Learn how to build an application that can verify an mDoc from another app on the same device
Overview
In this tutorial you will use the mDocs Mobile Verifier SDKs to build an application that can verify an mDoc presented from a different application on the same device via OID4VP, as defined in ISO 18013-7 Annex B.
- A relying party uses the Mobile Verifier SDK to embed a remote verification workflow into a mobile application.
- When a user interacts with the mobile application, a matching wallet application installed on their mobile device is invoked to request an mDoc for verification.
- The user consents to sharing the requested information.
- The user's wallet application shares the matching mDoc with the MATTR VII tenant configured by the Mobile Verifier SDK to perform the verification workflow.
- The MATTR VII tenant performs the required checks and returns the verification results via the Mobile Verifier SDK to the verifier application.
- The user journey continues based on the verification results.
The result will look something like this:
Coming soon...
To achieve this, you will build the following capabilities into your verifier application:
- Initialize the SDK, so that your application can use its functions and classes.
- Request an mDoc for verification from a compliant wallet application.
- Handle the redirect from the wallet application.
- Display the verification results.
Prerequisites
Before you get started, let's make sure you have everything you need.
Prior knowledge
-
The remote verification workflow described in this tutorial is based on the OID4VP specification and the ISO 18013-7 standard. If you are unfamiliar with these, refer to the following resources for more information:
- What are mDocs?
- What is remote verification?
- Breakdown of the remote mobile app verification workflow.
-
We assume you have experience developing applications in the relevant programming languages and frameworks (Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android).
Assets
- Complete the sign up form to get trial access to MATTR VII and the MATTR Portal, and then Create a tenant.
- As part of your MATTR Pi SDK onboarding process you should have been provided with access to the
following SDK resources:
- ZIP file which includes the required framework:
(
MobileCredentialVerifierSDK-*version*.xcframework.zip). - Sample Verifier app: You can use this app for reference as you work through this tutorial.
- ZIP file which includes the required framework:
(
This tutorial is only meant to be used with the most recent version of the iOS mDocs Verifier SDK.
- Complete the sign up form to get trial access to MATTR VII and the MATTR Portal, and then Create a tenant.
- As part of your MATTR Pi SDK onboarding process you should have been provided with access to the
following SDK resources:
- ZIP files which include the required libraries:
common-*version*.zipverifier-*version*.zip
- Sample Verifier app: You can use this app for reference as you work through this tutorial.
- ZIP files which include the required libraries:
This tutorial is only meant to be used with the most recent version of the Android mDocs Verifier SDK.
Coming soon...
Development environment
- Xcode setup with either:
- Local build settings if you are developing locally.
- iOS developer account if you intend to publish your app.
Coming soon...
Testing device
You will need a mobile device to test the workflow with.
Supported iOS device to run the built Verifier application on, setup with:
- Available internet connection
- A wallet application that can present an mDoc remotely. If you don't have one available, we recommend using the app built in our Holder SDK remote presentation tutorial.
- Use your testing wallet application to claim an mDoc by scanning the following QR code:

Supported Android device to run the built Verifier application on, setup with:
- Available internet connection
- A wallet application that can present an mDoc remotely. If you don't have one available, we recommend using the app built in our Holder SDK remote presentation tutorial.
- Use your testing wallet application to claim an mDoc by scanning the following QR code:

Coming soon...
Got everything? Let's get going!
Overview
The following diagram depicts the workflow you will build in this tutorial:
- The user triggers the workflow by interacting with the verifier application.
- The verifier application uses the embedded Mobile Verifier SDK capabilities to start a presentation-based verification session with the configured MATTR VII tenant.
- The MATTR VII tenant responds with a link to invoke a matching wallet application.
- The verifier application uses the link to invoke a matching wallet application using a redirect.
- The wallet application makes a request to the MATTR VII tenant to retrieve a request object, defining what information is requested for verification.
- The MATTR VII tenant returns the request object to the wallet application.
- The wallet application (upon user consent) returns an authorization response to the MATTR VII tenant, which includes the information required for verification.
- The MATTR VII tenant returns the verification results to the verifier application.
- The verifier application surfaces the verification results to the user and the interaction continues.
You will build this workflow in two parts:
- Part 1: Setup the MATTR VII Verifier tenant.
- Part 2: Build a mobile application with mDocs verification capabilities.
Part 1: Setup the MATTR VII Verifier tenant
The MATTR VII tenant will be used to interact with your mobile application (generating a verification request) and the wallet application (presenting an mDoc for verification) as per OID4VP and ISO/IEC 18013-7 Annex B. To enable this, you must:
- Create a verifier application configuration: Define what applications can create verification sessions with the MATTR VII tenant, and how to handle these requests.
- Create a supported wallet configuration: Define how to invoke specific wallet applications as part of a remote verification workflow.
- Configure a trusted issuer: The MATTR VII verifier tenant will only accept mDocs issued by these trusted issuers.
You can perform these steps via the MATTR Portal or by making API requests to your MATTR VII tenant.
Create a verifier application configuration
Each MATTR VII tenant can interact with multiple verifier applications, and can handle requests differently for each application. This means you must create a verifier application configuration that defines how to handle verification requests from your mobile application.
- Log in to the MATTR Portal.
- In the navigation panel on the left-hand side, expand the Credential Verification menu.
- Select Applications.
- Select Create new.
- Enter a meaningful Name for your application (e.g. "My iOS Mobile Verifier Application").
- Use the Type dropdown to select
iOSas you are building an iOS application. - Enter your Apple Developer Team ID in the Team ID field. You can find it in the Membership details section of your Apple Developer account.
- Enter your iOS application bundle identifier in the Bundle ID field. This is the unique identifier of your iOS application, which you can set in your Xcode project settings. This will be used by the MATTR VII tenant to validate incoming requests are from a known and trusted application.
- In the OpenID4VP Configuration section, enter your redirect URI in the Redirect URI field. This should be structured as follows:
{your_app_bundleId}://my/path. This is the URI the user is redirected to after presenting the credential from their wallet. This can point to your app via a custom URI scheme or a web page. - Select Create.
- Make note of the generated application
ID. You will need this value to initialize the SDK in your mobile application later in this tutorial.
Make the following request to your MATTR VII tenant to create a verifier application configuration:
POST /v2/presentations/applications{
"name": "My iOS Mobile Verifier Application",
"type": "ios",
"teamId": "A2B3C4D5E6",
"bundleId": "io.mattrlabs.dev.sampleApp.MdocSampleApp",
"openid4vpConfiguration": {
"redirectUri": "io.mattrlabs.dev.sampleApp.MdocSampleApp://my/path"
},
"resultAvailableInFrontChannel": true
}name: You can use whatever name you'd like, as long as it is unique on your tenant.type: Useiosas you are building an iOS application.teamId: Replace with your Apple Developer Team ID associated with your iOS application. You can find it in the Membership details section of your Apple Developer account.bundleId: Replace with your iOS application bundle identifier. This is the unique identifier of your iOS application, which you can set in your Xcode project settings. This will be used by the MATTR VII tenant to validate incoming requests are from a known and trusted application.openid4vpConfiguration:redirectUri: This is the URI the user is redirected to after presenting the credential from their wallet. This can point to your app via a custom URI scheme or a web page. Make sure to use your actual app bundle ID, so that the redirect URI is structured as follows:{your_app_bundleId}://my/path.
resultAvailableInFrontChannel: Setting this totruemakes the verification results available directly to the mobile application.
Response
{
"id": "0eaa8074-8cc4-41ec-9e42-072d36e2acb0",
"name": "My Mobile Verifier Application"
//... rest of application configuration
}id: You will use this value later to initialize the SDK so that requests coming from your verifier application can be recognized and trusted by the MATTR VII tenant.
- Log in to the MATTR Portal.
- In the navigation panel on the left-hand side, expand the Credential Verification menu.
- Select Applications.
- Select Create new.
- Enter a meaningful Name for your application (e.g. "My Android Mobile Verifier Application").
- Use the Type dropdown to select
Androidas you are building an Android application. - In the Package Name field, enter your Android application package name. This is the unique identifier of your Android application, which must match the package name you set later in this tutorial.
- In the Signing certificate thumbprints field, enter a temporary placeholder value (e.g.
3A9F6C1D4E8B72F0A5C3D6E19B4F8A2C7D1E0B9F3A6C5D4E7B8F2A1C9D0E3F5B). MATTR VII uses this to verify requests come from your signed app. You will update the placeholder value after you retrieve the signing certificate in Step 1: Environment setup. - In the OpenID4VP configuration section, enter a redirect URI in the Redirect URI field. This is the URI used to return the user to your app after the wallet presents the credential. It must resolve to a path your app can handle (via custom URI scheme or web page). In this tutorial you'll use a custom scheme based on your package name:
{your_app_packageName}://oid4vp-callback. - Select Create.
- Make note of the generated application
ID. You will need this value to initialize the SDK in your mobile application later in this tutorial.
Make the following request to your MATTR VII tenant to create a verifier application configuration:
POST /v2/presentations/applications{
"name": "My Android Mobile Verifier Application",
"type": "android",
"packageName": "com.example.mobileverifiertutorial",
"openid4vpConfiguration": {
"redirectUri": "com.example.mobileverifiertutorial://oid4vp-callback"
},
"packageSigningCertificateThumbprints" : ["3A9F6C1D4E8B72F0A5C3D6E19B4F8A2C7D1E0B9F3A6C5D4E7B8F2A1C9D0E3F5B"]
}name: You can use whatever name you'd like, as long as it is unique on your tenant.type: Useandroidas you are building an Android application.packageName: This is the unique identifier of your Android application, which must match the package name you set later in this tutorial.openid4vpConfiguration:redirectUri: URI used to return the user to your app after the wallet presents the credential. It must resolve to a path your app can handle (via custom URI scheme or web page). In this tutorial you'll use a custom scheme based on your package name:{your_app_packageName}://oid4vp-callback.
packageSigningCertificateThumbprints: Temporary placeholder for SHA-256 app signing certificate thumbprints. MATTR VII uses these to verify requests come from your signed app. You will update the placeholder value after you retrieve the signing certificate in Step 1: Environment setup.
Response
{
"id": "0eaa8074-8cc4-41ec-9e42-072d36e2acb0",
"name": "My Android Mobile Verifier Application"
//... rest of application configuration
}id: You will use this value later to:- Initialize the SDK so that requests coming from your verifier application can be recognized and trusted by the MATTR VII tenant.
- Update the
packageSigningCertificateThumbprintsvalue once we retrieve the app signing certificate.
Coming soon...
Create a supported wallet configuration
Verifier applications can define specific wallet applications to accept mDocs from as part of their verification workflows. The MATTR VII verifier tenant needs to be configured with a specific URI scheme that will be used to invoke these wallets.
- Log in to the MATTR Portal (if you haven't already).
- In the navigation panel on the left-hand side, expand the Credential Verification menu.
- Click on Supported wallets.
- Click on Create new.
- Enter a meaningful Name for the new supported wallet (e.g. "My Supported Wallet").
- Enter
mdoc-openid4vp://in the Authorization Endpoint field. This is the URI scheme that will be used to invoke the wallet application. More information on applying different URI schemes and the resulting user experience can be found in the workflow page. - Click on Create.
The authorizationEndpoint configured in the example above
(mdoc-openid4vp://) is the default OID4VP scheme. While this is technically
redundant, we chose to include this step to explain how to configure this
endpoint for wallet application using different schemes. More information on applying different URI schemes and the resulting user experience can be found in the workflow page.
Make the following request to your MATTR VII tenant to create a trusted wallet provider configuration:
POST /v2/presentations/wallet-providers{
"name": "My Trusted Wallet Provider",
"openid4vpConfiguration": {
"authorizationEndpoint": "mdoc-openid4vp://"
}
}name: Unique name to identify this trusted wallet provider.authorizationEndpoint: URI scheme that will be used to invoke the wallet application. More information on applying different URI schemes and the resulting user experience can be found in the workflow page.
The authorizationEndpoint configured in the example above
(mdoc-openid4vp://) is the default OID4VP scheme. While this is technically
redundant, we chose to include this step to explain how to configure this
endpoint for wallet application using different schemes.
Response
{
"id": "99890c34-e4b7-4a23-84d6-e5de57114c00",
"name": "My Trusted Wallet Provider",
"openid4vpConfiguration": {
"authorizationEndpoint": "mdoc-openid4vp://"
}
}id: You will use this value later to indicate this is the wallet the verifier application expects to receive mDocs from.
Configure a trusted issuer
- In the navigation panel on the left-hand side, expand the Credential Verification menu.
- Click on Trusted issuers.
- Click on Create new.
- Copy and paste the following certificate in the Certificate PEM file field:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIICYzCCAgmgAwIBAgIKXhjLoCkLWBxREDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAjA4MQswCQYDVQQG
EwJBVTEpMCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0Ew
HhcNMjQwMTE4MjMxNDE4WhcNMzQwMTE1MjMxNDE4WjA4MQswCQYDVQQGEwJBVTEp
MCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0EwWTATBgcq
hkjOPQIBBggqhkjOPQMBBwNCAASBnqobOh8baMW7mpSZaQMawj6wgM5e5nPd6HXp
dB8eUVPlCMKribQ7XiiLU96rib/yQLH2k1CUeZmEjxoEi42xo4H6MIH3MBIGA1Ud
EwEB/wQIMAYBAf8CAQAwDgYDVR0PAQH/BAQDAgEGMB0GA1UdDgQWBBRFZwEOI9yq
232NG+OzNQzFKa/LxDAuBgNVHRIEJzAlhiNodHRwczovL21vbnRjbGlmZi1kbXYu
bWF0dHJsYWJzLmNvbTCBgQYDVR0fBHoweDB2oHSgcoZwaHR0cHM6Ly9tb250Y2xp
ZmYtZG12LnZpaS5hdTAxLm1hdHRyLmdsb2JhbC92Mi9jcmVkZW50aWFscy9tb2Jp
bGUvaWFjYXMvMjk0YmExYmMtOTFhMS00MjJmLThhMTctY2IwODU0NWY0ODYwL2Ny
bDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAgNIADBFAiAlZYQP95lGzVJfCykhcpCzpQ2LWE/AbjTGkcGI
SNsu7gIhAJfP54a2hXz4YiQN4qJERlORjyL1Ru9M0/dtQppohFm6
-----END CERTIFICATE------ Click on Add.
You must configure trusted issuers on your MATTR VII verifier tenant, as presented mDocs will only be verified if they had been issued by a trusted issuer.
This is achieved by providing the PEM certificate of the IACA used by these issuers to sign mDocs. In production environments the issuer can provide it out of band or you can obtain it via their issuer's metadata.
Make the following request to your MATTR VII tenant to configure a truster issuer:
POST /v2/credentials/mobile/trusted-issuers{
"certificatePem": "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\nMIICYzCCAgmgAwIBAgIKXhjLoCkLWBxREDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAjA4MQswCQYDVQQG\nEwJBVTEpMCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0Ew\nHhcNMjQwMTE4MjMxNDE4WhcNMzQwMTE1MjMxNDE4WjA4MQswCQYDVQQGEwJBVTEp\nMCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0EwWTATBgcq\nhkjOPQIBBggqhkjOPQMBBwNCAASBnqobOh8baMW7mpSZaQMawj6wgM5e5nPd6HXp\ndB8eUVPlCMKribQ7XiiLU96rib/yQLH2k1CUeZmEjxoEi42xo4H6MIH3MBIGA1Ud\nEwEB/wQIMAYBAf8CAQAwDgYDVR0PAQH/BAQDAgEGMB0GA1UdDgQWBBRFZwEOI9yq\n232NG+OzNQzFKa/LxDAuBgNVHRIEJzAlhiNodHRwczovL21vbnRjbGlmZi1kbXYu\nbWF0dHJsYWJzLmNvbTCBgQYDVR0fBHoweDB2oHSgcoZwaHR0cHM6Ly9tb250Y2xp\nZmYtZG12LnZpaS5hdTAxLm1hdHRyLmdsb2JhbC92Mi9jcmVkZW50aWFscy9tb2Jp\nbGUvaWFjYXMvMjk0YmExYmMtOTFhMS00MjJmLThhMTctY2IwODU0NWY0ODYwL2Ny\nbDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAgNIADBFAiAlZYQP95lGzVJfCykhcpCzpQ2LWE/AbjTGkcGI\nSNsu7gIhAJfP54a2hXz4YiQN4qJERlORjyL1Ru9M0/dtQppohFm6\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----"
}certificatePem: This is the IACA identifying the MATTR Labs demo issuer which issues the credential referenced in the Testing device prerequisite.
If you intend to test this tutorial with a credential different than the one
recommended in our Testing device prerequisite, replace the
certificatePem value with your own issuer's IACA.
A successful 201 response indicates that this issuer's certificate was added to your MATTR VII
tenant's trusted issuer's list. This means that mDocs that use this IACA as their root certificate
can be trusted and verified.
Part 2: Build a mobile application with mDocs verification capabilities
Now that the MATTR VII verifier tenant is properly configured, you can proceed with the steps required to embed verification capabilities into your mobile verifier application:
- Setup your environment: Setup the required infrastructure for your mobile application.
- Initialize the SDK: So that the SDK functions are available in your mobile application.
- Request a credential from wallet application: Build the capability to request an mDoc for verification from a wallet application.
- Display verification results:
Step 1: Environment setup
Step 1: Create a new project
Follow the detailed instructions to Create a new Xcode Project and add your organization's identifier.
Step 2: Unzip the dependencies file
- Unzip the
MobileCredentialVerifierSDK-*version*.xcframework.zipfile. - Drag the
MobileCredentialVerifierSDK-*version*.xcframeworkfolder into your project. - Configure
MobileCredentialVerifierSDK.xcframeworkto Embed & sign.
See Add existing files and folders for detailed instructions.
This should result in the the following framework being added to your project:

Step 3: Run the application
Select Run and make sure the application launches with a “Hello, world!” text in the middle of the display, as shown in the following image:
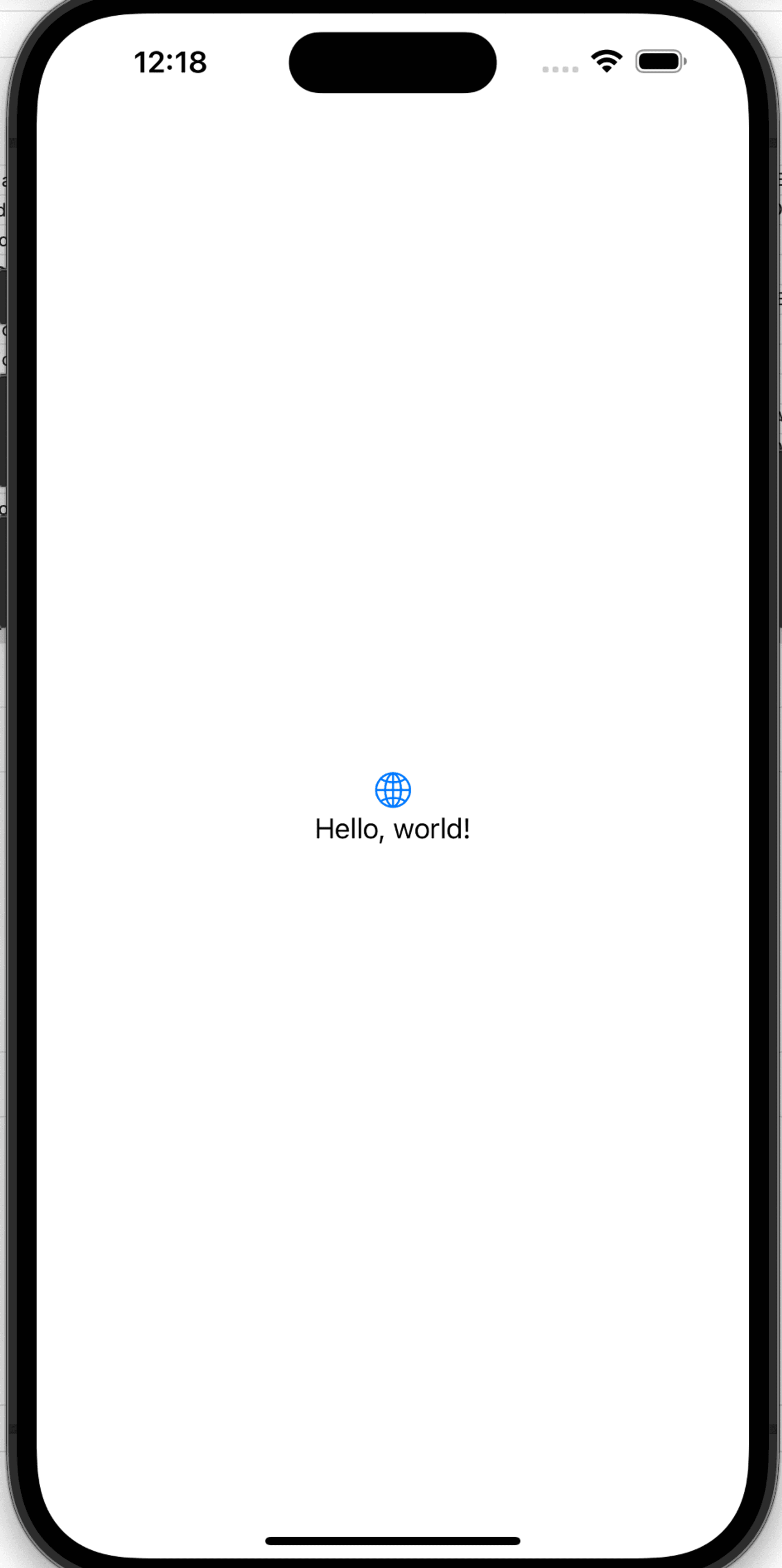
Step 1: Create a new project
- Create a new Android Studio project, using the Empty Activity template.
- Name the project
Mobile Verifier Tutorial. - Select API 24 as the
Minimum SDKversion. - Select Kotlin DSL as the
Build configuration language.

- Click Finish.
- Sync the project with Gradle files.
Step 2: Add required dependencies
-
Select the Project view.
-
Create a new directory named
repoin your project's folder. -
Unzip the
common-*version*.zipandverifier-*version*.zipfiles and copy the unzippedglobalfolders into the newrepofolder, merging the top-level directories. -
Open the
settings.gradle.ktsfile in theMobileVerifierTutorialfolder and add the following Maven repository to thedependencyResolutionManagement.repositoriesblock:settings.gradle.kts maven { url = uri("repo") } -
Open the
app/build.gradle.ktsfile in your app folder and add the following dependencies to thedependenciesblock:
implementation("global.mattr.mobilecredential:verifier:5.2.0")
implementation("androidx.navigation:navigation-compose:2.9.0")- The
verifierdependency version should match the version of the unzippedverifier-*version*.zipfile you copied to therepofolder. - The required
navigation-composeversion may differ based on your version of the IDE, Gradle, and other project dependencies.
-
Open the Build tab and select
Syncto make sure that the project has synced successfully.
Step 3: Run the application
- Connect a debuggable mobile device to your machine.
- Build and run the app on the connected mobile device. The app should launch with a “Hello, Android!” text displayed.
Step 4: Update app signing certificate
- Open a terminal inside your project's root folder.
- Run the following command to retrieve your application's signing certificate:
./gradlew signingReport - Locate the
SHA-256value in theVariant: debugsection. - Copy the
SHA-256value and:- Remove all colons (
:). - Convert all letters to lowercase.
- Remove all colons (
echo '91:F7:CB:F9:D6:81:53:1B:C7:A5:8F:B8:33:CC:A1:4D:AB:ED:E5:09:C5' | tr -d ':' | tr 'A-F' 'a-f'- Make a request of the following structure to update your MATTR VII verifier application's
packageSigningCertificateThumbprintsvalue with the retrieved signing certificate thumbprint:
PUT /v2/presentations/applications/{applicationId}applicationId: Replace with theidof your MATTR VII verifier application created in Create a verifier application configuration.
{
"name": "My Android Mobile Verifier Application",
"type": "android",
"packageName": "com.example.mobileverifiertutorial",
"openid4vpConfiguration": {
"redirectUri": "com.example.mobileverifiertutorial://oid4vp-callback"
},
"packageSigningCertificateThumbprints" : ["91f7cbf9d681531bc7a58fb833cca14dabede509c5"]
}packageSigningCertificateThumbprints: Replace with the retrieved signing certificate thumbprint.
This thumbprint is only valid for your debug builds. If you intend to publish your app, you will need to repeat this process with the release signing certificate. Refer to Android App Signing for more information.
Coming soon...
Step 2: Initialize the SDK
The first capability you will build into your app is to initialize the SDK so that the app can use
its functions and classes. To achieve this, you need to import the MobilecredentialVerifierSDK
framework and then initialize the MobileCredentialVerifier class.
-
Open the
ContentViewfile in your new project and replace any existing code with the following:ContentView import SwiftUI import Combine // Step 2.3: Import MobileCredentialVerifierSDK struct ContentView: View { @ObservedObject var viewModel: VerifierViewModel = VerifierViewModel() var body: some View { NavigationStack(path: $viewModel.navigationPath) { VStack { Button("Request credentials") { viewModel.requestCredentials() } .padding() } .navigationDestination(for: NavigationState.self) { destination in switch destination { case .viewResponse: presentationResponseView } } } // Step 4.2: Handle MATTR VII redirect } // MARK: Verification Views var presentationResponseView: some View { // Step 4.4: Create PresentationResponseView EmptyView() } } // MARK: VerifierViewModel final class VerifierViewModel: ObservableObject { @Published var navigationPath = NavigationPath() // Step 2.4: Setup platform configuration // Step 2.5: Add MobileCredentialVerifier var // Step 2.6: Initialize the SDK // Step 3.1: Create MobileCredentialRequest instance // Step 3.2: Create receivedDocuments variable } // MARK: Same Device Verification extension VerifierViewModel { func requestCredentials() { // Step 3.3: Request credentials } } // MARK: - Navigation enum NavigationState: Hashable { case viewResponse }This will serve as the basic structure for your application. You will copy and paste different code snippets into specific locations to achieve the different functionalities. These locations are indicated by comments that reference both the section and the step.
We recommend copying and pasting the comment text in Xcode search field (e.g.
Step 2.3: Import MobileCredentialVerifierSDK) to easily locate it in the code. -
Create a new file named
Constantsand paste the following code into it to define constants which are required to initialize the SDK:Constants import Foundation enum Constants { static let tenantHost = URL(string: "https://learn.vii.au01.mattr.global")! static let applicationID = "74f91a0f-5909-43b0-a431-6da2397d1f86" }tenantHost: Replace with the URL of your MATTR VII tenant.applicationID: Replace with theidreturned when you created the MATTR VII verifier application.
-
Return to the
ContentViewfile and add the following code after theStep 2.3: Import MobileCredentialVerifierSDKcomment to importMobileCredentialVerifierSDKand gain access to the SDK capabilities:ContentView import MobileCredentialVerifierSDK -
Add the following code under the
Step 2.4: Setup platform configurationcomment to create aPlatformConfigurationinstance:ContentView let platformConfiguration = PlatformConfiguration( tenantHost: Constants.tenantHost )This instance configures the MATTR VII tenant that the SDK will interact with (
tenantHost) based on the constants defined in theConstantsfile. -
Add the following code after the
Step 2.5: Add MobileCredentialVerifier varcomment to create a variable that will hold themobileCredentialVerifierinstance when the SDK is initialized:ContentView var mobileCredentialVerifier: MobileCredentialVerifier -
Add the following code after the
Step 2.6: Initialize the SDKcomment to initialize theMobileCredentialVerifierinstance with the parameters defined in theplatformConfigurationinstance:ContentView init() { do { mobileCredentialVerifier = MobileCredentialVerifier.shared try mobileCredentialVerifier.initialize(platformConfiguration: platformConfiguration) } catch { print(error.localizedDescription) } } -
Run the app to ensure it compiles successfully.
The first capability you will build into your app is to initialize the SDK so that the app can use
its functions and classes. To achieve this, you need to import the MobilecredentialVerifierSDK
framework and then initialize the MobileCredentialVerifier class.
-
Open the
MainActivityfile in your new project and replace any existing code with the following:MainActivity package com.example.mobileverifiertutorial import android.app.Activity import android.os.Bundle import androidx.activity.ComponentActivity import androidx.activity.compose.setContent import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.* import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.LazyColumn import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.items import androidx.compose.material3.Button import androidx.compose.material3.Scaffold import androidx.compose.material3.Text import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.runtime.collectAsState import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.platform.LocalContext import androidx.compose.ui.tooling.preview.Preview import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope import androidx.lifecycle.viewmodel.compose.viewModel import com.example.mobileverifiertutorial.ui.theme.MobileVerifierTutorialTheme import global.mattr.mobilecredential.common.deviceretrieval.devicerequest.DataElements import global.mattr.mobilecredential.common.deviceretrieval.devicerequest.NameSpaces import global.mattr.mobilecredential.common.dto.MobileCredentialPresentation import global.mattr.mobilecredential.common.dto.MobileCredentialRequest import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.MobileCredentialVerifier import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.PlatformConfiguration import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.StateFlow import kotlinx.coroutines.launch import java.net.URL class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) enableEdgeToEdge() setContent { MobileVerifierTutorialTheme { Scaffold(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { innerPadding -> Content( modifier = Modifier.padding(innerPadding) ) } } } // Step 2.3: Setup platform configuration // Step 2.4: Initialize the SDK } } @Composable fun Content(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) { val activity = (LocalContext.current) as Activity val viewModel: VerifierViewModel = viewModel() val documents by viewModel.receivedDocuments.collectAsState() Column( modifier = modifier .fillMaxSize(), verticalArrangement = Arrangement.Center, horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally ) { Button(onClick = { viewModel.requestCredentials(activity) }) { Text("Request credentials") } LazyColumn(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { items(documents) { document -> // Step 4.5: Display received documents } } } } @Preview(showBackground = true) @Composable fun ContentPreview() { MobileVerifierTutorialTheme { Content() } } class VerifierViewModel : ViewModel() { private val _receivedDocuments = MutableStateFlow<List<MobileCredentialPresentation>>(emptyList()) val receivedDocuments: StateFlow<List<MobileCredentialPresentation>> = _receivedDocuments fun requestCredentials(activity: Activity) { // Step 3.1: Create MobileCredentialRequest instance viewModelScope.launch { _receivedDocuments.value = emptyList() try { // Step 3.2: Request credentials // Step 4.2: Handle response } catch (e: Exception) { e.printStackTrace() } } } }This will serve as the basic structure for your application. You will copy and paste different code snippets into specific locations to achieve the different functionalities. These locations are indicated by comments that reference both the section and the step.
We recommend copying and pasting the comment text in the Android Studio search field (e.g.
Step 2.3: Setup platform configuration) to easily locate it in the code. -
Create a new file named
Constantsand paste the following code, replacing the values as indicated, to define constants which are required to initialize the SDK:Constants package com.example.mobileverifiertutorial object Constants { const val TENANT_HOST = "https://learn.vii.au01.mattr.global" const val APPLICATION_ID = "74f91a0f-5909-43b0-a431-6da2397d1f86" }TENANT_HOST: Replace with the URL of your MATTR VII tenant. This indicates the tenant that the SDK will interact with.APPLICATION_ID: Replace with theidreturned when you created the MATTR VII verifier application. This indicates the verifier application that the SDK will represent.
-
Add the following code under the
Step 2.3: Setup platform configurationcomment to create aPlatformConfigurationinstance:MainActivity val platformConfiguration = PlatformConfiguration( tenantHost = URL(Constants.TENANT_HOST) )This instance configures the MATTR VII tenant that the SDK will interact with (
tenantHost) based on the constants defined in theConstantsfile. -
Add the following code after the
Step 2.4: Initialize the SDKcomment to initialize theMobileCredentialVerifierinstance with the parameters defined in theplatformConfigurationinstance:MainActivity lifecycleScope.launch { MobileCredentialVerifier.initialize( context = this@MainActivity, platformConfiguration = platformConfiguration ) } -
Run the app to ensure it compiles successfully.
Coming soon...
Step 3: Request a credential from wallet application
Once the SDK is initialized, you can start building the capabilities to request an mDoc for verification from a wallet application. This is done by:
- Creating a request object that defines what information is required for verification.
- Sending this request to the wallet application installed on the device.
- Redirecting the user to the wallet application to present the requested mDoc.
-
Open the
ContentViewfile and add the following code under theStep 3.1: Create MobileCredentialRequest instancecomment to create a new MobileCredentialRequest instance:ContentView let mobileCredentialRequest = MobileCredentialRequest( docType: "org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL", namespaces: [ "org.iso.18013.5.1": [ "family_name": false, "given_name": false, "birth_date": false ] ] )This object defines what information is required for verification:
- The requested credential type (e.g.
org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL). - The claims required for verification (e.g.
family_name). - The requested namespace (e.g.
org.iso.18013.5.1). - Whether or not the verifier intends to persist the claim value (
true/false). Declarative only and not currently enforced by the SDK. For the verification to be successful, the presented credential must include the referenced claim against the specific namespace defined in the request. Our example requests thebirth_dateunder theorg.iso.18013.5.1namespace. If a wallet responds to this request with a credential that includes abirth_datebut rather under theorg.iso.18013.5.1.USnamespace, the claim will not be verified.
- The requested credential type (e.g.
-
Add the following code under the
Step 3.2: Create receivedDocuments variablecomment to create a newreceivedDocumentsvariable that will hold the response received from the wallet application:ContentView @Published var receivedDocuments: [MobileCredentialPresentation] = [] -
Add the following code under the
Step 3.3: Request credentialscomment to call the SDK'srequestMobileCredentialsmethod:ContentView Task { @MainActor in // Clean the response before fetching a new one receivedDocuments = [] do { let onlinePresentationResult = try await mobileCredentialVerifier.requestMobileCredentials(request: [mobileCredentialRequest], challenge: UUID().uuidString, applicationId: Constants.applicationID) guard let receivedCredentials = onlinePresentationResult.mobileCredentialResponse?.credentials else { let errorMessage = onlinePresentationResult.error?.message ?? "No error message" print("No response received: \(errorMessage)") return } receivedDocuments = receivedCredentials } catch { print(error.localizedDescription) } }The following parameters are passed to the
requestMobileCredentialsmethod:request: Defines what information to request. This example is passing themobileCredentialRequestinstance you created in the previous step.challenge: Unique challenge generated by the SDK to identify this specific presentation session. Should be a unique, unpredictable value generated for each verification session to mitigate replay attacks by ensuring the response from the wallet app is tied to the current request and cannot be reused maliciously. Always generate a new challenge for every same credential request.applicationId: Identifier of the application that will be used to verify the request. In this example it is retrieved from the information defined in theConstantsfile.
-
Run the app and press
Request credentialsbutton.You will be redirected to a compliant wallet application, where you will see the verification request details and choose what mDoc to present for verification.
Once you send the response from the wallet nothing will happen, which is expected at this stage. In the next step you will build the capability to redirect the user back to the verifier application and handle the response from the wallet.
-
Open the
MainActivityfile and add the following code under theStep 3.1: Create MobileCredentialRequest instancecomment to create a new MobileCredentialRequest instance:MainActivity val mobileCredentialRequest = MobileCredentialRequest( docType = "org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL", namespaces = NameSpaces( mapOf( "org.iso.18013.5.1" to DataElements( mapOf( "family_name" to false, "given_name" to false, "birth_date" to false ) ) ) ) )This object defines what information is required for verification:
- The requested credential type (e.g.
org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL). - The claims required for verification (e.g.
family_name). - The requested namespace (e.g.
org.iso.18013.5.1). - Whether or not the verifier intends to persist the claim value (
true/false). Declarative only and not currently enforced by the SDK.
For the verification to be successful, the presented credential must include the referenced claim against the specific namespace defined in the request. Our example requests the
birth_dateunder theorg.iso.18013.5.1namespace. If a wallet responds to this request with a credential that includes abirth_datebut rather under theorg.iso.18013.5.1.USnamespace, the claim will not be verified. - The requested credential type (e.g.
-
Add the following code under the
Step 3.2: Request credentialscomment to call the SDK'srequestMobileCredentialsmethod:MainActivity val onlinePresentationResult = MobileCredentialVerifier.requestMobileCredentials( activity = activity, request = listOf(mobileCredentialRequest), applicationId = Constants.APPLICATION_ID )The following parameters are passed to the
requestMobileCredentialsmethod:activity: Defines the current activity context.request: Defines what information to request. This example is passing themobileCredentialRequestinstance you created in the previous step.applicationId: Identifier of the application that will be used to verify the request. In this example it is retrieved from the information defined in theConstantsfile.
-
Run the app and press
Request credentialsbutton.You will be redirected to a compliant wallet application, where you will see the verification request details and choose what mDoc to present for verification.
Once you send the response from the wallet nothing will happen, which is expected at this stage. In the next step you will build the capability to redirect the user back to the verifier application and handle the response from the wallet.
Coming soon...
Step 4: Display verification results
Once the user provides their consent to share the requested information, the wallet application will send the response back to the MATTR VII tenant, which will then return the verification results to your verifier application and redirect the user back to the configured redirect URI. In this part of the tutorial you will build the capability to handle this redirect and display the verification results in your application.
To enable the redirect back to your verifier application you must register a redirection link. This could be either a Universal link or a custom URL scheme. In this tutorial you will use a custom URL scheme.
-
Register a custom URL scheme in your verifier application:
- Open the project view and select your application target.
- Select the Info tab.
- Scroll down and expand the URL Types area.
- Select the plus button.
- Insert
io.mattrlabs.dev.sampleApp.MdocSampleAppin both the Identifier and URL Schemes fields.

If you used a different bundle identifier when you configured the MATTR VII verifier application, make sure to replace
io.mattrlabs.dev.sampleApp.MdocSampleApp with the bundle identifier you used.
-
In your
ContentViewfile, add the following code under theStep 4.2: Handle MATTR VII redirectcomment to handle the redirect from the wallet application:ContentView .onOpenURL { url in // Navigate to response screen viewModel.navigationPath.append(NavigationState.viewResponse) viewModel.mobileCredentialVerifier.handleDeepLink(url) }This will pass the redirect URL to the SDK's
handleDeepLinkmethod, which will process the response from the wallet application and update thereceivedDocumentsvariable with the verification results. -
Create a new file named
DocumentViewand add the following code to display the retrieved verification results:DocumentView import MobileCredentialVerifierSDK import SwiftUI import Combine struct DocumentView: View { var viewModel: DocumentViewModel var body: some View { VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 10) { Text(viewModel.docType) .font(.title) .fontWeight(.bold) .padding(.bottom, 5) Text(viewModel.verificationResult) .font(.title) .fontWeight(.bold) .foregroundStyle(viewModel.verificationFailedReason == nil ? .green : .red) .padding(.bottom, 5) if let verificationFailedReason = viewModel.verificationFailedReason { Text(verificationFailedReason) .font(.title3) .fontWeight(.bold) .foregroundStyle(.red) .padding(.bottom, 5) } ForEach(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { key in VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 5) { Text(key) .font(.headline) .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.gray.opacity(0.2)) .cornerRadius(5) ForEach(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims[key]!.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { claim in HStack { Text(claim) .fontWeight(.semibold) Spacer() Text(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims[key]![claim]! ?? "") .fontWeight(.regular) } .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.white) .cornerRadius(5) .shadow(radius: 1) } } .padding(.vertical, 5) } if !viewModel.claimErrors.isEmpty { Text("Failed Claims:") .font(.headline) .padding(.vertical, 5) ForEach(viewModel.claimErrors.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { key in VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 5) { Text(key) .font(.headline) .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.gray.opacity(0.2)) .cornerRadius(5) ForEach(viewModel.claimErrors[key]!.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { claim in HStack { Text(claim) .fontWeight(.semibold) Spacer() Text(viewModel.claimErrors[key]![claim]! ?? "") .fontWeight(.regular) } .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.white) .cornerRadius(5) .shadow(radius: 1) } } .padding(.vertical, 5) } } } .padding() .background(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10).fill(Color.white).shadow(radius: 5)) .padding(.horizontal) } } // MARK: DocumentViewModel class DocumentViewModel: ObservableObject { let docType: String let namespacesAndClaims: [String: [String: String?]] let claimErrors: [String: [String: String?]] let verificationResult: String let verificationFailedReason: String? init(from presentation: MobileCredentialPresentation) { self.docType = presentation.docType self.verificationResult = presentation.verificationResult.verified ? "Verified" : "Invalid" self.verificationFailedReason = presentation.verificationResult.reason?.message self.namespacesAndClaims = presentation.claims?.reduce(into: [String: [String: String]]()) { result, outerElement in let (outerKey, innerDict) = outerElement result[outerKey] = innerDict.mapValues { $0.textRepresentation } } ?? [:] self.claimErrors = presentation.claimErrors?.reduce(into: [String: [String: String]]()) { result, outerElement in let (outerKey, innerDict) = outerElement result[outerKey] = innerDict.mapValues { "\($0)" } } ?? [:] } } // MARK: Helper extension MobileCredentialElementValue { var textRepresentation: String { switch self { case .bool(let bool): return "\(bool)" case .string(let string): return string case .int(let int): return "\(int)" case .unsigned(let uInt): return "\(uInt)" case .float(let float): return "\(float)" case .double(let double): return "\(double)" case let .date(date): let dateFormatter = DateFormatter() dateFormatter.dateStyle = .short dateFormatter.timeStyle = .none return dateFormatter.string(from: date) case let .dateTime(date): let dateFormatter = DateFormatter() dateFormatter.dateStyle = .short dateFormatter.timeStyle = .short return dateFormatter.string(from: date) case .data(let data): return "Data \(data.count) bytes" case .map(let dictionary): let result = dictionary.mapValues { value in value.textRepresentation } return "\(result)" case .array(let array): return array.reduce("") { partialResult, element in partialResult + element.textRepresentation } .appending("") @unknown default: return "Unknown type" } } }The
DocumentViewfile comprises the following elements:DocumentView: Basic UI layout for viewing received documents and verification results.DocumentViewModel: This class takesMobileCredentialPresentationand converts its elements into strings that are displayed in theDocumentView.- Extension of
MobileCredentialElementValuewhich converts the values of received claims into a human-readable format.
-
Return to the
ContentViewfile and replace theEmptyView()under theStep 4.4: Create PresentationResponseViewcomment with the following code to display theDocumentViewview when verification results are available:ContentView ZStack { if viewModel.receivedDocuments.isEmpty { VStack(spacing: 40) { Text("Waiting for response...") .font(.title) ProgressView() .progressViewStyle(.circular) .scaleEffect(2) } } else { ScrollView { ForEach(viewModel.receivedDocuments, id: \.docType) { doc in DocumentView(viewModel: DocumentViewModel(from: doc)) .padding(10) } } } }
To enable the redirect back to your verifier application you must register a redirection link. This could be either App Links or a Custom deep links. In this tutorial you will use a custom deep link.
-
In your app's
AndroidManifest.xmlfile, add the following activity declaration to register the callback url:AndroidManifest.xml <activity android:name="global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.a2apresentation.callback.Openid4VpCallbackActivity" android:exported="true"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /> <!-- Match the openid4vpConfiguration you configured in the MATTR VII Verifier application --> <data android:scheme="com.example.mobileverifiertutorial" android:host="oid4vp-callback" /> </intent-filter> </activity>android:scheme: This must match the redirect custom scheme you defined when you created the verifier application.android:host: This must match the redirect host you defined when you created the verifier application.
-
Add the following code under the
Step 4.2: Handle responseto navigate the user to the response screen, where they can see the retrieved credentials, if the retrieval was successful:MainActivity.kt _receivedDocuments.value = onlinePresentationResult.mobileCredentialResponse?.credentials ?: emptyList() -
Create a new file named
DocumentView.ktthat will be used to display the response to the verifier application user. -
Copy and paste the following code into the new file:
DocumentView.kt package com.example.mobileverifiertutorial import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.* import androidx.compose.material3.Card import androidx.compose.material3.CardDefaults import androidx.compose.material3.MaterialTheme import androidx.compose.material3.Text import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color import androidx.compose.ui.text.font.FontWeight import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp import global.mattr.mobilecredential.common.dto.MobileCredentialPresentation @Composable fun DocumentView(document: MobileCredentialPresentation, modifier: Modifier = Modifier) { val verified: Boolean = document.verificationResult.verified val statusText: String = if (verified) "Verified" else "Invalid" val statusColor: Color = if (verified) Color.Green else Color.Red val flatClaims: List<String> = document.claims?.flatMap { (_, claimsMap) -> claimsMap.map { (claim, value) -> "$claim: ${value.value}" } } ?: emptyList() Card( modifier = modifier.fillMaxWidth(), colors = CardDefaults.cardColors(containerColor = Color.White), elevation = CardDefaults.cardElevation(defaultElevation = 2.dp) ) { Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)) { Text( text = document.docType, color = Color.Black, style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleLarge, fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold, ) Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(4.dp)) Text( text = statusText, color = statusColor, style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium, fontWeight = FontWeight.SemiBold ) Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(12.dp)) if (flatClaims.isEmpty()) { Text( text = "No claims", color = Color.Black, style = MaterialTheme.typography.labelMedium, ) } else { flatClaims.forEach { line -> Text( text = line, color = Color.Black, style = MaterialTheme.typography.labelMedium ) } } } } } -
Back in the
MainActivity.ktfile, add the following code under theStep 4.5: Display received documentscomment:MainActivity.kt DocumentView(document)
Coming soon...
Test the end-to-end workflow
- Run the app.
- Select the Request credentials button.
You should be redirected to a compliant wallet application, where you will see the verification request details and choose what mDoc to present for verification. - Use the wallet application to present the requested mDoc.
You will be redirected back to the verifier application where you will see the verification results.
You should see a result similar to the following:
Coming soon...
- The verifier app starts a presentation session and gets redirected.
- The user is redirected to a compliant wallet application.
- The user provides their consent to share the requested information.
- The wallet application sends the response back to the MATTR VII tenant.
- The MATTR VII tenant redirects the user back to the verifier app with the verification results.
- The verifier app fetches the result and presents the result to user.
Congratulations! Your verifier application can now verify mDocs presented from a compliant wallet installed on the same mobile device.
Summary
You have just used the mDocs Mobile Verifier SDKs to build an application that can verify an mDoc presented from a compliant wallet on the same device using a remote presentation workflow as per OID4VP and ISO/IEC 18013-7 Annex B.
This was achieved by building the following capabilities into the application:
- Initialize the SDK, so that your application can use its functions and classes.
- Request an mDoc for verification from a compliant wallet application.
- Display verification results in your verifier application.
What's next?
How would you rate this page?
Last updated on
