Learn how to build an application that can verify an mDoc presented via a proximity workflow
Overview
In this tutorial you will use the mDocs mobile verifier SDKs to build an application that can verify an mDoc presented via a proximity workflow as per ISO 18013-5:
- The credential holder presents a QR code generated by their wallet application.
- The verifier uses their application to scan the QR code, connect with the wallet and request an mDoc for verification.
- The wallet application displays matching credentials to the holder and asks for consent to share them with the verifier.
- The verifier application receives the wallet's response and verifies the provided credential.
- Verification results are displayed to the verifier.
The result will look something like this:
To achieve this, you will build the following capabilities into your verifier application:
- Initialize the SDK, so that your application can use its functions and classes.
- Manage certificates, which enable your application to verify mDocs that were issued by trusted issuers.
- Scan a QR code presented by a wallet application and establish a secure communication channel.
- Send presentation requests to the wallet application, receive a presentation response and verify its content.
- Display the results to the verifier app user.
Prerequisites
Before we get started, let's make sure you have everything you need.
Prior knowledge
-
The proximity verification workflow described in this tutorial is based on the ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021 standard. If you are unfamiliar with this standard, refer to the following Docs for more information:
- What are mDocs?
- What is credential verification?
- Breakdown of the proximity presentation workflow.
-
We assume you have experience developing applications in the relevant programming languages and frameworks (Swift for iOS, Kotlin for Android, and JavaScript/TypeScript for React Native).
If you need to get a verifier solution up and running quickly with minimal development resources and in-house domain expertise, talk to us about our white-label MATTR GO Verify which might be a good fit for you.
Assets
- As part of your onboarding process you should have been provided with access to the following
assets:
- ZIP file which includes the required framework:
(
MobileCredentialVerifierSDK-*version*.xcframework.zip). - Sample Verifier app: You can use this app for reference as we work through this tutorial.
- ZIP file which includes the required framework:
(
This tutorial is only meant to be used with the most recent version of the iOS mDocs Verifier SDK.
- As part of your onboarding process you should have been provided with access to the following
assets:
- A ZIP file that includes the required library (
mobile-credential-verifier-*version*.zip). - Sample Verifier app: You can use this app for reference as we work through this tutorial.
- A ZIP file that includes the required library (
This tutorial is only meant to be used with the most recent version of the Android mDocs Verifier SDK.
- As part of your onboarding process you should have been provided with access to the following
assets:
- Access to the @mattrglobal/mobile-credential-verifier-react-native npm package.
- Sample Verifier app: You can use this app for reference as we work through this tutorial.
This tutorial is only meant to be used with the most recent version of the React Native mDocs Verifier SDK.
Development environment
- Xcode setup with either:
- Local build settings if you are developing locally.
- iOS developer account if you intend to publish your app.
- Code editor (such as VS Code).
- Android Studio.
- Xcode.
- yarn (v1.22.22 was used during development).
- Java v17.
This tutorial uses Expo Go, leveraging Development Builds.
Testing devices
As this tutorial implements a proximity presentation workflow, you will need two different mobile devices to test the end-to-end result:
- Verifier device:
- Supported iOS device to run the built Verifier application on, setup with:
- Bluetooth access.
- Available internet connection.
- Supported iOS device to run the built Verifier application on, setup with:
- Holder device:
- Mobile device with the
MATTR GO Hold example app installed and
setup with:
- Biometric authentication.
- Bluetooth access.
- Available internet connection.
- Mobile device with the
MATTR GO Hold example app installed and
setup with:
- Verifier device:
- Supported Android device to run the built Verifier application on, setup with:
- Bluetooth access.
- Available internet connection.
- USB debugging enabled.
- Supported Android device to run the built Verifier application on, setup with:
- Holder device:
- Mobile device with the
MATTR GO Hold example app installed and
setup with:
- Biometric authentication.
- Bluetooth access.
- Available internet connection.
- Mobile device with the
MATTR GO Hold example app installed and
setup with:
- Verifier device:
- Supported iOS or Android device to run the built Verifier application on, setup with:
- Bluetooth access.
- Available internet connection.
- Supported iOS or Android device to run the built Verifier application on, setup with:
- Holder device:
- Mobile device with the
MATTR GO Hold example app installed and
setup with:
- Biometric authentication.
- Bluetooth access.
- Available internet connection.
- Mobile device with the
MATTR GO Hold example app installed and
setup with:
mDoc
-
Download and install the MATTR GO Hold example app on your holder testing device.
-
Use the GO Hold example app to claim an mDoc by scanning the following QR code:

Got everything? Let's get going!
Environment setup
Perform the following steps to setup and configure your development environment:
Step 1: Create a new project
Please follow the detailed instructions to Create a new Xcode Project and add your organization's identifier.
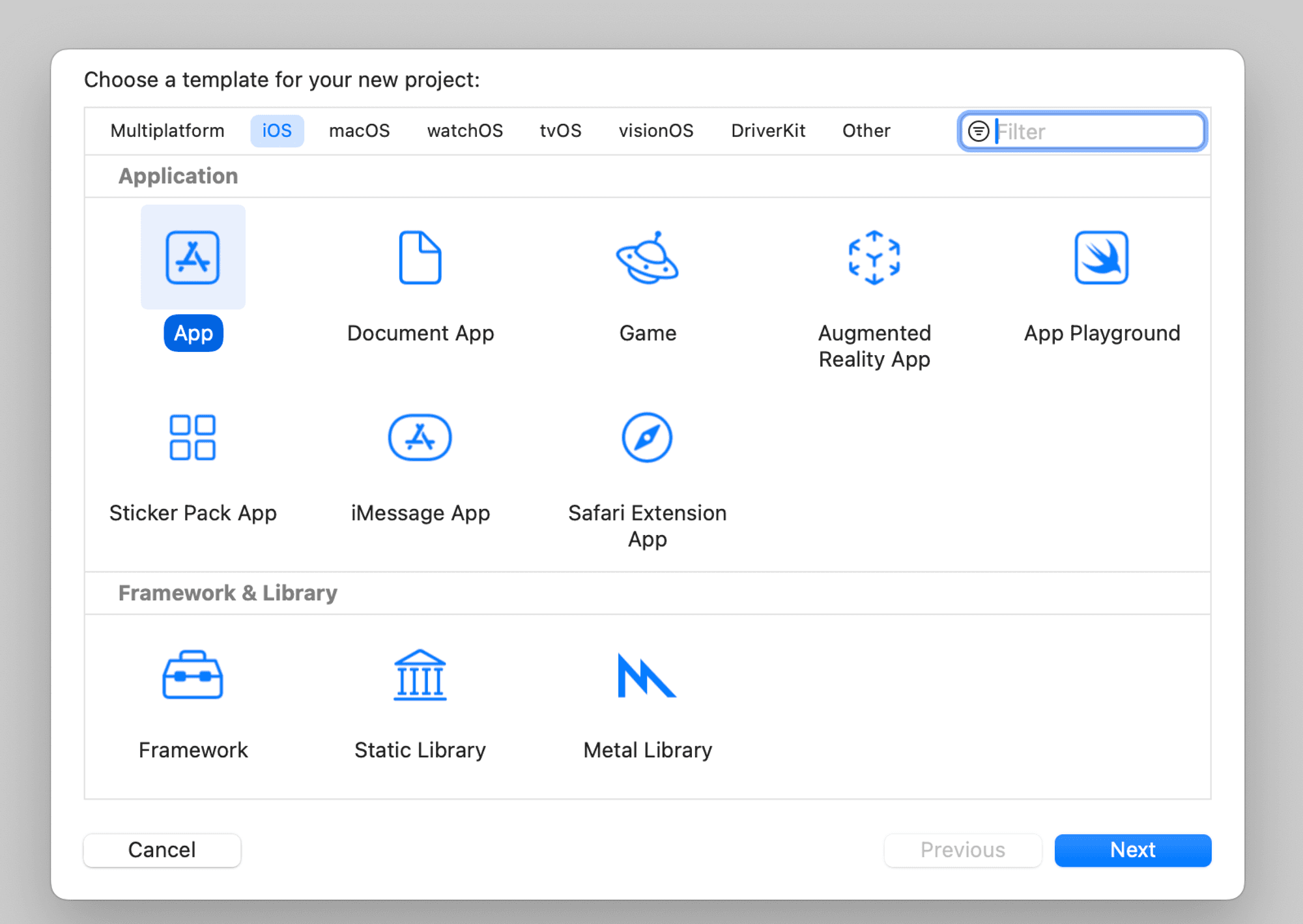
Step 2: Unzip the dependencies file
- Unzip the
MobileCredentialVerifierSDK-*version*.xcframework.zipfile. - Drag the
MobileCredentialVerifierSDK-*version*.xcframeworkfolder into your project. - Configure
MobileCredentialVerifierSDK.xcframeworkto Embed & sign.
See Add existing files and folders for detailed instructions.
This should result in the the following framework being added to your project:

Step 3: Add Bluetooth permissions
The SDK requires access to the mobile device Bluetooth capabilities as part of the proximity
presentation workflow.
Configure these permissions in the Info
tab of the Application target:
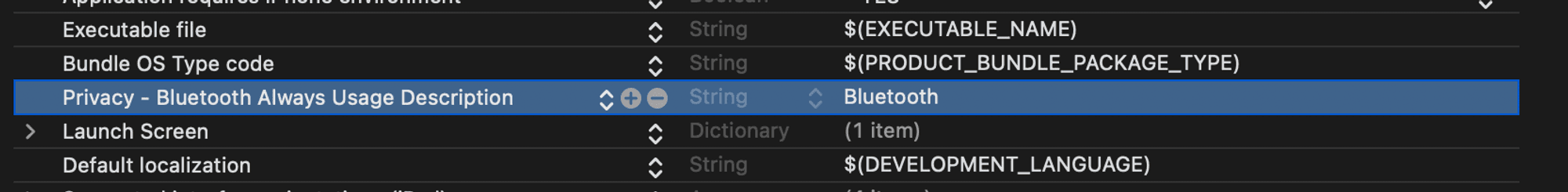
Step 4: Run the application
Select Run and make sure the application launches with a “Hello, world!” text in the middle of the display, as shown in the following image:
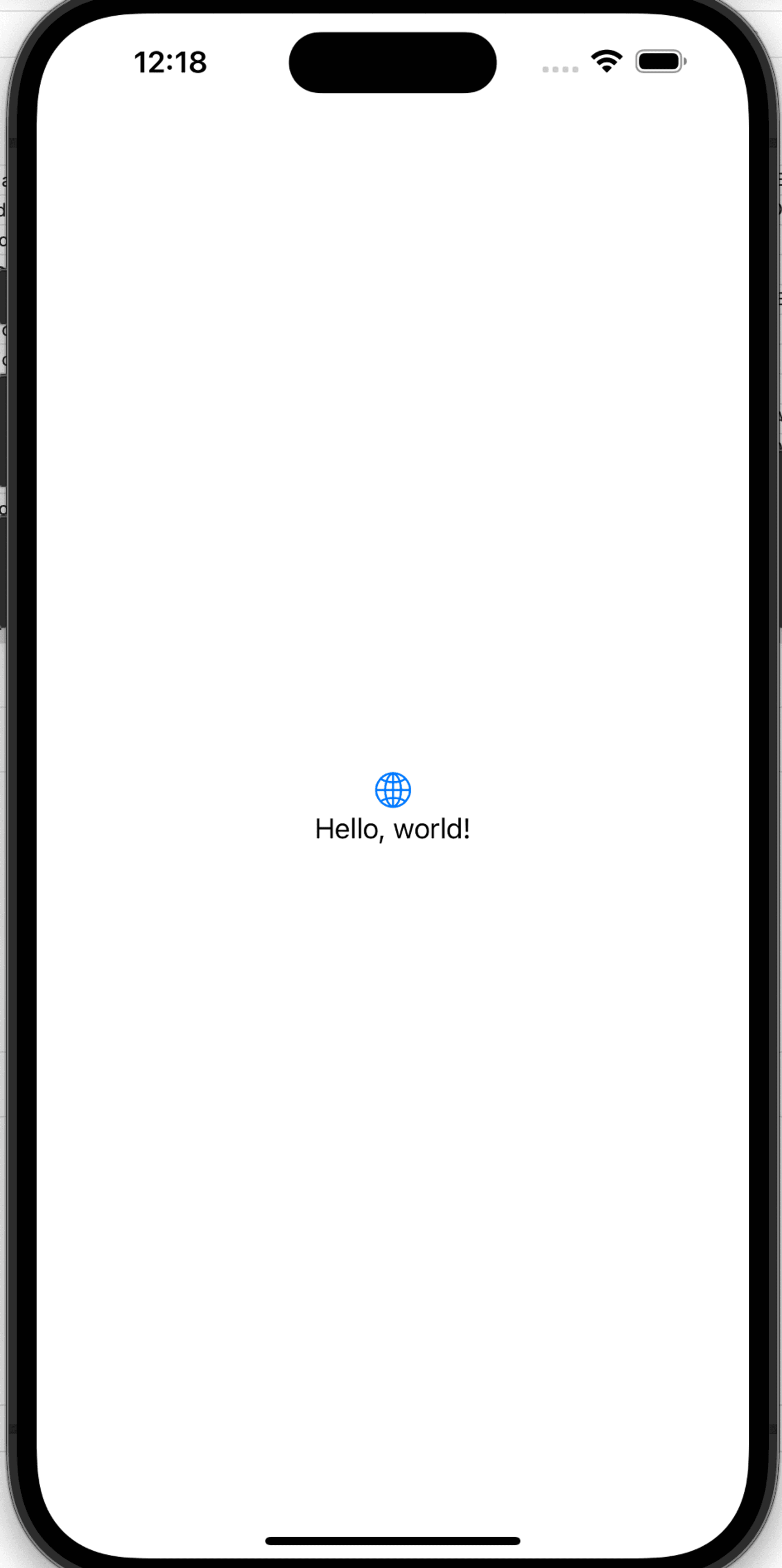
Step 1: Create a new project
- Create a new Android Studio project, using the Empty Activity template.
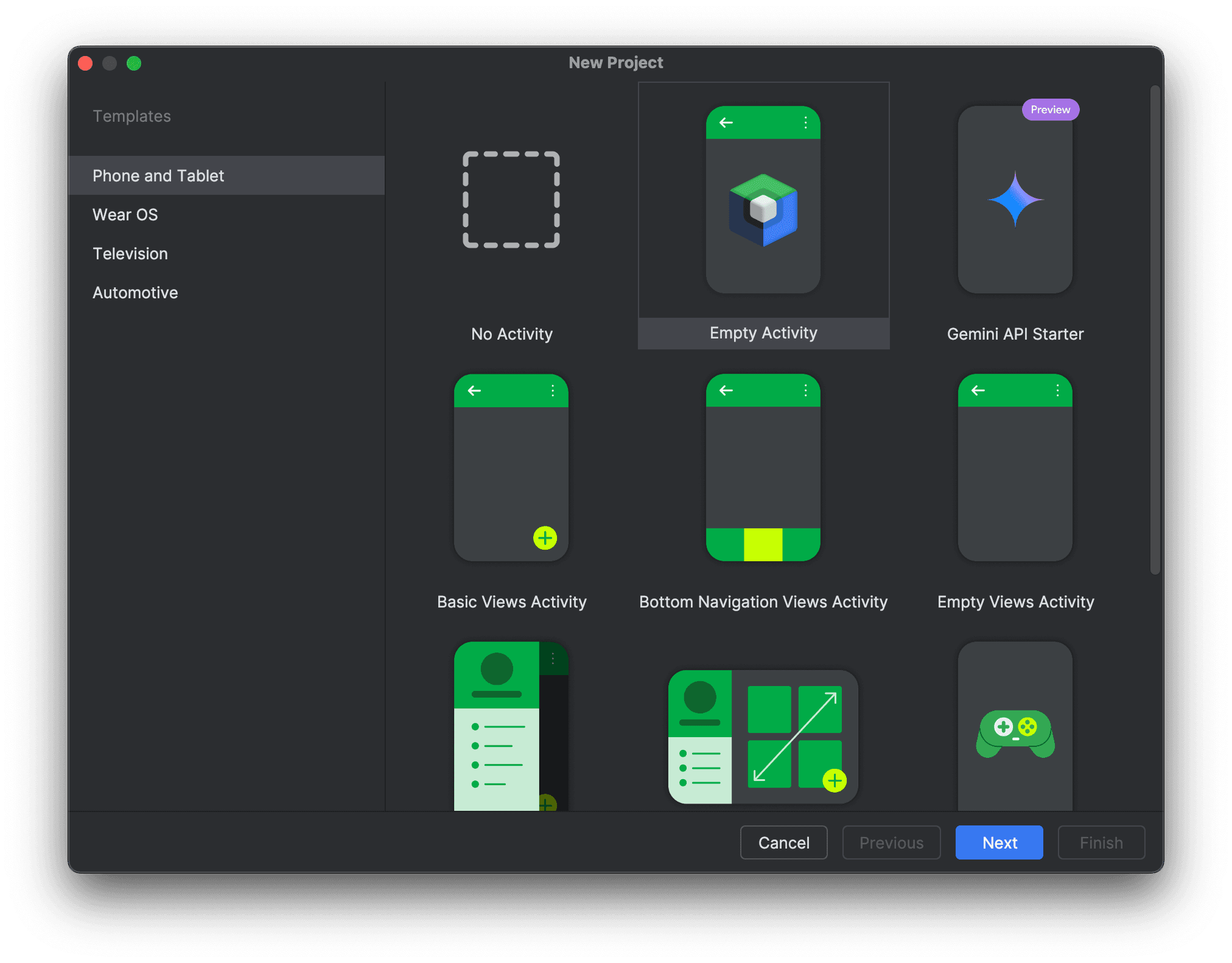
- Name the project
Verifier Tutorial. - Select API 24 as the
Minimum SDKversion. - Select Kotlin DSL as the
Build configuration language.
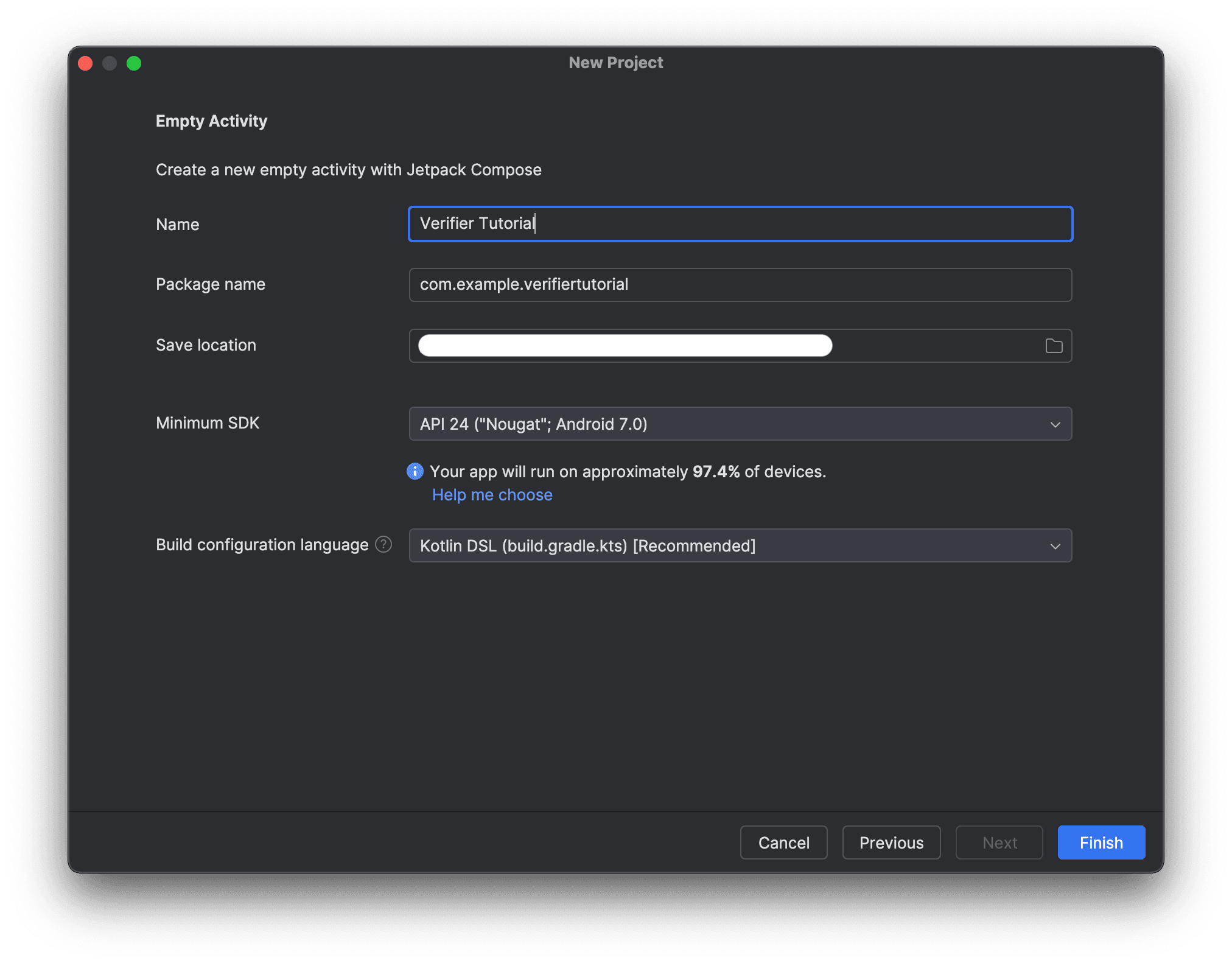
- Select Finish.
- Sync the project with Gradle files.
Step 2: Add required dependencies
-
Select the Project view.
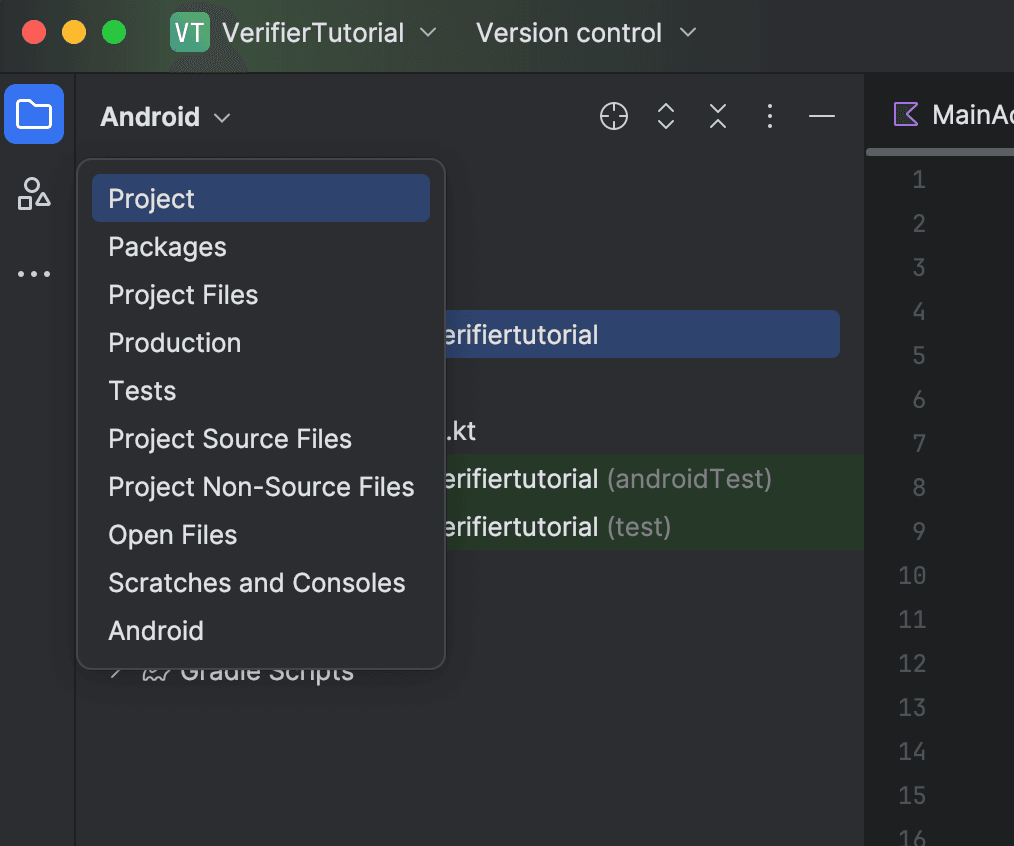
-
Create a new directory named
repoin your project's folder. -
Unzip the
mobile-credential-verifier-*version*.zipfile and copy the unzippedglobalfolder into the newrepofolder.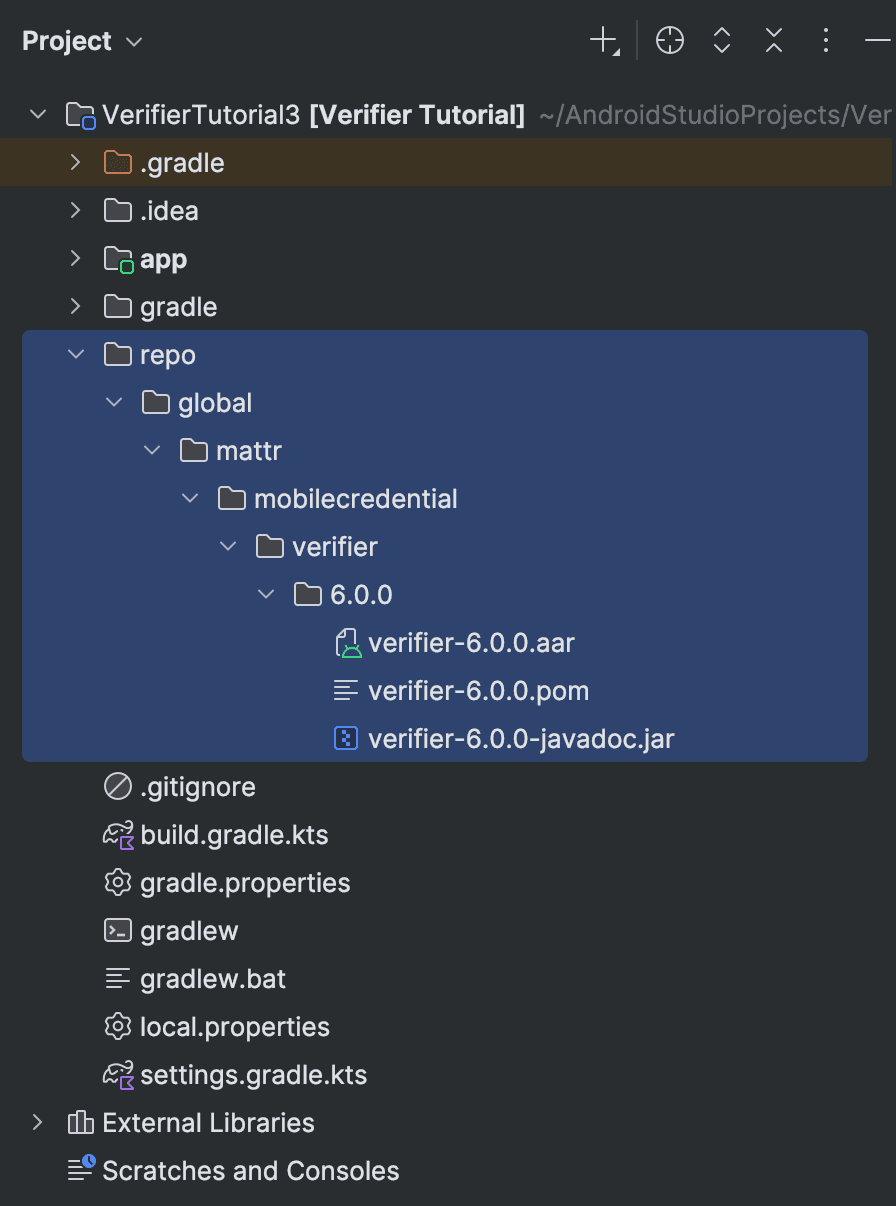
-
Open the
settings.gradle.ktsfile in theVerifierTutorialfolder and add the following Maven repository to thedependencyResolutionManagement.repositoriesblock:settings.gradle.kts maven { url = uri("repo") } -
Open the
app/build.gradle.ktsfile in your app folder and add the following dependencies to thedependenciesblock:app/build.gradle.kts implementation("global.mattr.mobilecredential:verifier:6.0.0") implementation("androidx.navigation:navigation-compose:2.9.0")
- The
verifierdependency version should match the version of the unzippedmobile-credential-verifier-*version*.zipfile you copied to therepofolder. - The required
navigation-composeversion may differ based on your version of the IDE, Gradle, and other project dependencies.
-
Sync the project with Gradle files.
-
Open the Build tab and select
Syncto make sure that the project has synced successfully.
Step 3: Run the application
-
Connect a debuggable mobile device to your machine.
-
Build and run the app on the connected mobile device.
The app should launch with a “Hello, Android!” text displayed:

Step 1: Access the tutorial codebase
-
Access the tutorial starter codebase by either:
-
Cloning the MATTR sample-apps repository:
Clone the repository git clone https://github.com/mattrglobal/sample-apps.gitor
-
Downloading just the starter directory using the download-directory.github.io utility.
-
-
Open the tutorial project in your code editor. You can find it in the
sample-apps/react-native-mdocs-verifier-tutorial/react-native-mdocs-verifier-tutorial-starter/directory.
You can find the completed tutorial code in the sample-apps/react-native-mdocs-verifier-tutorial/react-native-mdocs-verifier-tutorial-complete
directory and use it as a reference as you work along this tutorial.
Step 2: iOS Application configuration
-
Open the
app.config.tsfile and update thebundleIdentifiervalue under the// Update the bundle identifiercomment to a unique value for your application, e.g.com.mycompany.myapp.app.config.ts bundleIdentifier: "com.mycompany.myapp",
iOS requires each app to have a unique bundle identifier for App Store and development environments.
-
Add the following camera and Bluetooth permissions to the
ios.infoPlistobject under the// Add necessary permissions for camera and Bluetoothcomment:app.config.ts NSCameraUsageDescription: "Camera is used to scan QR codes.", NSBluetoothAlwaysUsageDescription: "This app uses Bluetooth to communicate with verifiers or holders.", NSBluetoothPeripheralUsageDescription: "This app uses Bluetooth to communicate with verifiers or holders.",These permissions are required for the app to use the camera for QR code scanning, and Bluetooth for proximity communication with the holder's app.
Step 3: Configure the app plugins
Add the following code under the // Configure the app plugins comment to import required plugin
configurations:
"./withMobileCredentialAndroidVerifierSdk",
[
"expo-build-properties",
{
android: {
minSdkVersion: 24,
compileSdkVersion: 35,
targetSdkVersion: 34,
kotlinVersion: "2.0.21",
},
},
],
[
"expo-camera",
{
cameraPermission: "Allow $(PRODUCT_NAME) to access your camera",
},
],The SDK requires platform-specific configurations to work correctly. A plugin file specifically for Android has already been created in your project root directory. You can also follow the instructions in the mDocs Verifier SDK Docs to perform this platform-specific configuration manually.
Step 4: Install the dependencies
- Open a terminal in the project's root and navigate to the starter project directory:
cd sample-apps/react-native-mdocs-verifier-tutorial/react-native-mdocs-verifier-tutorial-starter/- Install the application dependencies:
yarn installStep 5: Generate the iOS and Android project files
Run the following command to generate the iOS and Android project files:
yarn expo prebuildYou should now see the ios and android folders in your project root.
Step 6: Start the application
Connect your testing device(s) and run the following command to start the application(s):
iOS
yarn ios --deviceAndroid
yarn android --deviceNice work, your application is now all set to begin using the SDK!
Initialize the SDK
The first capability you will build into your app is to initialize the SDK so that your app can use
SDK functions and classes. To achieve this, we need to import the MobileCredentialVerifierSDK
framework and then initialize the MobileCredentialVerifier class.
Step 1: Create the application structure
-
Open the
ContentViewfile in your new project and replace any existing code with the following:ContentView import SwiftUI import Combine // Initialize SDK - Step 2.1: import MobileCredentialVerifierSDK struct ContentView: View { @ObservedObject var viewModel: VerifierViewModel = VerifierViewModel() var body: some View { NavigationStack(path: $viewModel.navigationPath) { VStack { Button("Certificate Management") { viewModel.navigationPath.append(NavigationState.certificateManagement) } .padding() Button("Scan QR Code") { viewModel.navigationPath.append(NavigationState.scanQRCode) } .padding() Button("View Response") { viewModel.navigationPath.append(NavigationState.viewResponse) } .padding() } .navigationDestination(for: NavigationState.self) { destination in switch destination { case .certificateManagement: certificateManagementView case .scanQRCode: codeScannerView case .viewResponse: presentationResponseView } } } } // MARK: Verification Views var codeScannerView: some View { // Verify mDocs - Step 2.4: Create QRScannerView EmptyView() } // Manage Certificates - Step 1.2: Create CertificateManagementView var certificateManagementView: some View { EmptyView() } var presentationResponseView: some View { // Verify mDocs - Step 4.2: Create PresentationResponseView EmptyView() } } // MARK: VerifierViewModel final class VerifierViewModel: ObservableObject { @Published var navigationPath = NavigationPath() // Initialize SDK - Step 2.2: Add MobileCredentialVerifier var // Verify mDocs - Step 1.1: Create MobileCredentialRequest instance // Verify mDocs - Step 1.2: Create receivedDocuments variable // Initialize SDK - Step 2.3: Initialize the SDK } // MARK: Proximity Presentation extension VerifierViewModel { func setupProximityPresentationSession(_ deviceEngagementString: String) { // Verify mDocs - Step 3.2: Create setupProximityPresentationSession print("This method will use qr code string do setup proximity session") } func sendDeviceRequest() { // Verify mDocs - Step 3.3: Create sendDeviceRequest function print("This method will send preconfigured device request to holder app") } } // Verify mDocs - Step 3.1: Extend VerifierViewModel class // MARK: - Navigation enum NavigationState: Hashable { case certificateManagement case scanQRCode case viewResponse }
This will serve as the basic structure for your application. We will copy and paste different code snippets into specific locations to achieve the different functionalities. These locations are indicated by comments that reference both the section and the step.
We recommend copying and pasting the comment text in Xcode search field (e.g.
// Initialize SDK - Step 2.2: Add MobileCredentialVerifier var) to easily locate it in the code.
Open the app/src/main/com/example/verifiertutorial/MainActivity.kt file in your project and
replace any existing code with the following:
package com.example.verifiertutorial
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.activity.ComponentActivity
import androidx.activity.compose.setContent
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth
import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding
import androidx.compose.material3.Button
import androidx.compose.material3.Text
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier
import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import androidx.navigation.NavController
import androidx.navigation.compose.NavHost
import androidx.navigation.compose.composable
import androidx.navigation.compose.rememberNavController
import com.example.verifiertutorial.ui.theme.VerifierTutorialTheme
import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.dto.MobileCredentialResponse
import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.MobileCredentialVerifier
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class MainActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// Initialize SDK - Step 1.1: Initialize the SDK
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContent {
VerifierTutorialTheme {
val navController = rememberNavController()
NavHost(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(vertical = 72.dp, horizontal = 8.dp),
startDestination = "home",
navController = navController,
) {
composable("home") {
HomeScreen(navController)
}
composable("certManagement") {
// Manage Certificates - Step 2.3: Add certificates management screen call
}
composable("scanOffer") {
// Verify mDocs - Step 1.7: Add "Scan Offer" screen call
}
composable("viewResponse") {
// Verify mDocs - Step 4.4: Add "View Response" screen call
}
}
}
}
}
}
@Composable
fun HomeScreen(navController: NavController) {
Column(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) {
Button(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
onClick = { navController.navigate("certManagement") }
) {
Text("Certificate Management")
}
Button(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
onClick = { navController.navigate("scanOffer") }
) {
Text("Scan QR Code")
}
}
}
// Verify mDocs - Step 2.2: Add shared dataThis will serve as the basic structure for your application. We will copy and paste different code snippets into specific locations in this codebase to achieve the different functionalities. These locations are indicated by comments that reference both the section and the step.
-
Open the
App.tsxfile in your project and replace the existing code with the skeleton structure:App.tsx import { type MobileCredentialResponse, type TrustedIssuerCertificate, createProximityPresentationSession, getTrustedIssuerCertificates, initialize, sendProximityPresentationRequest, terminateProximityPresentationSession, } from "@mattrglobal/mobile-credential-verifier-react-native"; // import { CertificateManagementModal } from "./CertificateManagementModal"; // import { QRScannerModal } from "./QRScannerModal"; // import { VerificationResultsModal } from "./VerificationResultsModal"; import { useCameraPermissions } from "expo-camera"; import { StatusBar } from "expo-status-bar"; import { useEffect, useState } from "react"; import { ActivityIndicator, Alert, SafeAreaView, Text, TouchableOpacity, View } from "react-native"; import { styles } from "./styles"; export default function App() { // State variables for SDK initialization, UI and loading messages const [isSDKInitialized, setIsSDKInitialized] = useState(false); const [loadingMessage, setLoadingMessage] = useState<string | false>(false); const [trustedCertificates, setTrustedCertificates] = useState<TrustedIssuerCertificate[]>([]); const [verificationResults, setVerificationResults] = useState<MobileCredentialResponse | null>(null); // Modal states const [showCertificateManagement, setShowCertificateManagement] = useState(false); const [isScanning, setIsScanning] = useState(false); const [showVerificationResults, setShowVerificationResults] = useState(false); const [permission, requestPermission] = useCameraPermissions(); // Initialize SDK - Step 2.1: Initialize the SDK // Verify mDocs - Step 1.2: Create handleQRCodeDetected function return ( <SafeAreaView style={styles.container}> <StatusBar style="auto" /> <View style={styles.header}> <Text style={styles.title}>mDocs Verifier</Text> </View> {loadingMessage ? ( <View style={[styles.content, styles.center]}> <ActivityIndicator size="large" color="#007AFF" /> <Text style={styles.loadingText}>{loadingMessage}</Text> </View> ) : ( <View style={styles.content}> <View style={styles.buttonContainer}> {/* Manage Certificates - Step 1.2: Create Certificate Management Button */} {/* Verify mDocs - Step 1.5: Create Scan QR Code Button */} </View> {!isSDKInitialized && <Text style={styles.errorText}>SDK not initialized. Please restart the app.</Text>} {isSDKInitialized && trustedCertificates.length === 0 && ( <Text style={styles.errorText}> No trusted issuer certificates added. Add certificates to verify mDocs. </Text> )} </View> )} {/* Manage Certificates - Step: 2.6: Use CertificateManagementModal */} {/* Verify mDocs - Step 1.4: Use QRScannerModal */} {/* Verify mDocs - Step 2.3: Use VerificationResultModal */} </SafeAreaView> ); }
This will serve as the basic structure for your application. We will add code to specific locations to achieve the different functionalities. These locations are indicated by comments that reference both the section and the step.
We recommend using your editor's search functionality to locate comments like // Initialize SDK - Step 1.3: Initialize the SDK when adding new code.
Step 2: Initialize the MobileCredentialVerifier class
-
Add the following code after the
// Initialize SDK - Step 2.1: Import MobileCredentialVerifierSDKcomment to importMobileCredentialVerifierSDKand gain access to the SDK's capabilities:ContentView import MobileCredentialVerifierSDK -
Add the following code after the
// Initialize SDK - Step 2.2: Add MobileCredentialVerifier varcomment to create a variable that holds themobileCredentialVerifierinstance:ContentView var mobileCredentialVerifier: MobileCredentialVerifier -
Add the following code after the
// Initialize SDK - Step 2.3: Initialize the SDKcomment to assign a shared instance of the class to ourmobileCredentialVerifiervariable and initialize the SDK:ContentView init() { do { mobileCredentialVerifier = MobileCredentialVerifier.shared try mobileCredentialVerifier.initialize() } catch { print(error.localizedDescription) } } -
Run the app to ensure it compiles successfully.
Once the app launches you will see a screen with three buttons, each leading to an empty view. In the following steps, you will implement proximity presentation functionalities into these views.
-
Add the following code after the
// Initialize SDK - Step 1.1: Initialize the SDKcomment to initialize the SDK:We recommend leaving the comment text (e.g.
// Initialize SDK - Step 1.1: Initialize the SDK) even after you have pasted the code snippet, as it will later help you to easily locate the step in the code.MainActivity.kt lifecycleScope.launch { MobileCredentialVerifier.initialize(this@MainActivity) } -
Run the app to make sure it compiles properly.
-
Add the following code after the
// Initialize SDK - Step 2.1: Initialize the SDKcomment to initialize the SDK:We recommend leaving the comment text (e.g.
// Initialize SDK - Step 2.1: Initialize the SDK) even after you have pasted the code snippet, as it will later help you to easily locate the step in the code.App.tsx useEffect(() => { const initializeSDK = async () => { try { setLoadingMessage("Initializing SDK..."); await initialize(); setIsSDKInitialized(true); setLoadingMessage("Loading certificates..."); const certificates = await getTrustedIssuerCertificates(); if (certificates) { setTrustedCertificates(certificates); } } catch (error) { console.error("Failed to initialize SDK:", error); Alert.alert("Error", "Failed to initialize the verifier SDK"); } finally { setLoadingMessage(false); } }; initializeSDK(); }, []); -
Run the app.
Manage certificates
Once the SDK is initialized, the next step is to build the capability for the application to manage certificates.
Every mDoc is signed by a series of certificates, referred to as a chain of trust. For your application to verify a presented mDoc it must validate it was signed using a root certificate (IACA) associated with a trusted issuer.
To enable this, your application should provide an interface for the user to manage (add, view and
remove) certificates. We will achieve this by creating a new CertificateManagementView view and
building certificate management capabilities into it.
Step 1: Create the Certificate Management view/screen
-
Create a new file named
CertificateManagementViewand paste the following code in it:CertificateManagementView import SwiftUI import Combine import MobileCredentialVerifierSDK struct CertificateManagementView: View { @ObservedObject var viewModel = CertificateManagementViewModel() @State var certificateString = "" var body: some View { Form { Section( header: Text("IACA Certificate").font(.headline), footer: HStack { Spacer() Button("Add") { viewModel.addCertificate(certificateString) } Spacer().frame(width: 30) Button("Clear") { certificateString = "" } .foregroundColor(.red) .contentShape(Rectangle()) .frame(alignment: .trailing) } ) { TextField("IACA certificate string", text: $certificateString) } Section( header: Text("Stored Certificates").font(.headline) ) { certificateListView } } .navigationBarTitle("Certificate Setting") .onAppear { viewModel.getCertificates() } } // MARK: Certificate Management Views var certificateListView: some View { // Manage Certificates - Step 2.3: Display retrieved certificates EmptyView() } } final class CertificateManagementViewModel: ObservableObject { // Manage Certificates - Step 2.1: Add certificates and verifier variable func getCertificates() { // Manage Certificates - Step 2.2: Create getCertificates function print("This will fetch certificates from storage") } func addCertificate(_ certificate: String) { // Manage Certificates - Step 2.4: Create addCertificate function print("This will add certificate to storage and get a new list of certificates") } func removeCertificate(_ certificateID: String) { // Manage Certificates - Step 2.5: Create removeCertificate function print("This will remove certificates from storage and get a new list of certificates") } }
The CertificateManagementView file provides a basic user interface for displaying a list of
certificates and controls for managing certificate storage. The CertificateManagementViewModel
class contains the logic for adding, retrieving, and removing certificates.
-
Return to the
ContentViewfile and replace theEmptyView()under the// Manage certificates - Step 1.2: Create CertificateManagementViewcomment with a reference to the new view you created in the previous step:ContentView CertificateManagementView() -
Run the app and select the Certificate Management button. You should see a result similar to the following:
As the user selects the Certificate Management button they are navigated to the new
CertificateManagement view where they can see controls that would enable them to add, view and
remove certificates. We will build these capabilities into the controls in the next step.
-
In your package, create a new file
CertManagementScreen.kt.
-
Add the following code to the file to display the basic UI that enables the user to add, view and remove certificates:
CertManagementScreen.kt import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Arrangement import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Row import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.height import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.LazyColumn import androidx.compose.foundation.lazy.items import androidx.compose.material.icons.Icons import androidx.compose.material.icons.filled.Delete import androidx.compose.material3.Card import androidx.compose.material3.Icon import androidx.compose.material3.IconButton import androidx.compose.material3.MaterialTheme import androidx.compose.material3.Text import androidx.compose.material3.TextButton import androidx.compose.material3.TextField import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf import androidx.compose.runtime.remember import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.dto.TrustedCertificate import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.MobileCredentialVerifier @Composable fun CertManagementScreen() { Column(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(), verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(4.dp)) { var certText by remember { mutableStateOf("") } var storedCerts by remember { mutableStateOf(listOf<TrustedCertificate>()) } // Manage Certificates - Step 2.3: Load certificates when screen enters the composition Text("IACA CERT", style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium) TextField( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), value = certText, onValueChange = { certText = it }, singleLine = true ) Row(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.End) { // Manage Certificates - Step 2.1: Add "Add certificate" button TextButton(onClick = { certText = "" }) { Text("Clear") } } Text("STORED CERTIFICATES", style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium) LazyColumn( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(6.dp) ) { items(storedCerts, key = { it.id }) { cert -> Row(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) { Card(Modifier.weight(1f).height(85.dp)) { Text(cert.pem, Modifier.padding(6.dp)) } // Manage Certificates - Step 2.2: Add "Delete certificate" button } } } } } -
Back in the
MainActivityfile, add the following code under the// Manage Certificates - Step 2.3: Add certificates management screen callcomment to connect the created composable to the navigation graph:MainActivity.kt CertManagementScreen() -
Run the app and select the Certificate Management button. You should be navigated to the new certificate management screen, where you can see controls that would enable the user to add, view and remove certificates. We will build these capabilities into the controls in the next step.
The Certificate Management functionality is implemented as a separate modal component. Let's build it step by step:
-
Create a new file named
CertificateManagementModal.tsxand add the following code to it:CertificateManagementModal.tsx import { type TrustedIssuerCertificate, addTrustedIssuerCertificates, deleteTrustedIssuerCertificate, getTrustedIssuerCertificates, } from "@mattrglobal/mobile-credential-verifier-react-native"; import { useState } from "react"; import { Alert, Modal, SafeAreaView, ScrollView, Text, TextInput, TouchableOpacity, View } from "react-native"; import { styles } from "./styles"; interface CertificateManagementModalProps { visible: boolean; onClose: () => void; trustedCertificates: TrustedIssuerCertificate[]; setTrustedCertificates: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<TrustedIssuerCertificate[]>>; } export function CertificateManagementModal({ visible, onClose, trustedCertificates, setTrustedCertificates, }: CertificateManagementModalProps) { const [certificateData, setCertificateData] = useState(""); // Sample certificate for testing purposes - montcliff-dmv.mattrlabs.com IACA const sampleCertificate = `MIICYzCCAgmgAwIBAgIKXhjLoCkLWBxREDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAjA4MQswCQYDVQQG EwJBVTEpMCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0Ew HhcNMjQwMTE4MjMxNDE4WhcNMzQwMTE1MjMxNDE4WjA4MQswCQYDVQQGEwJBVTEp MCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0EwWTATBgcq hkjOPQIBBggqhkjOPQMBBwNCAASBnqobOh8baMW7mpSZaQMawj6wgM5e5nPd6HXp dB8eUVPlCMKribQ7XiiLU96rib/yQLH2k1CUeZmEjxoEi42xo4H6MIH3MBIGA1Ud EwEB/wQIMAYBAf8CAQAwDgYDVR0PAQH/BAQDAgEGMB0GA1UdDgQWBBRFZwEOI9yq 232NG+OzNQzFKa/LxDAuBgNVHRIEJzAlhiNodHRwczovL21vbnRjbGlmZi1kbXYu bWF0dHJsYWJzLmNvbTCBgQYDVR0fBHoweDB2oHSgcoZwaHR0cHM6Ly9tb250Y2xp ZmYtZG12LnZpaS5hdTAxLm1hdHRyLmdsb2JhbC92Mi9jcmVkZW50aWFscy9tb2Jp bGUvaWFjYXMvMjk0YmExYmMtOTFhMS00MjJmLThhMTctY2IwODU0NWY0ODYwL2Ny bDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAgNIADBFAiAlZYQP95lGzVJfCykhcpCzpQ2LWE/AbjTGkcGI SNsu7gIhAJfP54a2hXz4YiQN4qJERlORjyL1Ru9M0/dtQppohFm6 `; // Manage Certificates - Step 2.1: Create addCertificate function // Manage Certificates - Step 2.4: Create removeCertificate function return ( <Modal visible={visible} animationType="slide" transparent={false}> <SafeAreaView style={styles.container}> <View style={styles.header}> <Text style={styles.title}>Certificate Management</Text> <TouchableOpacity onPress={onClose}> <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Close</Text> </TouchableOpacity> </View> <ScrollView style={styles.content}> {/* Manage Certificates - Step 2.2: Add new certificate form */} {/* Manage Certificates - Step 2.3: Display retrieved certificates */} </ScrollView> </SafeAreaView> </Modal> ); } -
Return to your
App.tsxfile and add the following code under theManage Certificates - Step 1.2: Create Certificate Management Buttoncomment to create a button that opens the certificate management modal:App.tsx <TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={() => setShowCertificateManagement(true)} > <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Manage Certificates</Text> </TouchableOpacity>
Step 2: Add Certificate Management functionalities
Currently our Certificate Management view/screen has no functionalities. Let's fix this by adding the capabilities to add, view and remove certificates.
-
Open the
CertificateManagementViewfile and add the following code under the// Manage Certificates - Step 2.1: Add certificates variablecomment to add a newcertificatesvariable that will hold the certificates added to the application and a reference to a shared instance ofMobileCredentialVerifier:CertificateManagementView @Published var certificates: [TrustedCertificate] = [] let mobileCredentialVerifier = MobileCredentialVerifier.shared -
Replace the
printstatement under the// Manage Certificates - Step 2.2: Create getCertificates functioncomment to call the SDK getTrustedIssuerCertificates, retrieve all certificates and display them to the user:CertificateManagementView do { let fetchedCertificates = try mobileCredentialVerifier.getTrustedIssuerCertificates() certificates = fetchedCertificates } catch { print(error.localizedDescription) } -
Replace the
EmptyView()under the// Manage Certificates - Step 2.3: Display retrieved certificatescomment to iterate over retrieved certificates and display them to the user:CertificateManagementView ForEach(viewModel.certificates, id: \.id) { certificate in Text("\(certificate.pem)") .frame(maxHeight: 100) .swipeActions(edge: .trailing) { Button(role:. destructive) { viewModel.removeCertificate(certificate.id) } label: { Image(systemName: "trash") } } } -
Replace the
printstatement under the// Manage Certificates - Step 2.4: Create addCertificate functioncomment to call the SDK addTrustedIssuerCertificates, accept a string parameter and use it to add a new certificate:CertificateManagementView Task { @MainActor in do { _ = try await mobileCredentialVerifier.addTrustedIssuerCertificates(certificates: [certificate]) self.getCertificates() } catch { print(error.localizedDescription) } } -
Replace the
printstatement under the// Manage Certificates - Step 2.5: Create removeCertificate functionto call the SDK deleteTrustedIssuerCertificate and remove a selected certificate:CertificateManagementView do { try mobileCredentialVerifier.deleteTrustedIssuerCertificate(certificateId: certificateID) // Refresh the certificates list after deletion self.getCertificates() } catch { print(error.localizedDescription) } -
Run the app and perform the following instructions:
-
Select the Manage Certificates button.
-
Copy and paste the following text into the IACA Certificate text box.
MIICYzCCAgmgAwIBAgIKXhjLoCkLWBxREDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAjA4MQswCQYDVQQG EwJBVTEpMCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0Ew HhcNMjQwMTE4MjMxNDE4WhcNMzQwMTE1MjMxNDE4WjA4MQswCQYDVQQGEwJBVTEp MCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0EwWTATBgcq hkjOPQIBBggqhkjOPQMBBwNCAASBnqobOh8baMW7mpSZaQMawj6wgM5e5nPd6HXp dB8eUVPlCMKribQ7XiiLU96rib/yQLH2k1CUeZmEjxoEi42xo4H6MIH3MBIGA1Ud EwEB/wQIMAYBAf8CAQAwDgYDVR0PAQH/BAQDAgEGMB0GA1UdDgQWBBRFZwEOI9yq 232NG+OzNQzFKa/LxDAuBgNVHRIEJzAlhiNodHRwczovL21vbnRjbGlmZi1kbXYu bWF0dHJsYWJzLmNvbTCBgQYDVR0fBHoweDB2oHSgcoZwaHR0cHM6Ly9tb250Y2xp ZmYtZG12LnZpaS5hdTAxLm1hdHRyLmdsb2JhbC92Mi9jcmVkZW50aWFscy9tb2Jp bGUvaWFjYXMvMjk0YmExYmMtOTFhMS00MjJmLThhMTctY2IwODU0NWY0ODYwL2Ny bDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAgNIADBFAiAlZYQP95lGzVJfCykhcpCzpQ2LWE/AbjTGkcGI SNsu7gIhAJfP54a2hXz4YiQN4qJERlORjyL1Ru9M0/dtQppohFm6
-
You will need to copy this text from the device you are using to display this tutorial and paste it in the device where you are running the built application. There are several ways to achieve this on iOS devices, one of them is setting up a Universal Clipboard.
-
Select the Add button. The new certificate should appear in the STORED CERTIFICATES area.
-
Swipe left across the new certificate and select the Delete icon to remove it.
You should get a result similar to the following:
- When the user selects the Certificate Management button they are navigated to the
CertificateManagementview. - When the user adds the text and selects the Add button a new certificate is added and displayed in the STORED CERTIFICATES area.
- When the user swipes left and selects the Delete icon the certificate is removed.
You have now built the capabilities required to manage certificates into your applications. Now we can proceed to building the capabilities to handle the actual presentation workflow.
-
Open the
CertManagementScreen.ktfile and add the following code under the// Manage Certificates - Step 2.1: Add "Add certificate" buttoncomment to add a button, that will be responsible for adding the certificate, entered in the text field above:CertManagementScreen.kt TextButton( onClick = { MobileCredentialVerifier.addTrustedIssuerCertificates(listOf(certText)) storedCerts = MobileCredentialVerifier.getTrustedIssuerCertificates() } ) { Text("Add") } -
Add the following code under the
// Manage Certificates - Step 2.2: Add "Delete certificate" buttoncomment to add a button, that will delete the certificate, when pressed:CertManagementScreen.kt IconButton( onClick = { MobileCredentialVerifier.deleteTrustedIssuerCertificate(cert.id) storedCerts = MobileCredentialVerifier.getTrustedIssuerCertificates() }, modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.CenterVertically) ) { Icon( Icons.Default.Delete, contentDescription = "Delete Cert", tint = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary ) } -
Add the following code under the
// Manage Certificates - Step 2.3: Load certificates when screen enters the compositioncomment to enable loading the certificates from the local storage and showing them, when the screen enters the composition:CertManagementScreen.kt LaunchedEffect(Unit) { storedCerts = MobileCredentialVerifier.getTrustedIssuerCertificates() } -
Run the app and perform the following instructions:
-
Select the Manage Certificates button.
-
Copy and paste the following text into the IACA Certificate text box.
MIICYzCCAgmgAwIBAgIKXhjLoCkLWBxREDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAjA4MQswCQYDVQQG EwJBVTEpMCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0Ew HhcNMjQwMTE4MjMxNDE4WhcNMzQwMTE1MjMxNDE4WjA4MQswCQYDVQQGEwJBVTEp MCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0EwWTATBgcq hkjOPQIBBggqhkjOPQMBBwNCAASBnqobOh8baMW7mpSZaQMawj6wgM5e5nPd6HXp dB8eUVPlCMKribQ7XiiLU96rib/yQLH2k1CUeZmEjxoEi42xo4H6MIH3MBIGA1Ud EwEB/wQIMAYBAf8CAQAwDgYDVR0PAQH/BAQDAgEGMB0GA1UdDgQWBBRFZwEOI9yq 232NG+OzNQzFKa/LxDAuBgNVHRIEJzAlhiNodHRwczovL21vbnRjbGlmZi1kbXYu bWF0dHJsYWJzLmNvbTCBgQYDVR0fBHoweDB2oHSgcoZwaHR0cHM6Ly9tb250Y2xp ZmYtZG12LnZpaS5hdTAxLm1hdHRyLmdsb2JhbC92Mi9jcmVkZW50aWFscy9tb2Jp bGUvaWFjYXMvMjk0YmExYmMtOTFhMS00MjJmLThhMTctY2IwODU0NWY0ODYwL2Ny bDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAgNIADBFAiAlZYQP95lGzVJfCykhcpCzpQ2LWE/AbjTGkcGI SNsu7gIhAJfP54a2hXz4YiQN4qJERlORjyL1Ru9M0/dtQppohFm6
-
You will need to copy this text from the device you are using to display this tutorial and paste it in the device where you are running the built application. This can be achieved by navigating to this tutorial on your testing mobile device.
-
Select the Add button. The new certificate should appear in the STORED CERTIFICATES area.
-
Press Delete icon to remove the certificate.
You should get a result similar to the following:
- When the user selects the Certificate Management button they are navigated to the
CertManagementScreen. - When the user adds the text and selects the Add button a new certificate is added and displayed in the STORED CERTIFICATES area.
- When the user selects the Delete icon the certificate is removed.
-
Return to the
CertificateManagementModal.tsxfile and paste the following code under the// Manage Certificates - Step 2.1: Create addCertificate functioncomment to implement theaddCertificatefunction:CertificateManagementModal.tsx const addCertificate = async () => { if (!certificateData.trim()) { Alert.alert("Error", "Please enter certificate data"); return; } try { const result = await addTrustedIssuerCertificates([certificateData]); if (result.isErr()) { throw new Error(result.error.message); } // Reload certificates after adding const certificates = await getTrustedIssuerCertificates(); if (certificates.length > 0) { setTrustedCertificates(certificates); } // Clear input fields setCertificateData(""); Alert.alert("Success", "Certificate added successfully"); } catch (error) { console.error("Error adding certificate:", error); Alert.alert("Error", "Failed to add certificate"); } }; -
Paste the following code under the
// Manage Certificates - Step 2.2: Add new certificate formcomment to add a certificate input form:CertificateManagementModal.tsx <View style={styles.card}> <Text style={styles.cardTitle}>Add New Certificate</Text> <Text style={[styles.smallText, styles.grayColor]}>Certificate Data (Base64)</Text> <TextInput spellCheck={false} style={[styles.formField, styles.expandingInput]} multiline placeholder="Paste certificate data here..." value={certificateData} onChangeText={setCertificateData} /> <View style={styles.buttonRow}> <TouchableOpacity style={styles.button} onPress={addCertificate}> <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Add Certificate</Text> </TouchableOpacity> <TouchableOpacity style={[styles.button, styles.secondaryButton]} onPress={() => setCertificateData(sampleCertificate)} > <Text style={[styles.buttonText, styles.secondaryButtonText]}>Load Example</Text> </TouchableOpacity> </View> </View> -
Paste the following code under the
// Manage Certificates - Step 2.3: Display retrieved certificatescomment to display the trusted certificates list:CertificateManagementModal.tsx <View style={styles.card}> <Text style={styles.cardTitle}>Trusted Certificates ({trustedCertificates.length})</Text> {trustedCertificates.map((certificate: TrustedIssuerCertificate) => ( <View key={certificate.id} style={styles.listItem}> <View style={styles.listItemContent}> <Text style={styles.listItemTitle}>{certificate.commonName}</Text> <Text style={[styles.smallText, styles.grayColor]}>ID: {certificate.id.substring(0, 20)}...</Text> </View> {/* Manage Certificates - Step 2.5: Remove certificate button */} </View> ))} </View> -
Paste the following code under the
// Manage Certificates - Step 2.4: Create removeCertificate functioncomment to implement theremoveCertificatefunction:CertificateManagementModal.tsx const removeCertificate = async (id: string) => { try { await deleteTrustedIssuerCertificate(id); setTrustedCertificates( trustedCertificates.filter((certificate: TrustedIssuerCertificate) => certificate.id !== id) ); Alert.alert("Success", "Certificate removed successfully"); } catch (error) { console.error("Error removing certificate:", error); Alert.alert("Error", "Failed to remove certificate"); } }; -
Paste the following code under the
// Manage Certificates - Step 2.5: Remove certificate buttoncomment to add a remove button to each certificate:CertificateManagementModal.tsx <TouchableOpacity style={styles.dangerButton} onPress={() => removeCertificate(certificate.id)}> <Text style={styles.buttonText}>Remove</Text> </TouchableOpacity> -
Navigate to the
App.tsxfile and uncomment the following import at the top of the file:App.tsx import { CertificateManagementModal } from "./CertificateManagementModal"; -
Paste the following code under the
// Manage Certificates - Step 2.6: Use CertificateManagementModalcomment to integrate the certificates modal into the main app:App.tsx <CertificateManagementModal visible={showCertificateManagement} onClose={() => setShowCertificateManagement(false)} trustedCertificates={trustedCertificates} setTrustedCertificates={setTrustedCertificates} />
You have successfully built the certificate management capabilities for your verifier application. You can now add and remove trusted issuer certificates and view the stored certificate list.
Now you can proceed to building the capabilities to handle the actual presentation workflow.
Verify mDocs
In this part we will build the components that enable a verifier app to verify an mDoc presented via a proximity workflow as per ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021:
To achieve this, your application must be able to:
- Create a presentation request that defines the information required for verification.
- Scan and process a QR code presented by a wallet application. Your application must retrieve the information from that QR code and use it to establish a secure connection between the verifier and holder devices.
- Your verifier application then uses this secure connection to send a presentation request to which the holder wallet application responds with a presentation response.
- Finally, the SDK verifies any mDocs included in the response, stores the verification results in a variable and makes them available to your application to display.
Your application will use the SDK's createProximityPresentationSession function
that takes a string retrieved from the QR code and uses it to establish a proximity presentation
session with the wallet application and initiate the presentation workflow.
This function takes a listener argument of type ProximityPresentationSessionListener delegate,
which will receive proximity presentation session events.
Step 1: Create a presentation request
As a verifier, you can select what information you request for verification. Your application implements this by creating a MobileCredentialRequest instance to define the required information, and a new variable to hold the response from the wallet application.
-
Open the
ContentViewfile and add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 1.1: Create MobileCredentialRequest instancecomment to define what information to request from the wallet application user:ContentView let mobileCredentialRequest = MobileCredentialRequest( docType: "org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL", namespaces: [ "org.iso.18013.5.1": [ "family_name": false, "given_name": false, "birth_date": false ] ] )This object details:
- The requested credential type (e.g.
org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL). - The claims required for verification (e.g.
family_name). - The requested namespace (e.g.
org.iso.18013.5.1). - Whether or not the verifier intends to persist the claim value (
true/false).
For the verification to be successful, the presented credential must include the referenced claim against the specific namespace defined in the request. Our example requests the
birth_dateunder theorg.iso.18013.5.1namespace. If a wallet responds to this request with a credential that includes abirth_datebut rather under theorg.iso.18013.5.1.USnamespace, the claim will not be verified. - The requested credential type (e.g.
To simplify the tutorial, this is a hardcoded request. However, once you are comfortable with the basic functionalities you can create a UI in your verifier application that enables the user to create different requests on the fly by selecting different claims to include. Check out our GO Verify app to see this in action.
-
Add the following code under the
Verify mDocs - Step 1.2: Create receivedDocuments variablecomment to create a newreceivedDocumentsvariable that will hold the response from the wallet application:ContentView @Published var receivedDocuments: [MobileCredentialPresentation] = []
Your application now has an existing credential request to share, and a variable to hold any incoming responses. In the next step we will build the capabilities to send this request and handle the response.
Step 2: Scan and process a QR code
As defined in ISO/IEC 18130-5:2021, a proximity presentation workflow is always initiated by the holder (wallet application user), who must create a QR code for the verifier to scan in order to initiate the device engagement phase.
This means that your verifier application must be able to scan and process this QR code. For ease of implementation, we will use a third party framework to achieve this.
- Add camera usage permissions to the app target:
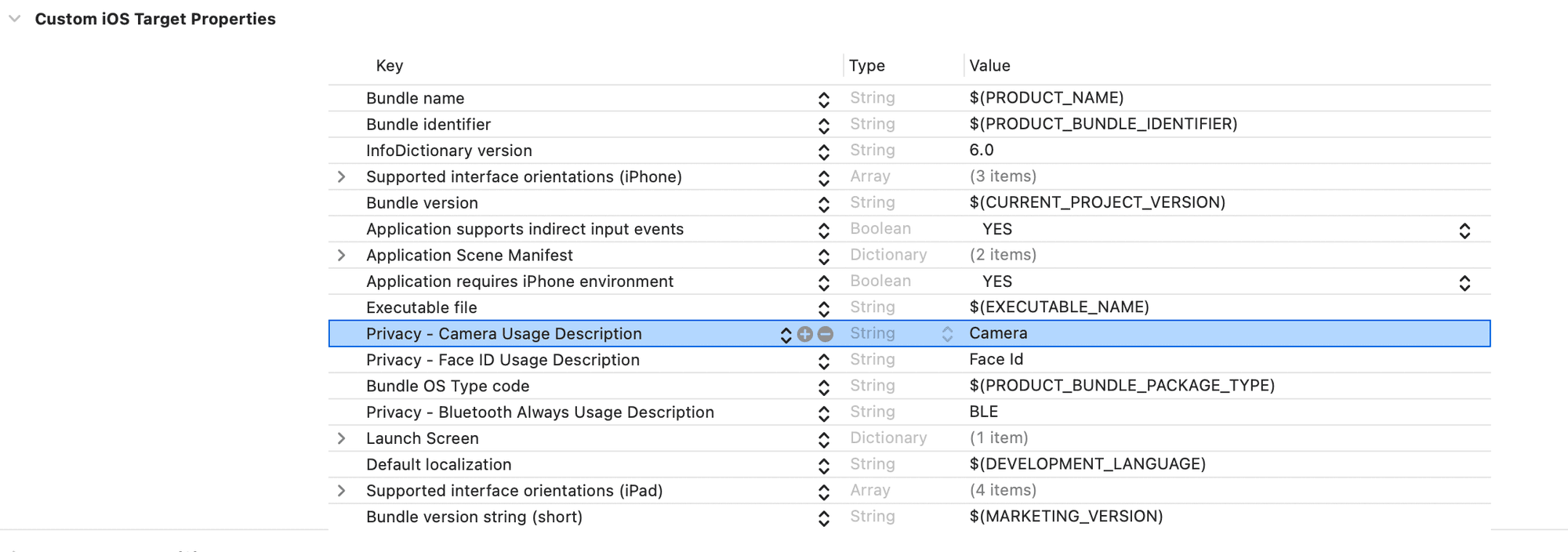
- Add the CodeScanner library via Swift Package Manager.
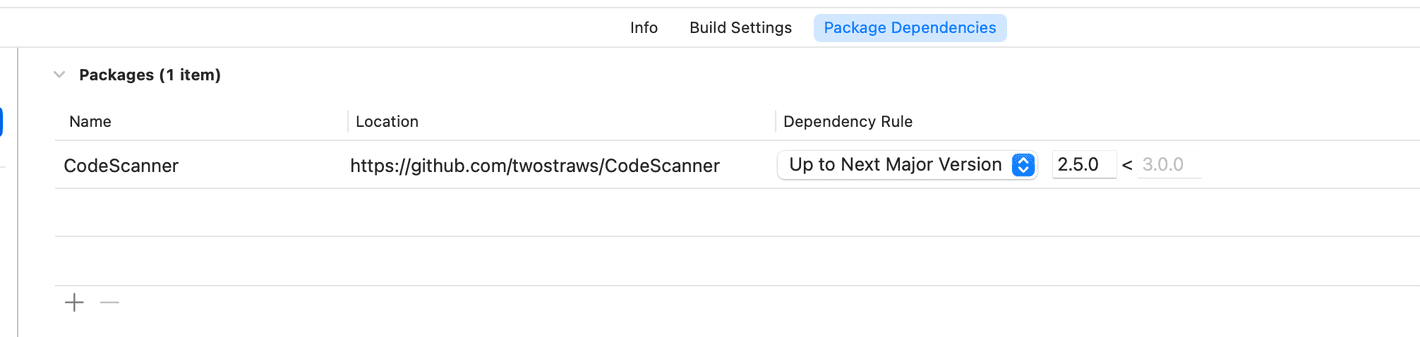
-
Create a new swift file named
QRScannerViewand add the following code into it to implement the QR scanning capability:QRScannerView import SwiftUI import CodeScanner import AVFoundation struct QRScannerView: View { private let completionHandler: (String) -> Void init(completion: @escaping (String) -> Void) { completionHandler = completion } var body: some View { CodeScannerView(codeTypes: [.qr]) { result in switch result { case .failure(let error): print(error.localizedDescription) case .success(let result): print(result.string) completionHandler(result.string) } } } } -
Back in the
ContentViewfile, replace theEmptyView()under the// Verify mDocs - Step 2.4: Create QRScannerViewcomment with the following code to create a new app view that the user will use to scan a QR code:ContentView QRScannerView( completion: { string in viewModel.setupProximityPresentationSession(string) } ) -
Run the app and select the Scan QR Code button. You should be navigated to the new
QRScannerViewwhere you can use the camera to scan a QR code.
Next we will build the logic that handles this QR code to establish a secure connection with the wallet application.
Step 3: Exchange presentation request and response
-
Add the following code under the
Verify mDocs - Step 3.1: Extend VerifierViewModel classto extend theVerifierViewModelclass with theProximityPresentationSessionListenerprotocol:ContentView extension VerifierViewModel: ProximityPresentationSessionListener { public func onEstablished() { sendDeviceRequest() } public func onTerminated(error: (any Error)?) { print("Session Terminated") } }Now, as soon as a connection is established, the app will send a device request. You will implement the functionality of
sendDeviceRequest()inVerifierViewModellater in the tutorial. -
Replace the
printstatement under the// Verify mDocs - Step 3.2: Create setupProximityPresentationSessioncomment with the following code to call the SDK'screateProximityPresentationSessionfunction, passing a device engagement string (retrieved from a QR code) andselfas a listener to create a proximity presentation session:ContentView mobileCredentialVerifier.createProximityPresentationSession(encodedDeviceEngagementString: deviceEngagementString, listener: self) -
Replace the
printstatement under the// Verify mDocs - Step 3.3: Create sendDeviceRequest functioncomment with following code to implement the logic to send a device request:ContentView Task { @MainActor in receivedDocuments = [] do { // Navigate to response screen navigationPath.append(NavigationState.viewResponse) // Request mDocs let deviceResponse = try await mobileCredentialVerifier.sendProximityPresentationRequest( request: [mobileCredentialRequest] ) // Assign new values from the response receivedDocuments = deviceResponse.credentials ?? [] // Terminate session after response is received (optional) await mobileCredentialVerifier.terminateProximityPresentationSession() } catch { print(error) receivedDocuments = [] } }This function now implements the following logic:
- Navigate to the
viewResponsescreen. - Send a proximity presentation request using the SDK's
requestMobileCredentialsfunction. - Store the wallet response in the
deviceResponsevariable. This includes the verification results of any credentials included in the response. - Store the verification results in the
receivedDocumentsvariable. - Terminate the presentation session once the response is received.
- Navigate to the
Step 4: Display verification results
-
Create a new file named
DocumentViewand add the following code to display available verification results:DocumentView import MobileCredentialVerifierSDK import SwiftUI import Combine struct DocumentView: View { var viewModel: DocumentViewModel var body: some View { VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 10) { Text(viewModel.docType) .font(.title) .fontWeight(.bold) .padding(.bottom, 5) Text(viewModel.verificationResult) .font(.title) .fontWeight(.bold) .foregroundStyle(viewModel.verificationFailedReason == nil ? .green : .red) .padding(.bottom, 5) if let verificationFailedReason = viewModel.verificationFailedReason { Text(verificationFailedReason) .font(.title3) .fontWeight(.bold) .foregroundStyle(.red) .padding(.bottom, 5) } ForEach(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { key in VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 5) { Text(key) .font(.headline) .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.gray.opacity(0.2)) .cornerRadius(5) ForEach(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims[key]!.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { claim in HStack { Text(claim) .fontWeight(.semibold) Spacer() Text(viewModel.namespacesAndClaims[key]![claim]! ?? "") .fontWeight(.regular) } .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.white) .cornerRadius(5) .shadow(radius: 1) } } .padding(.vertical, 5) } if !viewModel.claimErrors.isEmpty { Text("Failed Claims:") .font(.headline) .padding(.vertical, 5) ForEach(viewModel.claimErrors.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { key in VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 5) { Text(key) .font(.headline) .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.gray.opacity(0.2)) .cornerRadius(5) ForEach(viewModel.claimErrors[key]!.keys.sorted(), id: \.self) { claim in HStack { Text(claim) .fontWeight(.semibold) Spacer() Text(viewModel.claimErrors[key]![claim]! ?? "") .fontWeight(.regular) } .padding(.vertical, 5) .padding(.horizontal, 10) .background(Color.white) .cornerRadius(5) .shadow(radius: 1) } } .padding(.vertical, 5) } } } .padding() .background(RoundedRectangle(cornerRadius: 10).fill(Color.white).shadow(radius: 5)) .padding(.horizontal) } } // MARK: DocumentViewModel class DocumentViewModel: ObservableObject { let docType: String let namespacesAndClaims: [String: [String: String?]] let claimErrors: [String: [String: String?]] let verificationResult: String let verificationFailedReason: String? init(from presentation: MobileCredentialPresentation) { self.docType = presentation.docType self.verificationResult = presentation.verificationResult.verified ? "Verified" : "Invalid" self.verificationFailedReason = presentation.verificationResult.reason?.message self.namespacesAndClaims = presentation.claims?.reduce(into: [String: [String: String]]()) { result, outerElement in let (outerKey, innerDict) = outerElement result[outerKey] = innerDict.mapValues { $0.textRepresentation } } ?? [:] self.claimErrors = presentation.claimErrors?.reduce(into: [String: [String: String]]()) { result, outerElement in let (outerKey, innerDict) = outerElement result[outerKey] = innerDict.mapValues { "\($0)" } } ?? [:] } } // MARK: Helper extension MobileCredentialElementValue { var textRepresentation: String { switch self { case .bool(let bool): return "\(bool)" case .string(let string): return string case .int(let int): return "\(int)" case .unsigned(let uInt): return "\(uInt)" case .float(let float): return "\(float)" case .double(let double): return "\(double)" case let .date(date): let dateFormatter = DateFormatter() dateFormatter.dateStyle = .short dateFormatter.timeStyle = .none return dateFormatter.string(from: date) case let .dateTime(date): let dateFormatter = DateFormatter() dateFormatter.dateStyle = .short dateFormatter.timeStyle = .short return dateFormatter.string(from: date) case .data(let data): return "Data \(data.count) bytes" case .map(let dictionary): let result = dictionary.mapValues { value in value.textRepresentation } return "\(result)" case .array(let array): return array.reduce("") { partialResult, element in partialResult + element.textRepresentation } .appending("") @unknown default: return "Unknown type" } } }The
DocumentViewfile comprises the following elements:DocumentView: Basic UI layout for viewing received documents and verification results.DocumentViewModel: This class takesMobileCredentialPresentationand converts its elements into strings to display in theDocumentView.- Extension of
MobileCredentialElementValuewhich converts the values of received claims into a human-readable format.
-
Return to the
ContentViewfile and replace theEmptyView()under the// Verify mDocs - Step 4.2: Create PresentationResponseViewcomment with the following code to display theDocumentViewview when verification results are available:ContentView ZStack { if viewModel.receivedDocuments.isEmpty { VStack(spacing: 40) { Text("Waiting for response...") .font(.title) ProgressView() .progressViewStyle(.circular) .scaleEffect(2) } } else { ScrollView { ForEach(viewModel.receivedDocuments, id: \.docType) { doc in DocumentView(viewModel: DocumentViewModel(from: doc)) .padding(10) } } } }
Step 1: Create a screen for scanning the credential offer
As defined in ISO/IEC 18130-5:2021, a proximity presentation workflow is always initiated by the holder (wallet application user), who must create a QR code for the verifier to scan in order to initiate the device engagement phase.
This means that your verifier application must be able to scan and process this QR code. For ease of implementation, we will use a third party framework to achieve this.
-
Add dependencies to your
app/build.gradle.kts:app/build.gradle.kts implementation("com.google.accompanist:accompanist-permissions:0.36.0") implementation("com.journeyapps:zxing-android-embedded:4.3.0") -
In your package, create a new file called
ScanOfferScreen.ktand add the following code:ScanOfferScreen.kt import android.app.Activity import android.Manifest import android.widget.Toast import androidx.activity.compose.rememberLauncherForActivityResult import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize import androidx.compose.material3.CircularProgressIndicator import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.runtime.DisposableEffect import androidx.compose.runtime.LaunchedEffect import androidx.compose.runtime.getValue import androidx.compose.runtime.mutableStateOf import androidx.compose.runtime.remember import androidx.compose.runtime.rememberCoroutineScope import androidx.compose.runtime.setValue import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.platform.LocalContext import androidx.compose.ui.viewinterop.AndroidView import androidx.navigation.NavController import com.google.accompanist.permissions.ExperimentalPermissionsApi import com.google.accompanist.permissions.isGranted import com.google.accompanist.permissions.rememberPermissionState import com.journeyapps.barcodescanner.BarcodeCallback import com.journeyapps.barcodescanner.DecoratedBarcodeView import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.deviceretrieval.devicerequest.DataElements import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.deviceretrieval.devicerequest.NameSpaces import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.dto.MobileCredentialRequest import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.dto.MobileCredentialResponse import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.MobileCredentialVerifier import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.ProximityPresentationSessionListener import kotlinx.coroutines.CoroutineScope import kotlinx.coroutines.launch import kotlinx.coroutines.suspendCancellableCoroutine import kotlin.coroutines.Continuation import kotlin.coroutines.resume import kotlin.coroutines.resumeWithException @OptIn(ExperimentalPermissionsApi::class) @Composable fun ScanOfferScreen(activity: Activity, navController: NavController) { // Verify mDocs - Step 1.6: Add permission request logic } // Verify mDocs - Step 1.5: Add screen content // Verify mDocs - Step 1.4: Add QR scan callback // Verify mDocs - Step 3.1: Create session listener // Verify mDocs - Step 2.1: Create a sample request -
In the
ScanOfferScreen.ktfile, add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 1.4: Add QR scan callbackcomment to define a callback that is called when the QR code was successfully scanned (we will implement the callback logic at a later stage):ScanOfferScreen.kt private fun onQrScanned( activity: Activity, deviceEngagement: String, coroutineScope: CoroutineScope, navController: NavController ) { coroutineScope.launch { // Verify mDocs - Step 3.2: Create session // Verify mDocs - Step 4.1: Handle response } } -
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 1.5: Add screen contentcomment to define the main UI of the screen:ScanOfferScreen.kt @Composable private fun Content(activity: Activity, navController: NavController) { val context = LocalContext.current val barcodeView = remember { DecoratedBarcodeView(context) } val coroutineScope = rememberCoroutineScope() var isQrScanned by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } val barcodeCallback = remember { BarcodeCallback { result -> onQrScanned(activity, result.text, coroutineScope, navController) barcodeView.pause() isQrScanned = true } } DisposableEffect(Unit) { barcodeView.decodeContinuous(barcodeCallback) barcodeView.resume() onDispose { barcodeView.pause() } } if (!isQrScanned) { AndroidView(factory = { barcodeView }, modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) } else { Box(Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { CircularProgressIndicator(Modifier.align(Alignment.Center)) } } }Please have a quick look at the code. The screen will show a QR scanning view. As soon as the QR code is captured, it shows a progress spinning wheel, and calls
onQrScannedfunction. -
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 1.6: Add permission request logiccomment to define a basic logic for requesting the camera access permission at runtime:ScanOfferScreen.kt val cameraPermissionState = rememberPermissionState(Manifest.permission.CAMERA) val requestPermissionLauncher = rememberLauncherForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestPermission()) {} LaunchedEffect(cameraPermissionState) { if (!cameraPermissionState.status.isGranted) { requestPermissionLauncher.launch(Manifest.permission.CAMERA) } } if (cameraPermissionState.status.isGranted) Content(activity, navController) -
Back in the
MainActivityfile, add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 1.7: Add "Scan Offer" screen callto connect the created screen to the navigation graph:MainActivity.kt ScanOfferScreen(this@MainActivity, navController) -
Run the app and select the Scan QR Code button. You should be navigated to the new
QRScannerViewwhere you can use the camera to scan a QR code.
Now we will build the logic that handles this QR code to establish a secure connection with the wallet application.
Step 2: Create a presentation request
As a verifier, you can select what information you request for verification. Our application implements this by creating a MobileCredentialRequest instance to define the required information, and a new variable to hold the response from the wallet application.
-
In the
ScanOfferScreen.ktfile, add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 2.1: Create a sample requestcomment to define what information to request from the holder's application:ScanOfferScreen.kt private val sampleMdocRequest = MobileCredentialRequest( docType = "org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL", namespaces = NameSpaces( mapOf( "org.iso.18013.5.1" to DataElements( listOf("given_name", "family_name", "birth_date").associateWith { false } ) ) ) )This object details:
- The requested credential type (e.g.
org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL). - The claims required for verification (e.g.
given_name). - The requested namespace (e.g.
org.iso.18013.5.1). - Whether or not the verifier intends to persist the claim value (
true/false).
For the verification to be successful, the presented credential must include the referenced claim against the specific namespace defined in the request. Our example requests the
birth_dateunder theorg.iso.18013.5.1namespace. If a wallet responds to this request with a credential that includes abirth_datebut rather under theorg.iso.18013.5.1.USnamespace, the claim will not be verified. - The requested credential type (e.g.
To simplify the tutorial, this is a hardcoded request. However, once you are comfortable with the basic functionalities you can create a UI in your verifier application that enables the user to create different requests on the fly by selecting different claims to include. See our GO Verify app as an example.
-
Back in the
MainActivity.ktfile, add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 2.2: Add shared datacomment to create a newcredentialResponsevariable that will hold the response from the holder's application:MainActivity.kt object SharedData { var credentialResponse: MobileCredentialResponse? = null }
Now your application has an existing request to share, and a variable to hold any incoming responses. We can now proceed to build the capabilities to send the request and handle the response.
Step 3: Exchange presentation request and response
-
In
ScanOfferScreen.kt, add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 3.1: Create session listenerto define a listener that will react to the proximity presentation session lifecycle events:ScanOfferScreen.kt private class SessionListener( private val coroutineScope: CoroutineScope, private val continuation: Continuation<MobileCredentialResponse> ) : ProximityPresentationSessionListener { override fun onEstablished() { coroutineScope.launch { // Verify mDocs - Step 3.3: Request credentials } } override fun onTerminated(error: Throwable?) { /* no-op */ } override fun onError(error: Throwable?) { error?.let { continuation.resumeWithException(it) } } } -
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 3.2: Create sessionto create proximity presentation session and register a session listener:ScanOfferScreen.kt SharedData.credentialResponse = try { suspendCancellableCoroutine { continuation: Continuation<MobileCredentialResponse> -> val sessionListener = SessionListener(coroutineScope, continuation) MobileCredentialVerifier .createProximityPresentationSession(activity, deviceEngagement, sessionListener) } } catch (e: Exception) { Toast.makeText(activity, "Failed to request credentials", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() null }We pass
Continuationto the listener. It will be resumed either withMobileCredentialResponseif the whole presentation flow is successful, or with an exception if there was an issue during any stage of the credentials presentation. -
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 3.3: Request credentialsto request the mobile credentials:ScanOfferScreen.kt try { val response = MobileCredentialVerifier.sendProximityPresentationRequest( listOf(sampleMdocRequest), checkStatus = false ) MobileCredentialVerifier.terminateProximityPresentationSession() continuation.resume(response) } catch (e: Exception) { continuation.resumeWithException(e) }
The resulting code:
- Establishes a secure connection with the wallet application by calling
createProximityPresentationSession. - Calls
sendProximityPresentationRequestfunction as soon as the session is established. The function accepts a list ofMobileCredentialRequest, sends the requests to the wallet application, receives a response from the wallet application, and verifies any mDocs included in the response. - Stores the response in the
SharedData.credentialResponsevalue. - Handles the exceptions, if they were thrown from the above calls. An exception can be thrown if, for example, the Bluetooth connection between the Holder and Verifier devices was interrupted during the session.
Now that we have the verification results stored, you can implement different business logics to handle the results.
For this tutorial, we will display these results to the verifier app user, individually indicating the verification status of each claim included in the request.
Step 4: Display verification results
-
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 4.1: Handle responseto navigate the user to the response screen, where they can see the retrieved credentials, if the retrieval was successful:ScanOfferScreen.kt SharedData.credentialResponse?.let { navController.navigate("viewResponse") { popUpTo("home") } } -
Create a new file named
ViewResponseScreen.ktthat will be used to display the response to the verifier application user. -
Copy and paste the following code into the new file:
ViewResponseScreen.kt import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Arrangement import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Box import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Column import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.ColumnScope import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Row import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.Spacer import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxSize import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.fillMaxWidth import androidx.compose.foundation.layout.padding import androidx.compose.foundation.rememberScrollState import androidx.compose.foundation.verticalScroll import androidx.compose.material3.Card import androidx.compose.material3.MaterialTheme import androidx.compose.material3.Text import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable import androidx.compose.ui.Alignment import androidx.compose.ui.Modifier import androidx.compose.ui.graphics.Color import androidx.compose.ui.text.style.TextOverflow import androidx.compose.ui.unit.dp import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.deviceretrieval.deviceresponse.DataElementIdentifier import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.deviceretrieval.deviceresponse.NameSpace import global.mattr.mobilecredential.verifier.dto.MobileCredentialElement @Composable fun ViewResponseScreen() { // Verify mDocs - Step 4.5: Define content } // Verify mDocs - Step 4.8: Display claims // Verify mDocs - Step 4.7: Map a claim or an error to string -
Back in the
MainActivity.ktfile, add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 4.4: Add "View Response" screen callcomment to connect the created composable to the navigation graph:MainActivity.kt ViewResponseScreen() -
Return to the
ViewResponseScreen.ktscreen and add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 4.5: Define contentcomment to define the basic UI for displaying the response details to the verifier application user:ViewResponseScreen.kt val credential = SharedData.credentialResponse?.credentials?.firstOrNull() if (credential == null || SharedData.credentialResponse?.credentialErrors != null) { // Verify mDocs - Step 4.6: Show error } else { Column( modifier = Modifier .fillMaxSize() .verticalScroll(rememberScrollState()), verticalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(4.dp), ) { // Verify mDocs - Step 4.10: Show credential verification status // Verify mDocs - Step 4.9: Show retrieved claims and errors } }
While our SDK allows to request multiple document types (and thus, multiple credentials) at the same time, for the tutorial simplicity we requested only one document type, and expect to see only one mobile credential as the response. Because of that, we take and handle only the first element from the retrieved credentials list.
-
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 4.6: Show errorcomment to show an error message in case the response is empty or if there were major errors during the response retrieval:ViewResponseScreen.kt Box(Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { Text("There were errors while receiving the response", Modifier.align(Alignment.Center)) } -
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 4.7: Map a claim or an error to stringcomment to map the received claim value (or a claim error) to a string:ViewResponseScreen.kt private fun Any.claimToUiString() = when (this) { is MobileCredentialElement -> { when (this) { is MobileCredentialElement.ArrayElement, is MobileCredentialElement.DataElement, is MobileCredentialElement.MapElement -> this::class.simpleName ?: "Unknown element" else -> value.toString() } } else -> "Not returned" }
Claim error here means that the presentation session has completed successfully, without interruption, and the mobile credentials were received and verified, but some of the claim values were not sent to the verifier. Usually this can happen if they were absent in the document on the Holder side. For example, Verifier requested family name, given name, date of birth, and photo, but the document on the Holder contained only family name, given name_, and date of birth. Another case is if the wallet user did not give the consent for sharing some of the claims.
-
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 4.8: Display claimscomment to create a function that displays the retrieved and failed claims to the verifier application user:ViewResponseScreen.kt @Composable private fun ColumnScope.Claims( title: String, claims: Map<NameSpace, Map<DataElementIdentifier, Any>>? ) { Text( title, modifier = Modifier .fillMaxWidth() .align(Alignment.CenterHorizontally), style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleLarge ) claims?.forEach { (namespace, claims) -> Card { Column(Modifier.padding(6.dp)) { Text( namespace, style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium, modifier = Modifier.padding(vertical = 4.dp) ) claims.forEach { (name, value) -> Row { Text(name, Modifier .weight(1f) .padding(end = 4.dp)) Text(value.claimToUiString(), overflow = TextOverflow.Ellipsis) } } } } } ?: Text("Nothing here") } -
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 4.9: Show retrieved claims and errorscomment to create the UI for showing the retrieved and failed claims on the screen:ViewResponseScreen.kt Claims("Received claims", credential.claims) Spacer(Modifier.padding(8.dp)) Claims("Failed claims", credential.claimErrors) -
Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 4.10: Show credential verification statuscomment to show the overall verification status:ViewResponseScreen.kt val statusStyle = MaterialTheme.typography.titleLarge if (credential.verificationResult.verified) { Text("Verified", style = statusStyle, color = Color.Green) } else { Text("Not verified", style = statusStyle, color = Color.Red) }
Step 1: Create a component for scanning a QR code presented by the holder
- Create a new file called
QRScannerModal.tsxand add the following code into it to implement the QR scanning capability:
import { CameraView } from "expo-camera";
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
import { Alert, Modal, SafeAreaView, Text, TouchableOpacity, View } from "react-native";
import { styles } from "./styles";
interface QRScannerModalProps {
visible: boolean;
onClose: () => void;
permission: any;
requestPermission: () => Promise<any>;
onQRCodeDetected: (data: string) => void;
}
export function QRScannerModal({
visible,
onClose,
permission,
requestPermission,
onQRCodeDetected,
}: QRScannerModalProps) {
const [scanned, setScanned] = useState(false);
const [scanningEnabled, setScanningEnabled] = useState(true);
const handlerCalledRef = useRef(false);
const handleBarCodeScanned = ({ data }: { data: string }) => {
if (!scanningEnabled || scanned || handlerCalledRef.current) {
return;
}
// Immediately mark as handled and disable scanning
handlerCalledRef.current = true;
setScanningEnabled(false);
setScanned(true);
console.log(`Scanned barcode with data: ${data}`);
// Check if data starts with "mdoc:"
if (!data || !data.startsWith("mdoc:")) {
Alert.alert(
"Invalid QR Code",
"The QR code must be an mDoc QR code starting with 'mdoc:'. Please scan a valid mDoc QR code.",
[
{
text: "Try Again",
onPress: () => resetScanner(),
},
]
);
return;
}
console.log("Valid mDoc QR code detected:", data);
// Close modal immediately to stop camera
onClose();
// Call handler after modal is closed to prevent camera from firing again
setTimeout(() => {
onQRCodeDetected(data);
}, 300);
};
const resetScanner = () => {
handlerCalledRef.current = false;
setScanned(false);
setScanningEnabled(true);
};
const handleClose = () => {
resetScanner();
onClose();
};
// Reset scanner state when modal becomes visible
useEffect(() => {
if (visible) {
resetScanner();
}
}, [visible]);
if (!visible) return null;
return (
<Modal visible={visible} animationType="slide" transparent={false}>
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.title}>QR Code Scanner</Text>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={handleClose}>
<Text style={styles.buttonTextBold}>Close</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
<View style={styles.content}>
{!permission ? (
<View style={styles.centeredContent}>
<Text style={styles.errorText}>Camera permissions are still loading</Text>
</View>
) : !permission.granted ? (
<View style={styles.centeredContent}>
<Text style={styles.errorText}>Camera permission is required to scan QR codes</Text>
<TouchableOpacity style={[styles.button, styles.marginTop]} onPress={requestPermission}>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>Request Permission</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
) : (
<>
{!scanned && (
<CameraView
style={styles.camera}
facing="back"
barcodeScannerSettings={{
barcodeTypes: ["qr"],
}}
onBarcodeScanned={handleBarCodeScanned}
/>
)}
<View style={styles.qrOverlay}>
<View style={styles.qrFrame} />
<Text style={styles.qrOverlayText}>
{scanned ? "Processing QR code..." : "Point your camera at a QR code"}
</Text>
</View>
{scanned && (
<View style={styles.scannerControls}>
<TouchableOpacity style={[styles.button, styles.buttonSuccess]} onPress={resetScanner}>
<Text style={styles.buttonTextBold}>Scan Again</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
)}
</>
)}
</View>
</SafeAreaView>
</Modal>
);
}- This component uses the expo-camera package and handles camera permissions through props passed from
App.tsx. - It's configured to scan QR codes and validates that the scanned data starts with "mdoc:" prefix.
- The
handleBarCodeScannedfunction processes the scanned data and calls theonQRCodeDetectedcallback with the QR code data.
- Return to your
App.tsxfile and add the following code under the// Verify mDocs - Step 1.2: Create handleQRCodeDetected functioncomment to add a presentation workflow handler. This handler uses the SDK'screateProximityPresentationSessionandsendProximityPresentationRequestand methods to establish a session and request a credential:
const handleQRCodeDetected = async (qrData: string) => {
try {
setLoadingMessage("Establishing secure connection...");
await createProximityPresentationSession({
deviceEngagement: qrData,
onEstablished: async () => {
console.log("Session established successfully");
setLoadingMessage("Requesting verification data...");
try {
const response = await sendProximityPresentationRequest({
mobileCredentialRequests: [
{
docType: "org.iso.18013.5.1.mDL",
namespaces: {
"org.iso.18013.5.1": {
family_name: false,
given_name: false,
birth_date: false,
},
},
},
],
});
if (response.isErr()) {
throw new Error(`Failed to verify presentation: ${response.error.message}`);
}
setLoadingMessage("Verifying credentials...");
setVerificationResults(response.value);
setShowVerificationResults(true);
await terminateProximityPresentationSession();
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error during presentation request:", error);
Alert.alert("Error", "Failed to verify mDocs");
await terminateProximityPresentationSession();
} finally {
setLoadingMessage(false);
}
},
onTerminated: () => {
console.log("Session terminated");
setLoadingMessage(false);
},
onError: (error) => {
console.error("Session error:", JSON.stringify(error, null, 2));
Alert.alert(
"Error",
`Session failed: ${error.message || JSON.stringify(error)}`,
);
setLoadingMessage(false);
},
});
console.log(
"createProximityPresentationSession call completed (waiting for callbacks)",
);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error during QR code processing:", error);
Alert.alert(
"Error",
`Failed to process QR code: ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : String(error)}`,
);
setLoadingMessage(false);
}
};This function requests an mDL (mobile driver's license) credential with specific data elements: family_name, given_name, and birth_date.
- Uncomment the QRScannerModal import at the top of the file to integrate the QR Scanner modal:
import { QRScannerModal } from "./QRScannerModal";- Paste the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 1.4: Use QRScannerModalcomment to render the QR Scanner modal component in your app:
<QRScannerModal
visible={isScanning}
onClose={() => setIsScanning(false)}
permission={permission}
requestPermission={requestPermission}
onQRCodeDetected={handleQRCodeDetected}
/>- Add the following code under the
Verify mDocs - Step 1.5: Create Scan QR Code Buttoncomment to create a button that opens the QR Scanner modal:
<TouchableOpacity
style={[styles.button, styles.secondaryButton]}
onPress={() => setIsScanning(true)}
>
<Text style={[styles.buttonText, styles.secondaryButtonText]}>
Scan QR Code
</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>Step 2: Display verification results
- Create the Verification Results modal in a new file called
VerificationResultsModal.tsxand pasted the following code into it.MobileCredentialResponseis the type that holds the verification results from the MATTR Verifier SDK. The modal will display the verification results, including any claims and errors.
import type { MobileCredentialResponse } from "@mattrglobal/mobile-credential-verifier-react-native";
import { Modal, SafeAreaView, ScrollView, Text, TouchableOpacity, View } from "react-native";
import { styles } from "./styles";
interface VerificationResultsModalProps {
visible: boolean;
onClose: () => void;
verificationResults: MobileCredentialResponse | null;
}
export function VerificationResultsModal({ visible, onClose, verificationResults }: VerificationResultsModalProps) {
if (!visible || !verificationResults) return null;
// Helper function to render different claim value types
function renderClaimValue(claim: any): string {
if (!claim) return "undefined";
if (claim.type === "array" || claim.type === "object") {
return JSON.stringify(claim.value);
}
return String(claim.value);
}
return (
<Modal visible={visible} animationType="slide" transparent={false}>
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.title}>Verification Results</Text>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={onClose}>
<Text style={styles.buttonText}>Close</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
<ScrollView style={styles.content}>
{verificationResults.credentials && verificationResults.credentials.length > 0 ? (
<View>
{/* Basic verification status */}
<View style={[styles.center, styles.marginBottom]}>
<Text
style={
verificationResults.credentials[0].verificationResult?.verified
? styles.verificationSuccess
: styles.verificationFailed
}
>
{verificationResults.credentials[0].verificationResult?.verified
? "✓ Verified"
: "✗ Verification Failed"}
</Text>
<Text style={styles.verificationSubtext}>{verificationResults.credentials[0].docType}</Text>
</View>
{/* Display the raw credential data */}
{verificationResults.credentials.map((credential, credIndex) => (
<View key={`credential-${credIndex}`}>
{/* Claims data */}
{credential.claims &&
Object.keys(credential.claims).map((namespace, nsIndex) => (
<View key={`namespace-${nsIndex}`} style={styles.marginBottom}>
<Text style={styles.cardTitle}>{namespace}</Text>
<View style={styles.card}>
{credential.claims &&
Object.entries(credential.claims[namespace]).map(([key, value], idx) => (
<View key={`${namespace}-${key}-${idx}`} style={styles.listItem}>
<Text>{key}:</Text>
<Text>{renderClaimValue(value)}</Text>
</View>
))}
</View>
</View>
))}
{/* Error information */}
{!credential.verificationResult?.verified && credential.verificationResult?.reason && (
<View style={styles.card}>
<Text style={styles.listItemTitle}>Verification Failed:</Text>
<Text>Type: {credential.verificationResult.reason.type}</Text>
<Text>Message: {credential.verificationResult.reason.message}</Text>
</View>
)}
{/* Claim errors if any */}
{credential.claimErrors && Object.keys(credential.claimErrors).length > 0 && (
<View style={styles.marginBottom}>
<Text style={styles.cardTitle}>Claim Errors</Text>
<View style={styles.card}>
{Object.entries(credential.claimErrors).map(([namespace, errors]) =>
Object.entries(errors).map(([elementId, errorCode]) => (
<View key={`error-${namespace}-${elementId}`} style={styles.listItem}>
<Text>
{namespace}.{elementId}:
</Text>
<Text style={styles.errorColor}>Error: {errorCode}</Text>
</View>
))
)}
</View>
</View>
)}
</View>
))}
</View>
) : (
<View style={styles.card}>
<Text style={[styles.centeredText, styles.grayColor]}>No data available</Text>
</View>
)}
</ScrollView>
</SafeAreaView>
</Modal>
);
}- Return to your
App.tsxfile and uncomment the VerificationResultsModal import to integrate the verification results modal:
import { VerificationResultsModal } from "./VerificationResultsModal";- Add the following code under the
// Verify mDocs - Step 2.3: Use VerificationResultModalcomment to display the verification results modal when verification is complete:
<VerificationResultsModal
visible={showVerificationResults}
onClose={() => setShowVerificationResults(false)}
verificationResults={verificationResults}
/>Test the end-to-end workflow
-
Run the app.
-
Select the Certificate Management button.
-
Copy and paste the following text into the IACA Certificate text box.
MIICYzCCAgmgAwIBAgIKXhjLoCkLWBxREDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAjA4MQswCQYDVQQG EwJBVTEpMCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0Ew HhcNMjQwMTE4MjMxNDE4WhcNMzQwMTE1MjMxNDE4WjA4MQswCQYDVQQGEwJBVTEp MCcGA1UEAwwgbW9udGNsaWZmLWRtdi5tYXR0cmxhYnMuY29tIElBQ0EwWTATBgcq hkjOPQIBBggqhkjOPQMBBwNCAASBnqobOh8baMW7mpSZaQMawj6wgM5e5nPd6HXp dB8eUVPlCMKribQ7XiiLU96rib/yQLH2k1CUeZmEjxoEi42xo4H6MIH3MBIGA1Ud EwEB/wQIMAYBAf8CAQAwDgYDVR0PAQH/BAQDAgEGMB0GA1UdDgQWBBRFZwEOI9yq 232NG+OzNQzFKa/LxDAuBgNVHRIEJzAlhiNodHRwczovL21vbnRjbGlmZi1kbXYu bWF0dHJsYWJzLmNvbTCBgQYDVR0fBHoweDB2oHSgcoZwaHR0cHM6Ly9tb250Y2xp ZmYtZG12LnZpaS5hdTAxLm1hdHRyLmdsb2JhbC92Mi9jcmVkZW50aWFscy9tb2Jp bGUvaWFjYXMvMjk0YmExYmMtOTFhMS00MjJmLThhMTctY2IwODU0NWY0ODYwL2Ny bDAKBggqhkjOPQQDAgNIADBFAiAlZYQP95lGzVJfCykhcpCzpQ2LWE/AbjTGkcGI SNsu7gIhAJfP54a2hXz4YiQN4qJERlORjyL1Ru9M0/dtQppohFm6
You will need to copy this text from the device you are using to display this tutorial and paste it in the device where you are running the built application. There are several ways to achieve this on iOS devices, one of them is setting up a Universal Clipboard. For Android devices, you can simply visit the tutorial page on the device where you are running the built application and copy the text from there.
- Select the Add button.
- Return to the app main screen.
- Open your holder testing device and launch the GO Hold example app.
- Select the Wallet button.
- Locate the mDoc claimed as part of the prerequisites for this tutorial and select the share button to display a QR code.
- Use your verifier testing device and select the Scan QR Code button.
- Use the verifier testing device to scan the QR code displayed on the holder testing device.
- Use the holder testing device to consent to sharing the information with the verifier.
- Use the verifier testing device and select the View response button.
You should see a result similar to the following:
- The verifier app user adds a new certificate to the app. This is the certificate associated with the issuer of the mDoc we are about to verify.
- The wallet app user creates a QR code to initiate the proximity presentation workflow.
- The verifier app scans the QR code, establishes a secure connection and sends a presentation request.
- The wallet app user reviews the presentation request and agrees to share matching mDocs with the verifier.
- The verifier app receives and verifies the mDocs included in the presentation response.
- The verifier app user views the verification results.
Congratulations! Your verifier application can now verify mDocs presented via a proximity presentation workflow, as per ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021.
Summary
You have just used the mDocs Verifier SDKs to build an application that can verify an mDoc presented via a proximity workflow as per ISO/IEC 18013-5:2021:
This was achieved by building the following capabilities into the application:
- Initialize the SDK, so that your application can use its functions and classes.
- Manage certificates, which enable your application to verify mDocs that were issued by trusted issuers.
- Scan a QR code presented by a wallet application and establish a secure communication channel.
- Send presentation requests to the wallet application, receive a presentation response and verify its content.
- Display the results to the verifier app user.
What's next?
- You can check out SDKs reference documentation to learn more about available functions and classes:
- You can implement NFC based device engagement capabilities (currently supported by the Android Verifier SDK and the React Native SDK for Android platforms only).
How would you rate this page?
Last updated on









