.value); } setIsLoading(false);Now, once the user scans a QR Code that includes a credential offer (e.g. it is prefixed with
openid-credential-offer://), the SDK'sdiscoverCredentialOfferfunction is called and accepts the returnedscannedValuestring (Offer URI) as itsuriparameter.This is a URL-encoded Credential offer which in our example was embedded in a QR code. In other implementations you might have to retrieve this parameter from a deep-link.
The
discoverCredentialOfferfunction makes a request to theuriURL to retrieve the offer information and returns it as aDiscoveredCredentialOfferobject:DiscoveredCredentialOffer structure DiscoveredCredentialOffer: { issuer: string; credentials: OfferedCredential[]; transactionCode?: { description?: string; length?: number; }; }Your application can now use the
issuer(who is offering the credentials) andcredentials(what credentials are offered and what claims they contain) properties and present this information for the user to review. -
Add the following code under the
// Claim a Credential - Step 3.3: Display the offer details to the usercomment to display the offer details to the user:/app/claim-credential.tsx return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Text style={styles.title}>Credential Offer</Text> <Text style={styles.text}> Received {credentialOffer.credentials.length} credential {credentialOffer.credentials.length > 1 ? "s" : ""} from {credentialOffer.issuer} </Text> {/* Claim a Credential - Step 4.3: Add transaction code input if required */} {credentialOffer?.transactionCode && ( <View style={styles.transactionCodeContainer}> <Text style={styles.text}>Transaction Code Required:</Text> {credentialOffer.transactionCode.description && ( <Text style={styles.description}> {credentialOffer.transactionCode.description} </Text> )} <TextInput style={styles.textInput} value={transactionCode} onChangeText={setTransactionCode} placeholder="Enter transaction code" maxLength={credentialOffer.transactionCode.length} autoCapitalize="characters" autoCorrect={false} /> </View> )} <ScrollView style={{ flex: 1 }}> {credentialOffer.credentials.map((cred: OfferedCredential, index: number) => ( <View key={`${cred.doctype}-${index}`} style={styles.card}> <Text style={styles.cardTitle}>{cred.name}</Text> <Text style={styles.text}>Document Type: {cred.doctype}</Text> <Text style={styles.text}>Number of Claims: {cred.claims?.length}</Text> </View> ))} </ScrollView> {/* Claim a Credential - Step 4.4: Add the Consent and Retrieve button */} </View> ); -
Run the app, select the Claim Credential button and scan the following QR code:

You should see a result similar to the following:
As the user scans the QR code, the holder application displays the Credential offer details.
Step 4: Obtain user consent and initiate credential issuance
The next (and final!) step is to build the capability for the user to accept the credential offer. This should then trigger issuing the credential and storing it in the application storage.
Once the user provides their consent by selecting the Consent and retrieve Credential(s) button,
your application must call the SDK's
retrieveCredentials
function to trigger the credential issuance and store the issued credential in the application
storage.
- For Pre-authorized Code offers, this will happen within the application and after the user provided a transaction code (when required by the issuer).
- For Authorization Code offers, this will happen after the user had completed authentication with the issuer and was redirected back to the application.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim Credential - Step 4.1: Add retrievedCredentials varcomment to add a new variable that will hold the result returned by the SDK'sretrieveCredentialsmethod:ContentView @Published var retrievedCredentials: [MobileCredential] = [] -
Replace the
printstatement under the// Claim Credential - Step 4.2: Call retrieveCredential methodcomment with the following code to create a new function that will call the SDK'sretrieveCredentialsmethod:ContentView Task { do { let retrievedCredentialResults = try await mobileCredentialHolder.retrieveCredentials( credentialOffer: discoveredCredentialOfferURL, clientId: Constants.clientId, transactionCode: transactionCode ) Task { var credentials: [MobileCredential] = [] for result in retrievedCredentialResults { if let credentialId = result.credentialId { if let credential = try? await mobileCredentialHolder.getCredential(credentialId: credentialId) { credentials.append(credential) } } } self.retrievedCredentials = credentials // Clear navigation stack and display retrievedCredentials view navigationPath = NavigationPath() navigationPath.append(NavigationState.retrievedCredentials) } } catch { print(error.localizedDescription) } }
Let’s review the parameters passed to the retrieveCredentials function:
credentialOffer: This is the same credential offer string from the QR Code that we used to calldiscoverCredentialOfferwith.clientId: This was configured when setting up your development environment. It is used by the issuer to identify the wallet application that is making a request to claim credentials.transactionCode: This is only required for Pre-authorized Code credential offers. If your application is only using Authorization Code flows offers, you should set it tonil.
The
retrieveCredentials
function returns an array of
RetrieveCredentialResult
objects. Each object contains metadata about a credential that was retrieved:
struct RetrieveCredentialResult {
let docType: String
let credentialId: String?
let error: RetrieveCredentialError?
}
[
{
"docType":"org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL",
"credentialId":"F52084CF-8270-4577-8EDD-23149639D985"
}
]docType: Identifies the credential type.credentialId: Internally unique identifier of this credential.
After the result is received, your application can retrieve specific credentials by calling the
SDK's
getCredential
method with the credentialId of any retrieved credential.
The SDK's
getCredential
method returns a
MobileCredential
object which can be used to display the retrieved credential, its claims and verification status to
the user.
Since this object can be used across multiple views, it will make sense to create one view that will represent it. We will use this view in both the Proximity and Online presentation tutorials.
-
Create a new file named
DocumentViewand add the following content:DocumentView import MobileCredentialHolderSDK import SwiftUI import Combine struct DocumentView: View { var viewModel: DocumentViewModel var body: some View { VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 10) { Text(viewModel.docType) .font(.title) .fontWeight(.bold) .padding(.bottom, 5) ForEach(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { key in VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 5) { Text(key) .font(.headline) .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.gray.opacity(0.2)) .cornerRadius(5) ForEach(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims[key]!.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { claim in HStack { Text(claim) .fontWeight(.semibold) Spacer() Text(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims[key]![claim]! ?? "") .fontWeight(.regular) } .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.white) .cornerRadius(5) .shadow(radius: 1) } } .padding(.vertical, 5) } } .padding() .background(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10).fill(Color.white).shadow(radius: 5)) .padding(.horizontal) } } // MARK: DocumentViewModel class DocumentViewModel: ObservableObject { var docType: String var namespacesAndClaims: [String: [String: String?]] init(from credential: MobileCredential) { self.docType = credential.docType self.namespacesAndClaims = credential.claims?.reduce(into: [String: [String: String]]()) { result, outerElement in let (outerKey, innerDict) = outerElement result[outerKey] = innerDict.mapValues { $0.textRepresentation } } ?? [:] } init(from credentialMetadata: MobileCredentialMetadata) { self.docType = credentialMetadata.docType var result: [String: [String: String?]] = [:] credentialMetadata.claims?.forEach { namespace, claimIDs in var transformedClaims: [String: String?] = [:] claimIDs.forEach { claimID in transformedClaims[claimID] = Optional<String>.none } result[namespace] = transformedClaims } self.namespacesAndClaims = result } init(from request: MobileCredentialRequest) { self.docType = request.docType self.namespacesAndClaims = request.namespaces.reduce(into: [String: [String: String?]]()) { result, outerElement in let (outerKey, innerDict) = outerElement result[outerKey] = innerDict.mapValues { _ in nil } } } } // MARK: Helper extension MobileCredentialElementValue { var textRepresentation: String { switch self { case .bool(let bool): return "\(bool)" case .string(let string): return string case .int(let int): return "\(int)" case .unsigned(let uInt): return "\(uInt)" case .float(let float): return "\(float)" case .double(let double): return "\(double)" case let .date(date): let dateFormatter = DateFormatter() dateFormatter.dateStyle = .short dateFormatter.timeStyle = .none return dateFormatter.string(from: date) case let .dateTime(date): let dateFormatter = DateFormatter() dateFormatter.dateStyle = .short dateFormatter.timeStyle = .short return dateFormatter.string(from: date) case .data(let data): return "Data \(data.count) bytes" case .map(let dictionary): let result = dictionary.mapValues { value in value.textRepresentation } return "\(result)" case .array(let array): return array.reduce("") { partialResult, element in partialResult + element.textRepresentation } .appending("") @unknown default: return "Unknown type" } } }The file comprises the following components:
DocumentViewModel: This class stores the credentials' docType and claim values.DocumentView: This view takesDocumentViewModelas a parameter and displays its content in a human-readable format.MobileCredentialElementValue: This helper extension allows retrieving aMobileCredentialElementValuefrom aMobileCredential'sclaimsand present it in a human-readable format.
-
Return to
ContentViewand replaceEmptyViewunder the// Claim Credential - Step 4.4: Display retrieved credentialscomment with the following code to use theDocumentViewstructure to display retrieved credentials to the user:ContentView ScrollView { VStack { Text("Retrieved Credentials") .font(.title) ForEach(viewModel.retrievedCredentials, id: \.id) { credential in DocumentView(viewModel: DocumentViewModel(from: credential)) } } }
Once the app calls the retrieveCredentials function, the SDK processes the response based on the
type of credential offer retrieved:
- In the Authorization Code flow:
- The user is redirected to
authenticate
with the configured Authentication provider defined in the
authorizeEndpointelement of theDiscoveredCredentialOfferobject. - Upon successful authentication, the user can proceed to complete the
OID4VCI workflow configured by the issuer. This workflow can include
different steps based on the issuer’s configuration, but eventually the user is redirected to
the configured
redirectUriwhich should be handled by your application.
- The user is redirected to
authenticate
with the configured Authentication provider defined in the
- In the Pre-authorized Code flow the user is not redirected out of the application, but rather provides a transaction code (when required by the issuer) and the immediately proceeds to claiming the credential. If no transaction code is required, the user can claim the credential immediately after selecting the Consent and retrieve Credential(s) button.
The issuer then sends the issued mDocs to your application, and the SDK processes and validates them against the ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021 standard. Credentials who meet validation rules are stored in the application internal data storage.
In our example this is achieved by selecting a Consent and retrieve Credential(s) button. Once
the user provides their consent by selecting this button, your application must call the
retrieveCredentials
function to trigger the credential issuance.
- For Pre-authorized Code offers, this will happen within the application and after the user provided a transaction code (when required by the issuer).
- For Authorization Code offers, this will happen after the user had completed authentication with the issuer and was redirected back to the application.
-
In your
MainActivityfile, add the following code under the// Step 4.1: Add credential issuance configurationcomment to configure the redirect URI that will be used to redirect the user back to your application after completing the authentication:MainActivity.kt credentialIssuanceConfiguration = CredentialIssuanceConfiguration( redirectUri = "io.mattrlabs.sample.mobilecredentialtutorialholderapp:" + "//credentials/callback", autoTrustMobileCredentialIaca = true )redirectUriis constructed of the sameschemeandhostvalues you have set in theAndroidManifest.xmlfile.- This configuration is only required for the Authorization Code flow offers. If your application is only using Pre-authorized Code flow offers you can remove it.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim Credential - Step 4.2: Add retrieved credentials variablecomment to add a new variable that will hold the result returned by theretrieveCredentialsfunction:MainActivity.kt var retrievedCredentials: List<MobileCredential> = emptyList() -
Add the following code under the
// Claim Credential - Step 4.3: Add transaction code inputcomment to add a new text input field to allow the user to provide a transaction code when one is provided with a Pre-authorized Code flow offer:MainActivity.kt if (discoveredOffer.transactionCode != null) { OutlinedTextField( value = transactionCode, onValueChange = { transactionCode = it }, label = { Text("Transaction Code") }, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth() ) }This is only required for Pre-authorized Code flow offers. If your application should only handle Authorization Code flow offers you can remove it.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim Credential - Step 4.4: Create function to retrieve credentialscomment to create a new function that will call theretrieveCredentialsmethod when the user gives the consent for the credentials retrieval:MainActivity.kt private fun onRetrieveCredentials( coroutineScope: CoroutineScope, activity: Activity, navController: NavController, transactionCode: String ) { coroutineScope.launch { try { val mdocHolder = MobileCredentialHolder.getInstance() val retrieveCredentialResults = mdocHolder.retrieveCredentials( activity, SharedData.scannedOffer!!, clientId = "android-mobile-credential-tutorial-holder-app", transactionCode = transactionCode ) // Claim Credential - Step 4.6: Display retrieved credentials } catch (e: Exception) { Toast.makeText(activity, "Failed to retrieve credentials", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() } } }SharedData.scannedOfferis the same offer String that was used for thediscoverCredentialOfferfunction call.clientIdis used by the issuer to recognize the application. This is only used internally in the interaction between the application and the issuer and can be any string as long as it is registered with the issuer as a trusted application.transactionCodeis only required for Pre-authorized Code credential offers. If your application is only using Authorization Code flows offers you can remove it.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim Credential - Step 4.5: Add consent buttoncomment to add a button for calling the new function:MainActivity.kt Spacer(Modifier.weight(1f)) Button( onClick = { onRetrieveCredentials(coroutineScope, activity, navController, transactionCode) }, Modifier.fillMaxWidth() ) { Text("Consent and retrieve Credential(s)") }
The
retrieveCredentials
function then returns a
RetrieveCredentialResult
list, which references all retrieved credentials:
[RetrieveCredentialResult]
@Serializable
data class RetrieveCredentialResult(
val doctype: String,
val credentialId: String?,
val error: RetrieveCredentialError?
)
[
{
"doctype":"org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL",
"credentialId":"F52084CF-8270-4577-8EDD-23149639D985"
}
]doctype: Identifies the credential type.credentialId: Unique identifier (UUID) of this credential.
Your application can now retrieve specific credentials by calling the
getCredential
function with the credentialId of any of the retrieved credentials.
The
getCredential
function returns a
MobileCredential
object which represents the issued mDoc, and your application can now introduce UI elements to
enable the user to view the credential.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim Credential - Step 4.6: Display retrieved credentialscomment to retrieve the credentials by their IDs from the local storage, save them to theSharedData.retrievedCredentialsvariable and navigate to theretrievedCredentialscreen to display the retrieved credential:MainActivity.kt SharedData.retrievedCredentials = retrieveCredentialResults.mapNotNull { try { mdocHolder.getCredential(it.credentialId!!, fetchUpdatedStatusList = false) } catch (e: Exception) { val msg = "Failed to get credential from storage" Toast.makeText(activity, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() null } } navController.navigate("retrievedCredential") SharedData.discoveredCredentialOffer = null -
In your package, create a new file named
RetrievedCredentialsScreen.kt. -
Add the following code to the new file to display the
docTypeandclaimsof retrieved credentials to the user:RetrievedCredentialsScreen.kt package com.example.holdertutorial import androidx.compose.foundation.background import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.LazyColumn import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.items import androidx.compose.foundation.shape.RoundedCornerShape import androidx.compose.material3.MaterialTheme import androidx.compose.material3.Text import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp import global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.deviceretrieval.deviceresponse.NameSpace import global.mattr.mobilecredential.holder.dto.MobileCredentialElement @Composable fun RetrievedCredentialsScreen() { if (SharedData.retrievedCredentials.isEmpty()) { Text("No credentials received") } else { Column { Text( "Retrieved Credentials", modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleLarge ) LazyColumn(Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { items(SharedData.retrievedCredentials, key = { it.id }) { credential -> Document( credential.docType, credential.claims.mapValues { (_, claims) -> claims.map { (name, value) -> "$name: ${value.toUiString()}" }.toSet() } ) } } } } } @Composable fun Document(docType: String, namespacesAndClaims: Map<NameSpace, Set<String>>) { Column(Modifier.fillMaxWidth().padding(6.dp)) { Text(docType, Modifier.padding(6.dp), style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium) namespacesAndClaims.forEach { (namespace, claims) -> Text(namespace, Modifier.padding(6.dp), style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleSmall) Column( Modifier .padding(6.dp) .fillMaxWidth() .background(MaterialTheme.colorScheme.background, RoundedCornerShape(6.dp)) .padding(6.dp) ) { claims.forEach { claim -> Text(claim) } } } } } fun MobileCredentialElement.toUiString() = when (this) { is MobileCredentialElement.ArrayElement, is MobileCredentialElement.DataElement, is MobileCredentialElement.MapElement -> this::class.simpleName ?: "Unknown element" else -> value.toString() } -
Back in your
MainActivityfile, add the following code under the// Claim Credential - Step 4.9: Add "Retrieved Credential" screen callcomment to connect the created composable to the navigation graph:MainActivity.kt RetrievedCredentialsScreen()
Once the app calls the retrieveCredentials function, the SDK processes the response based on the
type of credential offer retrieved:
- In the Authorization Code flow:
- The user is redirected to
authenticate
with the configured Authentication provider defined in the
authorizeEndpointelement of theDiscoveredCredentialOfferobject. - Upon successful authentication, the user can proceed to complete the
OID4VCI workflow configured by the issuer. This workflow can include
different steps based on the issuer’s configuration, but eventually the user is redirected to
the configured
redirectUriwhich should be handled by your application.
- The user is redirected to
authenticate
with the configured Authentication provider defined in the
- In the Pre-authorized Code flow the user is not redirected out of the application, but rather provides a transaction code (when required by the issuer) and the immediately proceeds to claiming the credential. If no transaction code is required, the user can claim the credential immediately after selecting the Consent and retrieve Credential(s) button.
The issuer then sends the issued mDocs to your application, and the SDK processes and validates them against the ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021 standard. Credentials who meet validation rules are stored in the application internal data storage.
We will implement this by adding a Consent and Retrieve button. Once the user provides their consent by
selecting this button, your application must call the
retrieveCredentials
function to trigger the credential issuance.
- For Pre-authorized Code offers, this will happen within the application and after the user provided a transaction code (when required by the issuer).
- For Authorization Code offers, this will happen after the user had completed authentication with the issuer and was redirected back to the application.
-
Add the following constant variables to represent the Authentication provider we will use for this tutorial under the
// Claim a Credential - Step 4.1: define the CLIENT_ID constantcomment:/app/claim-credential.tsx const CLIENT_ID = 'react-native-mobile-credential-holder-tutorial-app'
CLIENT_ID: This is the identifier that is used by the issuer to recognize the holder application. This is only used internally in the interaction between the holder application and the issuer and can be any string as long as it is registered with the issuer as a trusted holder application.
The CLIENT_ID and redirectUri (configured during SDK initialization) are both required parameters for the OID4VCI Authorization Code workflow.
For this tutorial you will be claiming a credential from a MATTR Labs issuer which is pre-configured with
the correct parameters. We will help you configure your unique values
as you move your implementation into production.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim a Credential - 4.2: Retrieve Credentialscomment to call the SDK'sretrieveCredentialsfunction to retrieve the offered credentials:/app/claim-credential.tsx const retrieved = await retrieveCredentials({ credentialOffer: scannedValue, // Now takes the original URL string clientId: CLIENT_ID, transactionCode: credentialOffer?.transactionCode ? transactionCode || undefined : undefined, }) if (retrieved.isErr()) { setError( retrieved.error.message || "An unexpected error occurred during offer discovery.", ); Alert.alert( "Error", retrieved.error.message || "Failed to retrieve credentials.", ); } else { Alert.alert('Success', `Retrieved ${retrieved.value.length} credential(s) successfully!`) } // Refresh the list of mobile credentials in the holder application await getMobileCredentials(); router.replace("/");Let's review where all the parameters come from:
credentialOffer: Now takes the original URL string (scannedValue) directly instead of theCredentialOfferResponseobject. The SDK handles the offer discovery internally.CLIENT_ID: Defined in theclaim-credential.tsxfile. It is used by the issuer to identify the holder application that is making a request to claim credentials.transactionCode: Optional parameter used for pre-authorized flows. When the credential offer requires a transaction code, this should be provided by the user. Set toundefinedfor regular authorization code flows.
-
Add the following code under the
// Claim a Credential - Step 4.4: Add the Consent and Retrieve buttoncomment to display a Consent and Retrieve button which call the applications'handleConsentfunction:/app/claim-credential.tsx <View style={styles.buttonContainer}> <TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={handleConsent}> <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Consent and Retrieve</Text> </TouchableOpacity> <TouchableOpacity style={[styles.button, { backgroundColor: "#FF3B30" }]} onPress={() => router.replace("/")} > <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Cancel</Text> </TouchableOpacity> </View>
Once the handleConsent() function is called, it will execute the retrieveCredentials function.
The user will be redirected to
authenticate
with the configured Authentication provider as determined by the issuer's OID4VCI workflow configuration.
This tutorial uses a demo MATTR Labs Credential offer to issue the credential. This offer uses a workflow that doesn't actually authenticate the user before issuing a credential, but redirects them to select the credential they wish to issue. In production implementations this must be replaced by a proper authentication mechanism to comply with the ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021 standard and the OID4VCI specification.
Upon successful authentication, the user will proceed to complete the
OID4VCI workflow configured by the issuer. This workflow can include
different steps based on the issuer’s configuration, but eventually the user is redirected to the
configured REDIRECT_URI which should be handled by your application.
In the example Credential offer used in this tutorial, the issuance workflow immediately proceeds to claiming the credential. Check out our other issuance guides and tutorials for creating more rich and flexible user experiences.
As the user is redirected to REDIRECT_URI, the issuer sends the issued mDocs to your application.
The SDK then processes the received credentials and validates them against the
ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021 standard. Credentials who meet
validation rules are stored in the application.
Let's test the end-to-end flow of claiming a credential using the application you had just built.
Step 5: Test the application
Authorization code flow
- Run the application.
- Select the Scan Credential Offer button.
- Scan the following QR code:

- Select the Consent and retrieve Credential(s) button.
You should see a result similar to the following:
As the user scans the QR code, the wallet retrieves and displays the offer details. The user then provides consent to retrieving the credentials, and the wallet responds by initiating the issuance workflow and displaying the retrieved credentials to the user.
This tutorial uses a demo MATTR Labs Credential offer to issue the credential. This offer uses a workflow that doesn't actually authenticate the user before issuing a credential, but redirects them to select the credential they wish to issue. In production implementations this must be replaced by a proper Authentication provider to comply with the ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021 standard and the OID4VCI specification.
Pre-authorized Code flow
Let's test the end-to-end flow of claiming a credential using the Pre-authorized Code flow:
- Open the MATTR Labs Pre-authorized Offer tool.
- Turn on the Transaction Code option for the tool to generate a transaction code.
- Select the Generate Credential Offer button.
A QR code will be generated and rendered on the screen, along with a transaction code. - Run your application.
- Select the Scan Credential Offer button.
- Scan the QR code.
- Enter the transaction code retrieved from the MATTR Labs tool.
- Select the Consent and retrieve Credential(s) button.
In production implementations, the transaction code is generated by the issuer and shared with the intended holder by a separate secure channel. In this tutorial, the transaction code is generated by the MATTR Labs tool and displayed on the screen for demonstration purposes and to simplify testing.
Congratulations! Your application can now interact with an OID4VCI Credential offer to claim mDocs!
Summary
You have just used the mDocs Holder SDKs to build an application that can claim an mDoc issued via OID4VCI, supporting both the Authorization Code and Pre-authorized Code flows:
This was achieved by building the following capabilities into the application:
- Initialize the SDK so the application can use its functions and classes.
- Interact with a Credential offer formatted as a QR code.
- Retrieve the offer details and present them to the user.
- Obtain user consent and initiate the credential issuance workflow.
What's next?
- You can build additional capabilities into your new application:
- Present a claimed mDoc for verification via an online presentation workflow into your new application.
- Present a claimed mDoc for verification via a proximity presentation workflow.
- You can check out the SDKs reference documentation for more details on the available functions and classes:
How would you rate this page?
Last updated on





